8.8 KiB
| order |
|---|
| 2 |
Reactor
The Blocksync Reactor's high level responsibility is to enable peers who are far behind the current state of the consensus to quickly catch up by downloading many blocks in parallel, verifying their commits, and executing them against the ABCI application.
Tendermint full nodes run the Blocksync Reactor as a service to provide blocks to new nodes. New nodes run the Blocksync Reactor in "fast_sync" mode, where they actively make requests for more blocks until they sync up. Once caught up, "fast_sync" mode is disabled and the node switches to using (and turns on) the Consensus Reactor.
Architecture and algorithm
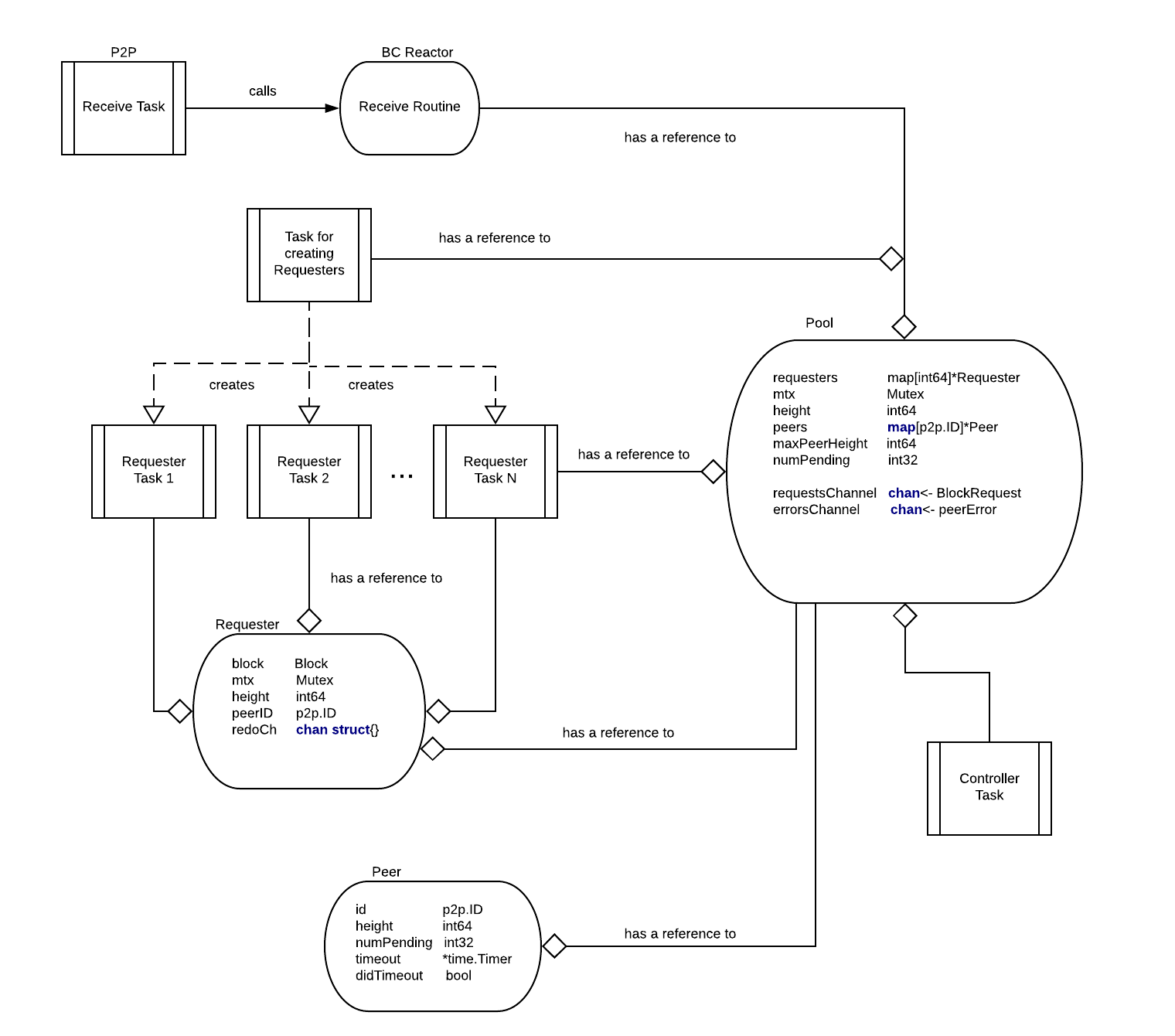
The Blocksync reactor is organised as a set of concurrent tasks:
- Receive routine of Blocksync Reactor
- Task for creating Requesters
- Set of Requesters tasks and - Controller task.
