No known key found for this signature in database
GPG Key ID: 7B6881D965918214
117 changed files with 7174 additions and 1715 deletions
Split View
Diff Options
-
+38 -5.circleci/config.yml
-
+2 -0.gitignore
-
+0 -1.golangci.yml
-
+31 -4CHANGELOG.md
-
+1 -1CHANGELOG_PENDING.md
-
+37 -25CONTRIBUTING.md
-
+18 -2Makefile
-
+0 -23ROADMAP.md
-
+7 -5abci/cmd/abci-cli/abci-cli.go
-
+1 -1abci/example/kvstore/kvstore_test.go
-
+1 -1abci/types/protoreplace/protoreplace.go
-
+4 -3blockchain/v0/pool.go
-
+80 -4blockchain/v0/reactor_test.go
-
+80 -4blockchain/v1/reactor_test.go
-
+387 -0blockchain/v2/schedule.go
-
+272 -0blockchain/v2/schedule_test.go
-
+34 -0cmd/contract_tests/main.go
-
+5 -3cmd/priv_val_server/main.go
-
+3 -2cmd/tendermint/commands/lite.go
-
+4 -4config/config.go
-
+114 -0config/config_test.go
-
+4 -3config/toml.go
-
+252 -0consensus/reactor_test.go
-
+15 -11consensus/replay.go
-
+1 -2consensus/replay_test.go
-
+14 -10consensus/state.go
-
+8 -8crypto/merkle/proof.go
-
+4 -4crypto/merkle/proof_key_path.go
-
+6 -5crypto/merkle/proof_simple_value.go
-
+4 -4crypto/merkle/proof_test.go
-
+7 -7crypto/merkle/simple_proof.go
-
+239 -0docs/architecture/adr-042-state-sync.md
-
+141 -0docs/architecture/adr-044-lite-client-with-weak-subjectivity.md
-
BINdocs/architecture/img/state-sync.png
-
+600 -0docs/guides/java.md
-
+31 -32docs/guides/kotlin.md
-
+2 -2docs/spec/abci/apps.md
-
+319 -103docs/spec/consensus/light-client.md
-
+1 -1docs/spec/p2p/connection.md
-
+3 -3docs/spec/reactors/mempool/messages.md
-
+25 -0docs/spec/rpc/index.html
-
+2679 -0docs/spec/rpc/swagger.yaml
-
+4 -3docs/tendermint-core/configuration.md
-
+33 -0dredd.yml
-
+1 -0go.mod
-
+2 -2go.sum
-
+4 -3libs/autofile/group.go
-
+8 -6libs/common/async_test.go
-
+1 -1libs/common/errors.go
-
+5 -4libs/log/tmfmt_logger.go
-
+4 -2lite/base_verifier.go
-
+13 -25lite/errors/errors.go
-
+4 -7lite/proxy/errors.go
-
+4 -3lite/proxy/query.go
-
+4 -3lite/proxy/verifier.go
-
+2 -2mempool/clist_mempool.go
-
+3 -3mempool/clist_mempool_test.go
-
+6 -5mempool/reactor.go
-
+17 -29node/node.go
-
+18 -11node/node_test.go
-
+6 -3p2p/conn/connection.go
-
+4 -3p2p/fuzz.go
-
+15 -12p2p/netaddress.go
-
+1 -1p2p/node_info_test.go
-
+4 -3p2p/peer_test.go
-
+2 -3p2p/switch.go
-
+3 -1p2p/test_util.go
-
+6 -6privval/doc.go
-
+13 -2privval/errors.go
-
+4 -4privval/file_deprecated_test.go
-
+2 -1privval/file_test.go
-
+13 -10privval/messages.go
-
+131 -0privval/signer_client.go
-
+257 -0privval/signer_client_test.go
-
+84 -0privval/signer_dialer_endpoint.go
-
+156 -0privval/signer_endpoint.go
-
+198 -0privval/signer_listener_endpoint.go
-
+198 -0privval/signer_listener_endpoint_test.go
-
+0 -192privval/signer_remote.go
-
+0 -68privval/signer_remote_test.go
-
+44 -0privval/signer_requestHandler.go
-
+107 -0privval/signer_server.go
-
+0 -139privval/signer_service_endpoint.go
-
+0 -230privval/signer_validator_endpoint.go
-
+0 -506privval/signer_validator_endpoint_test.go
-
+27 -4privval/socket_dialers_test.go
-
+2 -2privval/socket_listeners.go
-
+49 -7privval/utils.go
-
+3 -4privval/utils_test.go
-
+2 -0rpc/client/httpclient.go
-
+1 -1rpc/core/routes.go
-
+4 -3rpc/lib/client/http_client.go
-
+4 -3rpc/lib/server/handlers.go
-
+14 -0scripts/get_nodejs.sh
-
+1 -0scripts/get_tools.sh
-
+1 -1scripts/gitian-build.sh
-
+2 -2scripts/gitian-descriptors/gitian-darwin.yml
-
+2 -2scripts/gitian-descriptors/gitian-linux.yml
-
+2 -2scripts/gitian-descriptors/gitian-windows.yml
-
+1 -2state/execution.go
+ 38
- 5
.circleci/config.yml
View File
+ 2
- 0
.gitignore
View File
+ 0
- 1
.golangci.yml
View File
+ 31
- 4
CHANGELOG.md
View File
+ 1
- 1
CHANGELOG_PENDING.md
View File
+ 37
- 25
CONTRIBUTING.md
View File
+ 18
- 2
Makefile
View File
+ 0
- 23
ROADMAP.md
View File
| @ -1,23 +0,0 @@ | |||
| # Roadmap | |||
| BREAKING CHANGES: | |||
| - Better support for injecting randomness | |||
| - Upgrade consensus for more real-time use of evidence | |||
| FEATURES: | |||
| - Use the chain as its own CA for nodes and validators | |||
| - Tooling to run multiple blockchains/apps, possibly in a single process | |||
| - State syncing (without transaction replay) | |||
| - Add authentication and rate-limitting to the RPC | |||
| IMPROVEMENTS: | |||
| - Improve subtleties around mempool caching and logic | |||
| - Consensus optimizations: | |||
| - cache block parts for faster agreement after round changes | |||
| - propagate block parts rarest first | |||
| - Better testing of the consensus state machine (ie. use a DSL) | |||
| - Auto compiled serialization/deserialization code instead of go-wire reflection | |||
| BUG FIXES: | |||
| - Graceful handling/recovery for apps that have non-determinism or fail to halt | |||
| - Graceful handling/recovery for violations of safety, or liveness | |||
+ 7
- 5
abci/cmd/abci-cli/abci-cli.go
View File
+ 1
- 1
abci/example/kvstore/kvstore_test.go
View File
+ 1
- 1
abci/types/protoreplace/protoreplace.go
View File
+ 4
- 3
blockchain/v0/pool.go
View File
+ 80
- 4
blockchain/v0/reactor_test.go
View File
+ 80
- 4
blockchain/v1/reactor_test.go
View File
+ 387
- 0
blockchain/v2/schedule.go
View File
| @ -0,0 +1,387 @@ | |||
| // nolint:unused | |||
| package v2 | |||
| import ( | |||
| "fmt" | |||
| "math" | |||
| "math/rand" | |||
| "time" | |||
| "github.com/tendermint/tendermint/p2p" | |||
| ) | |||
| type Event interface{} | |||
| type blockState int | |||
| const ( | |||
| blockStateUnknown blockState = iota | |||
| blockStateNew | |||
| blockStatePending | |||
| blockStateReceived | |||
| blockStateProcessed | |||
| ) | |||
| func (e blockState) String() string { | |||
| switch e { | |||
| case blockStateUnknown: | |||
| return "Unknown" | |||
| case blockStateNew: | |||
| return "New" | |||
| case blockStatePending: | |||
| return "Pending" | |||
| case blockStateReceived: | |||