Data structures
These are the core data structures necessarily to provide the Blocksync Reactor logic.
Requester data structure is used to track assignment of request for block at position height to a peer with id equals to peerID.
type Requester {
mtx Mutex
block Block
height int64
peerID p2p.ID
redoChannel chan p2p.ID //redo may send multi-time; peerId is used to identify repeat
}
Pool is a core data structure that stores last executed block (height), assignment of requests to peers (requesters), current height for each peer and number of pending requests for each peer (peers), maximum peer height, etc.
type Pool {
mtx Mutex
requesters map[int64]*Requester
height int64
peers map[p2p.ID]*Peer
maxPeerHeight int64
numPending int32
store BlockStore
requestsChannel chan<- BlockRequest
errorsChannel chan<- peerError
}
Peer data structure stores for each peer current height and number of pending requests sent to the peer (numPending), etc.
type Peer struct {
id p2p.ID
height int64
numPending int32
timeout *time.Timer
didTimeout bool
}
BlockRequest is internal data structure used to denote current mapping of request for a block at some height to a peer (PeerID).
type BlockRequest {
Height int64
PeerID p2p.ID
}
Receive routine of Blocksync Reactor
It is executed upon message reception on the BlocksyncChannel inside p2p receive routine. There is a separate p2p receive routine (and therefore receive routine of the Blocksync Reactor) executed for each peer. Note that try to send will not block (returns immediately) if outgoing buffer is full.
handleMsg(pool, m):
upon receiving bcBlockRequestMessage m from peer p:
block = load block for height m.Height from pool.store
if block != nil then
try to send BlockResponseMessage(block) to p
else
try to send bcNoBlockResponseMessage(m.Height) to p
upon receiving bcBlockResponseMessage m from peer p:
pool.mtx.Lock()
requester = pool.requesters[m.Height]
if requester == nil then
error("peer sent us a block we didn't expect")
continue
if requester.block == nil and requester.peerID == p then
requester.block = m
pool.numPending -= 1 // atomic decrement
peer = pool.peers[p]
if peer != nil then
peer.numPending--
if peer.numPending == 0 then
peer.timeout.Stop()
// NOTE: we don't send Quit signal to the corresponding requester task!
else
trigger peer timeout to expire after peerTimeout
pool.mtx.Unlock()
upon receiving bcStatusRequestMessage m from peer p:
try to send bcStatusResponseMessage(pool.store.Height)
upon receiving bcStatusResponseMessage m from peer p:
pool.mtx.Lock()
peer = pool.peers[p]
if peer != nil then
peer.height = m.height
else
peer = create new Peer data structure with id = p and height = m.Height
pool.peers[p] = peer
if m.Height > pool.maxPeerHeight then
pool.maxPeerHeight = m.Height
pool.mtx.Unlock()
onTimeout(p):
send error message to pool error channel
peer = pool.peers[p]
peer.didTimeout = true
Requester tasks
Requester task is responsible for fetching a single block at position height.
fetchBlock(height, pool):
while true do {
peerID = nil
block = nil
peer = pickAvailablePeer(height)
peerID = peer.id
enqueue BlockRequest(height, peerID) to pool.requestsChannel
redo = false
while !redo do
select {
upon receiving Quit message do
return
upon receiving redo message with id on redoChannel do
if peerID == id {
mtx.Lock()
pool.numPending++
redo = true
mtx.UnLock()
}
}
}
pickAvailablePeer(height):
selectedPeer = nil
while selectedPeer = nil do
pool.mtx.Lock()
for each peer in pool.peers do
if !peer.didTimeout and peer.numPending < maxPendingRequestsPerPeer and peer.height >= height then
peer.numPending++
selectedPeer = peer
break
pool.mtx.Unlock()
if selectedPeer = nil then
sleep requestIntervalMS
return selectedPeer
sleep for requestIntervalMS
Task for creating Requesters
This task is responsible for continuously creating and starting Requester tasks.
createRequesters(pool):
while true do
if !pool.isRunning then break
if pool.numPending < maxPendingRequests or size(pool.requesters) < maxTotalRequesters then
pool.mtx.Lock()
nextHeight = pool.height + size(pool.requesters)
requester = create new requester for height nextHeight
pool.requesters[nextHeight] = requester
pool.numPending += 1 // atomic increment
start requester task
pool.mtx.Unlock()
else
sleep requestIntervalMS
pool.mtx.Lock()
for each peer in pool.peers do
if !peer.didTimeout && peer.numPending > 0 && peer.curRate < minRecvRate then
send error on pool error channel
peer.didTimeout = true
if peer.didTimeout then
for each requester in pool.requesters do
if requester.getPeerID() == peer then
enqueue msg on requestor's redoChannel
delete(pool.peers, peerID)
pool.mtx.Unlock()
Main blocksync reactor controller task
main(pool):
create trySyncTicker with interval trySyncIntervalMS
create statusUpdateTicker with interval statusUpdateIntervalSeconds
create switchToConsensusTicker with interval switchToConsensusIntervalSeconds
while true do
select {
upon receiving BlockRequest(Height, Peer) on pool.requestsChannel:
try to send bcBlockRequestMessage(Height) to Peer
upon receiving error(peer) on errorsChannel:
stop peer for error
upon receiving message on statusUpdateTickerChannel:
broadcast bcStatusRequestMessage(bcR.store.Height) // message sent in a separate routine
upon receiving message on switchToConsensusTickerChannel:
pool.mtx.Lock()
receivedBlockOrTimedOut = pool.height > 0 || (time.Now() - pool.startTime) > 5 Seconds
ourChainIsLongestAmongPeers = pool.maxPeerHeight == 0 || pool.height >= pool.maxPeerHeight
haveSomePeers = size of pool.peers > 0
pool.mtx.Unlock()
if haveSomePeers && receivedBlockOrTimedOut && ourChainIsLongestAmongPeers then
switch to consensus mode
upon receiving message on trySyncTickerChannel:
for i = 0; i < 10; i++ do
pool.mtx.Lock()
firstBlock = pool.requesters[pool.height].block
secondBlock = pool.requesters[pool.height].block
if firstBlock == nil or secondBlock == nil then continue
pool.mtx.Unlock()
verify firstBlock using LastCommit from secondBlock
if verification failed
pool.mtx.Lock()
peerID = pool.requesters[pool.height].peerID
redoRequestsForPeer(peerId)
delete(pool.peers, peerID)
stop peer peerID for error
pool.mtx.Unlock()
else
delete(pool.requesters, pool.height)
save firstBlock to store
pool.height++
execute firstBlock
}
redoRequestsForPeer(pool, peerId):
for each requester in pool.requesters do
if requester.getPeerID() == peerID
enqueue msg on redoChannel for requester
Channels
Defines maxMsgSize for the maximum size of incoming messages,
SendQueueCapacity and RecvBufferCapacity for maximum sending and
receiving buffers respectively. These are supposed to prevent amplification
attacks by setting up the upper limit on how much data we can receive & send to
a peer.
Sending incorrectly encoded data will result in stopping the peer.