| return "Received" | |||
| case blockStateProcessed: | |||
| return "Processed" | |||
| default: | |||
| return fmt.Sprintf("unknown blockState: %d", e) | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| type peerState int | |||
| const ( | |||
| peerStateNew = iota | |||
| peerStateReady | |||
| peerStateRemoved | |||
| ) | |||
| func (e peerState) String() string { | |||
| switch e { | |||
| case peerStateNew: | |||
| return "New" | |||
| case peerStateReady: | |||
| return "Ready" | |||
| case peerStateRemoved: | |||
| return "Removed" | |||
| default: | |||
| return fmt.Sprintf("unknown peerState: %d", e) | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| type scPeer struct { | |||
| peerID p2p.ID | |||
| state peerState | |||
| height int64 | |||
| lastTouched time.Time | |||
| lastRate int64 | |||
| } | |||
| func newScPeer(peerID p2p.ID) *scPeer { | |||
| return &scPeer{ | |||
| peerID: peerID, | |||
| state: peerStateNew, | |||
| height: -1, | |||
| lastTouched: time.Time{}, | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| // The schedule is a composite data structure which allows a scheduler to keep | |||
| // track of which blocks have been scheduled into which state. | |||
| type schedule struct { | |||
| initHeight int64 | |||
| // a list of blocks in which blockState | |||
| blockStates map[int64]blockState | |||
| // a map of peerID to schedule specific peer struct `scPeer` used to keep | |||
| // track of peer specific state | |||
| peers map[p2p.ID]*scPeer | |||
| // a map of heights to the peer we are waiting for a response from | |||
| pendingBlocks map[int64]p2p.ID | |||
| // the time at which a block was put in blockStatePending | |||
| pendingTime map[int64]time.Time | |||
| // the peerID of the peer which put the block in blockStateReceived | |||
| receivedBlocks map[int64]p2p.ID | |||
| } | |||
| func newSchedule(initHeight int64) *schedule { | |||
| sc := schedule{ | |||
| initHeight: initHeight, | |||
| blockStates: make(map[int64]blockState), | |||
| peers: make(map[p2p.ID]*scPeer), | |||
| pendingBlocks: make(map[int64]p2p.ID), | |||
| pendingTime: make(map[int64]time.Time), | |||
| receivedBlocks: make(map[int64]p2p.ID), | |||
| } | |||
| sc.setStateAtHeight(initHeight, blockStateNew) | |||
| return &sc | |||
| } | |||
| func (sc *schedule) addPeer(peerID p2p.ID) error { | |||
| if _, ok := sc.peers[peerID]; ok { | |||
| return fmt.Errorf("Cannot add duplicate peer %s", peerID) | |||
| } | |||
| sc.peers[peerID] = newScPeer(peerID) | |||
| return nil | |||
| } | |||
| func (sc *schedule) touchPeer(peerID p2p.ID, time time.Time) error { | |||
| peer, ok := sc.peers[peerID] | |||
| if !ok { | |||
| return fmt.Errorf("Couldn't find peer %s", peerID) | |||
| } | |||
| if peer.state == peerStateRemoved { | |||
| return fmt.Errorf("Tried to touch peer in peerStateRemoved") | |||
| } | |||
| peer.lastTouched = time | |||
| return nil | |||
| } | |||
| func (sc *schedule) removePeer(peerID p2p.ID) error { | |||
| peer, ok := sc.peers[peerID] | |||
| if !ok { | |||
| return fmt.Errorf("Couldn't find peer %s", peerID) | |||
| } | |||
| if peer.state == peerStateRemoved { | |||
| return fmt.Errorf("Tried to remove peer %s in peerStateRemoved", peerID) | |||
| } | |||
| for height, pendingPeerID := range sc.pendingBlocks { | |||
| if pendingPeerID == peerID { | |||
| sc.setStateAtHeight(height, blockStateNew) | |||
| delete(sc.pendingTime, height) | |||
| delete(sc.pendingBlocks, height) | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| for height, rcvPeerID := range sc.receivedBlocks { | |||
| if rcvPeerID == peerID { | |||
| sc.setStateAtHeight(height, blockStateNew) | |||
| delete(sc.receivedBlocks, height) | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| peer.state = peerStateRemoved | |||
| return nil | |||
| } | |||
| func (sc *schedule) setPeerHeight(peerID p2p.ID, height int64) error { | |||
| peer, ok := sc.peers[peerID] | |||
| if !ok { | |||
| return fmt.Errorf("Can't find peer %s", peerID) | |||
| } | |||
| if peer.state == peerStateRemoved { | |||
| return fmt.Errorf("Cannot set peer height for a peer in peerStateRemoved") | |||
| } | |||
| if height < peer.height { | |||
| return fmt.Errorf("Cannot move peer height lower. from %d to %d", peer.height, height) | |||
| } | |||
| peer.height = height | |||
| peer.state = peerStateReady | |||
| for i := sc.minHeight(); i <= height; i++ { | |||
| if sc.getStateAtHeight(i) == blockStateUnknown { | |||
| sc.setStateAtHeight(i, blockStateNew) | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| return nil | |||
| } | |||
| func (sc *schedule) getStateAtHeight(height int64) blockState { | |||
| if height < sc.initHeight { | |||
| return blockStateProcessed | |||
| } else if state, ok := sc.blockStates[height]; ok { | |||
| return state | |||
| } else { | |||
| return blockStateUnknown | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| func (sc *schedule) getPeersAtHeight(height int64) []*scPeer { | |||
| peers := []*scPeer{} | |||
| for _, peer := range sc.peers { | |||
| if peer.height >= height { | |||
| peers = append(peers, peer) | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| return peers | |||
| } | |||
| func (sc *schedule) peersInactiveSince(duration time.Duration, now time.Time) []p2p.ID { | |||
| peers := []p2p.ID{} | |||
| for _, peer := range sc.peers { | |||
| if now.Sub(peer.lastTouched) > duration { | |||
| peers = append(peers, peer.peerID) | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| return peers | |||
| } | |||
| func (sc *schedule) peersSlowerThan(minSpeed int64) []p2p.ID { | |||
| peers := []p2p.ID{} | |||
| for _, peer := range sc.peers { | |||
| if peer.lastRate < minSpeed { | |||
| peers = append(peers, peer.peerID) | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| return peers | |||
| } | |||
| func (sc *schedule) setStateAtHeight(height int64, state blockState) { | |||
| sc.blockStates[height] = state | |||
| } | |||
| func (sc *schedule) markReceived(peerID p2p.ID, height int64, size int64, now time.Time) error { | |||
| peer, ok := sc.peers[peerID] | |||
| if !ok { | |||
| return fmt.Errorf("Can't find peer %s", peerID) | |||
| } | |||
| if peer.state == peerStateRemoved { | |||
| return fmt.Errorf("Cannot receive blocks from removed peer %s", peerID) | |||
| } | |||
| if state := sc.getStateAtHeight(height); state != blockStatePending || sc.pendingBlocks[height] != peerID { | |||
| return fmt.Errorf("Received block %d from peer %s without being requested", height, peerID) | |||
| } | |||
| pendingTime, ok := sc.pendingTime[height] | |||
| if !ok || now.Sub(pendingTime) <= 0 { | |||
| return fmt.Errorf("Clock error. Block %d received at %s but requested at %s", | |||
| height, pendingTime, now) | |||
| } | |||
| peer.lastRate = size / int64(now.Sub(pendingTime).Seconds()) | |||
| sc.setStateAtHeight(height, blockStateReceived) | |||
| delete(sc.pendingBlocks, height) | |||
| delete(sc.pendingTime, height) | |||
| sc.receivedBlocks[height] = peerID | |||
| return nil | |||
| } | |||
| func (sc *schedule) markPending(peerID p2p.ID, height int64, time time.Time) error { | |||
| peer, ok := sc.peers[peerID] | |||
| if !ok { | |||
| return fmt.Errorf("Can't find peer %s", peerID) | |||
| } | |||
| state := sc.getStateAtHeight(height) | |||
| if state != blockStateNew { | |||
| return fmt.Errorf("Block %d should be in blockStateNew but was %s", height, state) | |||
| } | |||
| if peer.state != peerStateReady { | |||
| return fmt.Errorf("Cannot schedule %d from %s in %s", height, peerID, peer.state) | |||
| } | |||
| if height > peer.height { | |||
| return fmt.Errorf("Cannot request height %d from peer %s who is at height %d", | |||
| height, peerID, peer.height) | |||
| } | |||
| sc.setStateAtHeight(height, blockStatePending) | |||
| sc.pendingBlocks[height] = peerID | |||
| // XXX: to make this more accurate we can introduce a message from | |||
| // the IO routine which indicates the time the request was put on the wire | |||
| sc.pendingTime[height] = time | |||
| return nil | |||
| } | |||
| func (sc *schedule) markProcessed(height int64) error { | |||
| state := sc.getStateAtHeight(height) | |||
| if state != blockStateReceived { | |||
| return fmt.Errorf("Can't mark height %d received from block state %s", height, state) | |||
| } | |||
| delete(sc.receivedBlocks, height) | |||
| sc.setStateAtHeight(height, blockStateProcessed) | |||
| return nil | |||
| } | |||
| // allBlockProcessed returns true if all blocks are in blockStateProcessed and | |||
| // determines if the schedule has been completed | |||
| func (sc *schedule) allBlocksProcessed() bool { | |||
| for _, state := range sc.blockStates { | |||
| if state != blockStateProcessed { | |||
| return false | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| return true | |||
| } | |||
| // highest block | state == blockStateNew | |||
| func (sc *schedule) maxHeight() int64 { | |||
| var max int64 = 0 | |||
| for height, state := range sc.blockStates { | |||
| if state == blockStateNew && height > max { | |||
| max = height | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| return max | |||
| } | |||
| // lowest block | state == blockStateNew | |||
| func (sc *schedule) minHeight() int64 { | |||
| var min int64 = math.MaxInt64 | |||
| for height, state := range sc.blockStates { | |||
| if state == blockStateNew && height < min { | |||
| min = height | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| return min | |||
| } | |||
| func (sc *schedule) pendingFrom(peerID p2p.ID) []int64 { | |||
| heights := []int64{} | |||
| for height, pendingPeerID := range sc.pendingBlocks { | |||
| if pendingPeerID == peerID { | |||
| heights = append(heights, height) | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| return heights | |||
| } | |||
| func (sc *schedule) selectPeer(peers []*scPeer) *scPeer { | |||
| // FIXME: properPeerSelector | |||
| s := rand.NewSource(time.Now().Unix()) | |||
| r := rand.New(s) | |||
| return peers[r.Intn(len(peers))] | |||
| } | |||
| // XXX: this duplicates the logic of peersInactiveSince and peersSlowerThan | |||
| func (sc *schedule) prunablePeers(peerTimout time.Duration, minRecvRate int64, now time.Time) []p2p.ID { | |||
| prunable := []p2p.ID{} | |||
| for peerID, peer := range sc.peers { | |||
| if now.Sub(peer.lastTouched) > peerTimout || peer.lastRate < minRecvRate { | |||
| prunable = append(prunable, peerID) | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| return prunable | |||
| } | |||
| func (sc *schedule) numBlockInState(targetState blockState) uint32 { | |||
| var num uint32 = 0 | |||
| for _, state := range sc.blockStates { | |||
| if state == targetState { | |||
| num++ | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| return num | |||
| } | |||
+ 272
- 0
blockchain/v2/schedule_test.go
View File
| @ -0,0 +1,272 @@ | |||
| package v2 | |||
| import ( | |||
| "testing" | |||
| "time" | |||
| "github.com/stretchr/testify/assert" | |||
| "github.com/tendermint/tendermint/p2p" | |||
| ) | |||
| func TestScheduleInit(t *testing.T) { | |||
| var ( | |||
| initHeight int64 = 5 | |||
| sc = newSchedule(initHeight) | |||
| ) | |||
| assert.Equal(t, blockStateNew, sc.getStateAtHeight(initHeight)) | |||
| assert.Equal(t, blockStateProcessed, sc.getStateAtHeight(initHeight-1)) | |||
| assert.Equal(t, blockStateUnknown, sc.getStateAtHeight(initHeight+1)) | |||
| } | |||
| func TestAddPeer(t *testing.T) { | |||
| var ( | |||
| initHeight int64 = 5 | |||
| peerID p2p.ID = "1" | |||
| peerIDTwo p2p.ID = "2" | |||
| sc = newSchedule(initHeight) | |||
| ) | |||
| assert.Nil(t, sc.addPeer(peerID)) | |||
| assert.Nil(t, sc.addPeer(peerIDTwo)) | |||
| assert.Error(t, sc.addPeer(peerID)) | |||
| } | |||
| func TestTouchPeer(t *testing.T) { | |||
| var ( | |||
| initHeight int64 = 5 | |||
| peerID p2p.ID = "1" | |||
| sc = newSchedule(initHeight) | |||
| now = time.Now() | |||
| ) | |||
| assert.Error(t, sc.touchPeer(peerID, now), | |||
| "Touching an unknown peer should return errPeerNotFound") | |||
| assert.Nil(t, sc.addPeer(peerID), | |||
| "Adding a peer should return no error") | |||
| assert.Nil(t, sc.touchPeer(peerID, now), | |||
| "Touching a peer should return no error") | |||
| threshold := 10 * time.Second | |||
| assert.Empty(t, sc.peersInactiveSince(threshold, now.Add(9*time.Second)), | |||
| "Expected no peers to have been touched over 9 seconds") | |||
| assert.Containsf(t, sc.peersInactiveSince(threshold, now.Add(11*time.Second)), peerID, | |||
| "Expected one %s to have been touched over 10 seconds ago", peerID) | |||
| } | |||
| func TestPeerHeight(t *testing.T) { | |||
| var ( | |||
| initHeight int64 = 5 | |||
| peerID p2p.ID = "1" | |||
| peerHeight int64 = 20 | |||
| sc = newSchedule(initHeight) | |||
| ) | |||
| assert.NoError(t, sc.addPeer(peerID), | |||
| "Adding a peer should return no error") | |||
| assert.NoError(t, sc.setPeerHeight(peerID, peerHeight)) | |||
| for i := initHeight; i <= peerHeight; i++ { | |||
| assert.Equal(t, sc.getStateAtHeight(i), blockStateNew, | |||
| "Expected all blocks to be in blockStateNew") | |||
| peerIDs := []p2p.ID{} | |||
| for _, peer := range sc.getPeersAtHeight(i) { | |||
| peerIDs = append(peerIDs, peer.peerID) | |||
| } | |||
| assert.Containsf(t, peerIDs, peerID, | |||
| "Expected %s to have block %d", peerID, i) | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| func TestTransitionPending(t *testing.T) { | |||
| var ( | |||
| initHeight int64 = 5 | |||
| peerID p2p.ID = "1" | |||
| peerIDTwo p2p.ID = "2" | |||
| peerHeight int64 = 20 | |||
| sc = newSchedule(initHeight) | |||
| now = time.Now() | |||
| ) | |||
| assert.NoError(t, sc.addPeer(peerID), | |||
| "Adding a peer should return no error") | |||
| assert.Nil(t, sc.addPeer(peerIDTwo), | |||
| "Adding a peer should return no error") | |||
| assert.Error(t, sc.markPending(peerID, peerHeight, now), | |||
| "Expected scheduling a block from a peer in peerStateNew to fail") | |||
| assert.NoError(t, sc.setPeerHeight(peerID, peerHeight), | |||
| "Expected setPeerHeight to return no error") | |||
| assert.NoError(t, sc.setPeerHeight(peerIDTwo, peerHeight), | |||
| "Expected setPeerHeight to return no error") | |||
| assert.NoError(t, sc.markPending(peerID, peerHeight, now), | |||
| "Expected markingPending new block to succeed") | |||
| assert.Error(t, sc.markPending(peerIDTwo, peerHeight, now), | |||
| "Expected markingPending by a second peer to fail") | |||
| assert.Equal(t, blockStatePending, sc.getStateAtHeight(peerHeight), | |||
| "Expected the block to to be in blockStatePending") | |||
| assert.NoError(t, sc.removePeer(peerID), | |||
| "Expected removePeer to return no error") | |||
| assert.Equal(t, blockStateNew, sc.getStateAtHeight(peerHeight), | |||
| "Expected the block to to be in blockStateNew") | |||
| assert.Error(t, sc.markPending(peerID, peerHeight, now), | |||
| "Expected markingPending removed peer to fail") | |||
| assert.NoError(t, sc.markPending(peerIDTwo, peerHeight, now), | |||
| "Expected markingPending on a ready peer to succeed") | |||
| assert.Equal(t, blockStatePending, sc.getStateAtHeight(peerHeight), | |||
| "Expected the block to to be in blockStatePending") | |||
| } | |||
| func TestTransitionReceived(t *testing.T) { | |||
| var ( | |||
| initHeight int64 = 5 | |||
| peerID p2p.ID = "1" | |||
| peerIDTwo p2p.ID = "2" | |||
| peerHeight int64 = 20 | |||
| blockSize int64 = 1024 | |||
| sc = newSchedule(initHeight) | |||
| now = time.Now() | |||
| receivedAt = now.Add(1 * time.Second) | |||
| ) | |||
| assert.NoError(t, sc.addPeer(peerID), | |||
| "Expected adding peer %s to succeed", peerID) | |||
| assert.NoError(t, sc.addPeer(peerIDTwo), | |||
| "Expected adding peer %s to succeed", peerIDTwo) | |||
| assert.NoError(t, sc.setPeerHeight(peerID, peerHeight), | |||
| "Expected setPeerHeight to return no error") | |||
| assert.NoErrorf(t, sc.setPeerHeight(peerIDTwo, peerHeight), | |||
| "Expected setPeerHeight on %s to %d to succeed", peerIDTwo, peerHeight) | |||
| assert.NoError(t, sc.markPending(peerID, initHeight, now), | |||
| "Expected markingPending new block to succeed") | |||
| assert.Error(t, sc.markReceived(peerIDTwo, initHeight, blockSize, receivedAt), | |||
| "Expected marking markReceived from a non requesting peer to fail") | |||
| assert.NoError(t, sc.markReceived(peerID, initHeight, blockSize, receivedAt), | |||
| "Expected marking markReceived on a pending block to succeed") | |||
| assert.Error(t, sc.markReceived(peerID, initHeight, blockSize, receivedAt), | |||
| "Expected marking markReceived on received block to fail") | |||
| assert.Equalf(t, blockStateReceived, sc.getStateAtHeight(initHeight), | |||
| "Expected block %d to be blockHeightReceived", initHeight) | |||
| assert.NoErrorf(t, sc.removePeer(peerID), | |||
| "Expected removePeer removing %s to succeed", peerID) | |||
| assert.Equalf(t, blockStateNew, sc.getStateAtHeight(initHeight), | |||
| "Expected block %d to be blockStateNew", initHeight) | |||
| assert.NoErrorf(t, sc.markPending(peerIDTwo, initHeight, now), | |||
| "Expected markingPending %d from %s to succeed", initHeight, peerIDTwo) | |||
| assert.NoErrorf(t, sc.markReceived(peerIDTwo, initHeight, blockSize, receivedAt), | |||
| "Expected marking markReceived %d from %s to succeed", initHeight, peerIDTwo) | |||
| assert.Equalf(t, blockStateReceived, sc.getStateAtHeight(initHeight), | |||
| "Expected block %d to be blockStateReceived", initHeight) | |||
| } | |||
| func TestTransitionProcessed(t *testing.T) { | |||
| var ( | |||
| initHeight int64 = 5 | |||
| peerID p2p.ID = "1" | |||
| peerHeight int64 = 20 | |||
| blockSize int64 = 1024 | |||
| sc = newSchedule(initHeight) | |||
| now = time.Now() | |||
| receivedAt = now.Add(1 * time.Second) | |||
| ) | |||
| assert.NoError(t, sc.addPeer(peerID), | |||
| "Expected adding peer %s to succeed", peerID) | |||
| assert.NoErrorf(t, sc.setPeerHeight(peerID, peerHeight), | |||
| "Expected setPeerHeight on %s to %d to succeed", peerID, peerHeight) | |||
| assert.NoError(t, sc.markPending(peerID, initHeight, now), | |||
| "Expected markingPending new block to succeed") | |||
| assert.NoError(t, sc.markReceived(peerID, initHeight, blockSize, receivedAt), | |||
| "Expected marking markReceived on a pending block to succeed") | |||
| assert.Error(t, sc.markProcessed(initHeight+1), | |||
| "Expected marking %d as processed to fail", initHeight+1) | |||
| assert.NoError(t, sc.markProcessed(initHeight), | |||
| "Expected marking %d as processed to succeed", initHeight) | |||
| assert.Equalf(t, blockStateProcessed, sc.getStateAtHeight(initHeight), | |||
| "Expected block %d to be blockStateProcessed", initHeight) | |||
| assert.NoError(t, sc.removePeer(peerID), | |||
| "Expected removing peer %s to succeed", peerID) | |||
| assert.Equalf(t, blockStateProcessed, sc.getStateAtHeight(initHeight), | |||
| "Expected block %d to be blockStateProcessed", initHeight) | |||
| } | |||
| func TestMinMaxHeight(t *testing.T) { | |||
| var ( | |||
| initHeight int64 = 5 | |||
| peerID p2p.ID = "1" | |||
| peerHeight int64 = 20 | |||
| sc = newSchedule(initHeight) | |||
| now = time.Now() | |||
| ) | |||
| assert.Equal(t, initHeight, sc.minHeight(), | |||
| "Expected min height to be the initialized height") | |||
| assert.Equal(t, initHeight, sc.maxHeight(), | |||
| "Expected max height to be the initialized height") | |||
| assert.NoError(t, sc.addPeer(peerID), | |||
| "Adding a peer should return no error") | |||
| assert.NoError(t, sc.setPeerHeight(peerID, peerHeight), | |||
| "Expected setPeerHeight to return no error") | |||
| assert.Equal(t, peerHeight, sc.maxHeight(), | |||
| "Expected max height to increase to peerHeight") | |||
| assert.Nil(t, sc.markPending(peerID, initHeight, now.Add(1*time.Second)), | |||
| "Expected marking initHeight as pending to return no error") | |||
| assert.Equal(t, initHeight+1, sc.minHeight(), | |||
| "Expected marking initHeight as pending to move minHeight forward") | |||
| } | |||
| func TestPeersSlowerThan(t *testing.T) { | |||
| var ( | |||
| initHeight int64 = 5 | |||
| peerID p2p.ID = "1" | |||
| peerHeight int64 = 20 | |||
| blockSize int64 = 1024 | |||
| sc = newSchedule(initHeight) | |||
| now = time.Now() | |||
| receivedAt = now.Add(1 * time.Second) | |||
| ) | |||
| assert.NoError(t, sc.addPeer(peerID), | |||
| "Adding a peer should return no error") | |||
| assert.NoError(t, sc.setPeerHeight(peerID, peerHeight), | |||
| "Expected setPeerHeight to return no error") | |||
| assert.NoError(t, sc.markPending(peerID, peerHeight, now), | |||
| "Expected markingPending on to return no error") | |||
| assert.NoError(t, sc.markReceived(peerID, peerHeight, blockSize, receivedAt), | |||
| "Expected markingPending on to return no error") | |||
| assert.Empty(t, sc.peersSlowerThan(blockSize-1), | |||
| "expected no peers to be slower than blockSize-1 bytes/sec") | |||
| assert.Containsf(t, sc.peersSlowerThan(blockSize+1), peerID, | |||
| "expected %s to be slower than blockSize+1 bytes/sec", peerID) | |||
| } | |||
+ 34
- 0
cmd/contract_tests/main.go
View File
| @ -0,0 +1,34 @@ | |||
| package main | |||
| import ( | |||
| "fmt" | |||
| "strings" | |||
| "github.com/snikch/goodman/hooks" | |||
| "github.com/snikch/goodman/transaction" | |||
| ) | |||
| func main() { | |||
| // This must be compiled beforehand and given to dredd as parameter, in the meantime the server should be running | |||
| h := hooks.NewHooks() | |||
| server := hooks.NewServer(hooks.NewHooksRunner(h)) | |||
| h.BeforeAll(func(t []*transaction.Transaction) { | |||
| fmt.Println(t[0].Name) | |||
| }) | |||
| h.BeforeEach(func(t *transaction.Transaction) { | |||
| if strings.HasPrefix(t.Name, "Tx") || | |||
| // We need a proper example of evidence to broadcast | |||
| strings.HasPrefix(t.Name, "Info > /broadcast_evidence") || | |||
| // We need a proper example of path and data | |||
| strings.HasPrefix(t.Name, "ABCI > /abci_query") || | |||
| // We need to find a way to make a transaction before starting the tests, | |||
| // that hash should replace the dummy one in hte swagger file | |||
| strings.HasPrefix(t.Name, "Info > /tx") { | |||
| t.Skip = true | |||
| fmt.Printf("%s Has been skipped\n", t.Name) | |||
| } | |||
| }) | |||
| server.Serve() | |||
| defer server.Listener.Close() | |||
| fmt.Print("FINE") | |||
| } | |||
+ 5
- 3
cmd/priv_val_server/main.go
View File
+ 3
- 2
cmd/tendermint/commands/lite.go
View File
+ 4
- 4
config/config.go
View File
+ 114
- 0
config/config_test.go
View File
+ 4
- 3
config/toml.go
View File
+ 252
- 0
consensus/reactor_test.go
View File
+ 15
- 11
consensus/replay.go
View File
+ 1
- 2
consensus/replay_test.go
View File
+ 14
- 10
consensus/state.go
View File
+ 8
- 8
crypto/merkle/proof.go
View File
+ 4
- 4
crypto/merkle/proof_key_path.go
View File
+ 6
- 5
crypto/merkle/proof_simple_value.go
View File
+ 4
- 4
crypto/merkle/proof_test.go
View File
+ 7
- 7
crypto/merkle/simple_proof.go
View File
+ 239
- 0
docs/architecture/adr-042-state-sync.md
View File
| @ -0,0 +1,239 @@ | |||
| # ADR 042: State Sync Design | |||
| ## Changelog | |||
| 2019-06-27: Init by EB | |||
| 2019-07-04: Follow up by brapse | |||
| ## Context | |||
| StateSync is a feature which would allow a new node to receive a | |||
| snapshot of the application state without downloading blocks or going | |||
| through consensus. Once downloaded, the node could switch to FastSync | |||
| and eventually participate in consensus. The goal of StateSync is to | |||
| facilitate setting up a new node as quickly as possible. | |||
| ## Considerations | |||
| Because Tendermint doesn't know anything about the application state, | |||
| StateSync will broker messages between nodes and through | |||
| the ABCI to an opaque applicaton. The implementation will have multiple | |||
| touch points on both the tendermint code base and ABCI application. | |||
| * A StateSync reactor to facilitate peer communication - Tendermint | |||
| * A Set of ABCI messages to transmit application state to the reactor - Tendermint | |||
| * A Set of MultiStore APIs for exposing snapshot data to the ABCI - ABCI application | |||
| * A Storage format with validation and performance considerations - ABCI application | |||
| ### Implementation Properties | |||
| Beyond the approach, any implementation of StateSync can be evaluated | |||
| across different criteria: | |||
| * Speed: Expected throughput of producing and consuming snapshots | |||
| * Safety: Cost of pushing invalid snapshots to a node | |||
| * Liveness: Cost of preventing a node from receiving/constructing a snapshot | |||
| * Effort: How much effort does an implementation require | |||
| ### Implementation Question | |||
| * What is the format of a snapshot | |||
| * Complete snapshot | |||
| * Ordered IAVL key ranges | |||
| * Compressed individually chunks which can be validated | |||
| * How is data validated | |||
| * Trust a peer with it's data blindly | |||
| * Trust a majority of peers | |||
| * Use light client validation to validate each chunk against consensus | |||
| produced merkle tree root | |||
| * What are the performance characteristics | |||
| * Random vs sequential reads | |||
| * How parallelizeable is the scheduling algorithm | |||
| ### Proposals | |||
| Broadly speaking there are two approaches to this problem which have had | |||
| varying degrees of discussion and progress. These approach can be | |||
| summarized as: | |||
| **Lazy:** Where snapshots are produced dynamically at request time. This | |||
| solution would use the existing data structure. | |||
| **Eager:** Where snapshots are produced periodically and served from disk at | |||
| request time. This solution would create an auxiliary data structure | |||
| optimized for batch read/writes. | |||
| Additionally the propsosals tend to vary on how they provide safety | |||
| properties. | |||
| **LightClient** Where a client can aquire the merkle root from the block | |||
| headers synchronized from a trusted validator set. Subsets of the application state, | |||
| called chunks can therefore be validated on receipt to ensure each chunk | |||
| is part of the merkle root. | |||
| **Majority of Peers** Where manifests of chunks along with checksums are | |||
| downloaded and compared against versions provided by a majority of | |||
| peers. | |||
| #### Lazy StateSync | |||
| An [initial specification](https://docs.google.com/document/d/15MFsQtNA0MGBv7F096FFWRDzQ1vR6_dics5Y49vF8JU/edit?ts=5a0f3629) was published by Alexis Sellier. | |||
| In this design, the state has a given `size` of primitive elements (like | |||
| keys or nodes), each element is assigned a number from 0 to `size-1`, | |||
| and chunks consists of a range of such elements. Ackratos raised | |||
| [some concerns](https://docs.google.com/document/d/1npGTAa1qxe8EQZ1wG0a0Sip9t5oX2vYZNUDwr_LVRR4/edit) | |||
| about this design, somewhat specific to the IAVL tree, and mainly concerning | |||
| performance of random reads and of iterating through the tree to determine element numbers | |||
| (ie. elements aren't indexed by the element number). | |||
| An alternative design was suggested by Jae Kwon in | |||
| [#3639](https://github.com/tendermint/tendermint/issues/3639) where chunking | |||
| happens lazily and in a dynamic way: nodes request key ranges from their peers, | |||
| and peers respond with some subset of the | |||
| requested range and with notes on how to request the rest in parallel from other | |||
| peers. Unlike chunk numbers, keys can be verified directly. And if some keys in the | |||
| range are ommitted, proofs for the range will fail to verify. | |||
| This way a node can start by requesting the entire tree from one peer, | |||
| and that peer can respond with say the first few keys, and the ranges to request | |||
| from other peers. | |||
| Additionally, per chunk validation tends to come more naturally to the | |||
| Lazy approach since it tends to use the existing structure of the tree | |||
| (ie. keys or nodes) rather than state-sync specific chunks. Such a | |||
| design for tendermint was originally tracked in | |||
| [#828](https://github.com/tendermint/tendermint/issues/828). | |||
| #### Eager StateSync | |||
| Warp Sync as implemented in Parity | |||
| ["Warp Sync"](https://wiki.parity.io/Warp-Sync-Snapshot-Format.html) to rapidly | |||
| download both blocks and state snapshots from peers. Data is carved into ~4MB | |||
| chunks and snappy compressed. Hashes of snappy compressed chunks are stored in a | |||
| manifest file which co-ordinates the state-sync. Obtaining a correct manifest | |||
| file seems to require an honest majority of peers. This means you may not find | |||
| out the state is incorrect until you download the whole thing and compare it | |||
| with a verified block header. | |||
| A similar solution was implemented by Binance in | |||
| [#3594](https://github.com/tendermint/tendermint/pull/3594) | |||
| based on their initial implementation in | |||
| [PR #3243](https://github.com/tendermint/tendermint/pull/3243) | |||
| and [some learnings](https://docs.google.com/document/d/1npGTAa1qxe8EQZ1wG0a0Sip9t5oX2vYZNUDwr_LVRR4/edit). | |||
| Note this still requires the honest majority peer assumption. | |||
| As an eager protocol, warp-sync can efficiently compress larger, more | |||
| predicatable chunks once per snapshot and service many new peers. By | |||
| comparison lazy chunkers would have to compress each chunk at request | |||
| time. | |||
| ### Analysis of Lazy vs Eager | |||
| Lazy vs Eager have more in common than they differ. They all require | |||
| reactors on the tendermint side, a set of ABCI messages and a method for | |||
| serializing/deserializing snapshots facilitated by a SnapshotFormat. | |||
| The biggest difference between Lazy and Eager proposals is in the | |||
| read/write patterns necessitated by serving a snapshot chunk. | |||
| Specifically, Lazy State Sync performs random reads to the underlying data | |||
| structure while Eager can optimize for sequential reads. | |||
| This distinctin between approaches was demonstrated by Binance's | |||
| [ackratos](https://github.com/ackratos) in their implementation of [Lazy | |||
| State sync](https://github.com/tendermint/tendermint/pull/3243), The | |||
| [analysis](https://docs.google.com/document/d/1npGTAa1qxe8EQZ1wG0a0Sip9t5oX2vYZNUDwr_LVRR4/) | |||
| of the performance, and follow up implementation of [Warp | |||
| Sync](http://github.com/tendermint/tendermint/pull/3594). | |||
| #### Compairing Security Models | |||
| There are several different security models which have been | |||
| discussed/proposed in the past but generally fall into two categories. | |||
| Light client validation: In which the node receiving data is expected to | |||
| first perform a light client sync and have all the nessesary block | |||
| headers. Within the trusted block header (trusted in terms of from a | |||
| validator set subject to [weak | |||
| subjectivity](https://github.com/tendermint/tendermint/pull/3795)) and | |||
| can compare any subset of keys called a chunk against the merkle root. | |||
| The advantage of light client validation is that the block headers are | |||
| signed by validators which have something to lose for malicious | |||
| behaviour. If a validator were to provide an invalid proof, they can be | |||
| slashed. | |||
| Majority of peer validation: A manifest file containing a list of chunks | |||
| along with checksums of each chunk is downloaded from a | |||
| trusted source. That source can be a community resource similar to | |||
| [sum.golang.org](https://sum.golang.org) or downloaded from the majority | |||
| of peers. One disadantage of the majority of peer security model is the | |||
| vuliberability to eclipse attacks in which a malicious users looks to | |||
| saturate a target node's peer list and produce a manufactured picture of | |||
| majority. | |||
| A third option would be to include snapshot related data in the | |||
| block header. This could include the manifest with related checksums and be | |||
| secured through consensus. One challenge of this approach is to | |||
| ensure that creating snapshots does not put undo burden on block | |||
| propsers by synchronizing snapshot creation and block creation. One | |||
| approach to minimizing the burden is for snapshots for height | |||
| `H` to be included in block `H+n` where `n` is some `n` block away, | |||
| giving the block propser enough time to complete the snapshot | |||
| asynchronousy. | |||
| ## Proposal: Eager StateSync With Per Chunk Light Client Validation | |||
| The conclusion after some concideration of the advantages/disadvances of | |||
| eager/lazy and different security models is to produce a state sync | |||
| which eagerly produces snapshots and uses light client validation. This | |||
| approach has the performance advantages of pre-computing efficient | |||
| snapshots which can streamed to new nodes on demand using sequential IO. | |||
| Secondly, by using light client validation we cna validate each chunk on | |||
| receipt and avoid the potential eclipse attack of majority of peer based | |||
| security. | |||
| ### Implementation | |||
| Tendermint is responsible for downloading and verifying chunks of | |||
| AppState from peers. ABCI Application is responsible for taking | |||
| AppStateChunk objects from TM and constructing a valid state tree whose | |||
| root corresponds with the AppHash of syncing block. In particular we | |||
| will need implement: | |||
| * Build new StateSync reactor brokers message transmission between the peers | |||
| and the ABCI application | |||
| * A set of ABCI Messages | |||
| * Design SnapshotFormat as an interface which can: | |||
| * validate chunks | |||
| * read/write chunks from file | |||
| * read/write chunks to/from application state store | |||
| * convert manifests into chunkRequest ABCI messages | |||
| * Implement SnapshotFormat for cosmos-hub with concrete implementation for: | |||
| * read/write chunks in a way which can be: | |||
| * parallelized across peers | |||
| * validated on receipt | |||
| * read/write to/from IAVL+ tree | |||
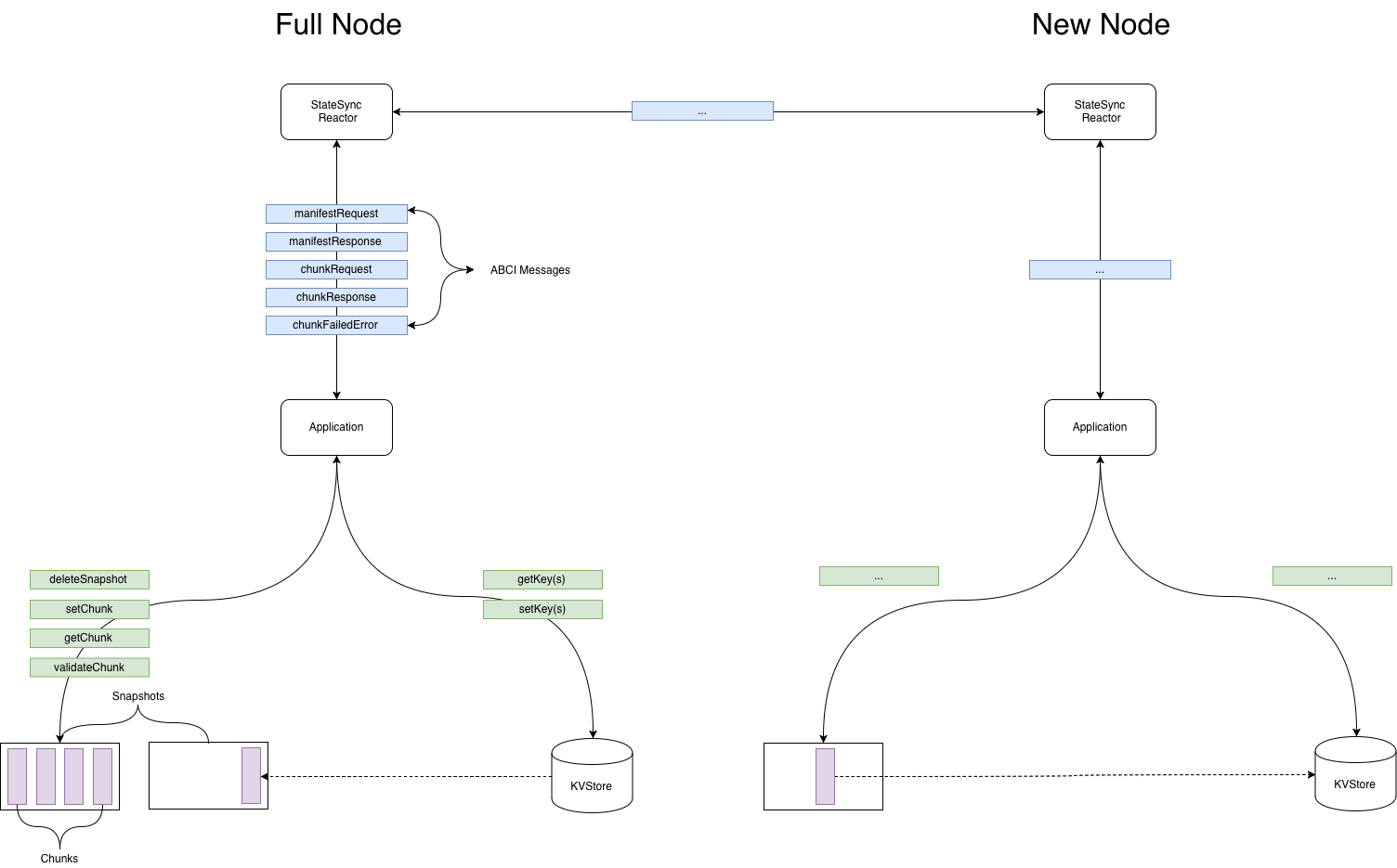
|  | |||
| ## Implementation Path | |||
| * Create StateSync reactor based on [#3753](https://github.com/tendermint/tendermint/pull/3753) | |||
| * Design SnapshotFormat with an eye towards cosmos-hub implementation | |||
| * ABCI message to send/receive SnapshotFormat | |||
| * IAVL+ changes to support SnapshotFormat | |||
| * Deliver Warp sync (no chunk validation) | |||
| * light client implementation for weak subjectivity | |||
| * Deliver StateSync with chunk validation | |||
| ## Status | |||
| Proposed | |||
| ## Concequences | |||
| ### Neutral | |||
| ### Positive | |||
| * Safe & performant state sync design substantiated with real world implementation experience | |||
| * General interfaces allowing application specific innovation | |||
| * Parallizable implementation trajectory with reasonable engineering effort | |||
| ### Negative | |||
| * Static Scheduling lacks opportunity for real time chunk availability optimizations | |||
| ## References | |||
| [sync: Sync current state without full replay for Applications](https://github.com/tendermint/tendermint/issues/828) - original issue | |||
| [tendermint state sync proposal](https://docs.google.com/document/d/15MFsQtNA0MGBv7F096FFWRDzQ1vR6_dics5Y49vF8JU/edit?ts=5a0f3629) - Cloudhead proposal | |||
| [tendermint state sync proposal 2](https://docs.google.com/document/d/1npGTAa1qxe8EQZ1wG0a0Sip9t5oX2vYZNUDwr_LVRR4/edit) - ackratos proposal | |||
| [proposal 2 implementation](https://github.com/tendermint/tendermint/pull/3243) - ackratos implementation | |||
| [WIP General/Lazy State-Sync pseudo-spec](https://github.com/tendermint/tendermint/issues/3639) - Jae Proposal | |||
| [Warp Sync Implementation](https://github.com/tendermint/tendermint/pull/3594) - ackratos | |||
| [Chunk Proposal](https://github.com/tendermint/tendermint/pull/3799) - Bucky proposed | |||
+ 141
- 0
docs/architecture/adr-044-lite-client-with-weak-subjectivity.md
View File
| @ -0,0 +1,141 @@ | |||
| # ADR 044: Lite Client with Weak Subjectivity | |||
| ## Changelog | |||
| * 13-07-2019: Initial draft | |||
| * 14-08-2019: Address cwgoes comments | |||
| ## Context | |||
| The concept of light clients was introduced in the Bitcoin white paper. It | |||
| describes a watcher of distributed consensus process that only validates the | |||
| consensus algorithm and not the state machine transactions within. | |||
| Tendermint light clients allow bandwidth & compute-constrained devices, such as smartphones, low-power embedded chips, or other blockchains to | |||
| efficiently verify the consensus of a Tendermint blockchain. This forms the | |||
| basis of safe and efficient state synchronization for new network nodes and | |||
| inter-blockchain communication (where a light client of one Tendermint instance | |||
| runs in another chain's state machine). | |||
| In a network that is expected to reliably punish validators for misbehavior | |||
| by slashing bonded stake and where the validator set changes | |||
| infrequently, clients can take advantage of this assumption to safely | |||
| synchronize a lite client without downloading the intervening headers. | |||
| Light clients (and full nodes) operating in the Proof Of Stake context need a | |||
| trusted block height from a trusted source that is no older than 1 unbonding | |||
| window plus a configurable evidence submission synchrony bound. This is called “weak subjectivity”. | |||
| Weak subjectivity is required in Proof of Stake blockchains because it is | |||
| costless for an attacker to buy up voting keys that are no longer bonded and | |||
| fork the network at some point in its prior history. See Vitalik’s post at | |||
| [Proof of Stake: How I Learned to Love Weak | |||
| Subjectivity](https://blog.ethereum.org/2014/11/25/proof-stake-learned-love-weak-subjectivity/). | |||
| Currently, Tendermint provides a lite client implementation in the | |||
| [lite](https://github.com/tendermint/tendermint/tree/master/lite) package. This | |||
| lite client implements a bisection algorithm that tries to use a binary search | |||
| to find the minimum number of block headers where the validator set voting | |||
| power changes are less than < 1/3rd. This interface does not support weak | |||
| subjectivity at this time. The Cosmos SDK also does not support counterfactual | |||
| slashing, nor does the lite client have any capacity to report evidence making | |||
| these systems *theoretically unsafe*. | |||
| NOTE: Tendermint provides a somewhat different (stronger) light client model | |||
| than Bitcoin under eclipse, since the eclipsing node(s) can only fool the light | |||
| client if they have two-thirds of the private keys from the last root-of-trust. | |||
| ## Decision | |||
| ### The Weak Subjectivity Interface | |||
| Add the weak subjectivity interface for when a new light client connects to the | |||
| network or when a light client that has been offline for longer than the | |||
| unbonding period connects to the network. Specifically, the node needs to | |||
| initialize the following structure before syncing from user input: | |||
| ``` | |||
| type TrustOptions struct { | |||
| // Required: only trust commits up to this old. | |||
| // Should be equal to the unbonding period minus some delta for evidence reporting. | |||
| TrustPeriod time.Duration `json:"trust-period"` | |||
| // Option 1: TrustHeight and TrustHash can both be provided | |||
| // to force the trusting of a particular height and hash. | |||
| // If the latest trusted height/hash is more recent, then this option is | |||
| // ignored. | |||
| TrustHeight int64 `json:"trust-height"` | |||
| TrustHash []byte `json:"trust-hash"` | |||
| // Option 2: Callback can be set to implement a confirmation | |||
| // step if the trust store is uninitialized, or expired. | |||
| Callback func(height int64, hash []byte) error | |||
| } | |||
| ``` | |||
| The expectation is the user will get this information from a trusted source | |||
| like a validator, a friend, or a secure website. A more user friendly | |||
| solution with trust tradeoffs is that we establish an https based protocol with | |||
| a default end point that populates this information. Also an on-chain registry | |||
| of roots-of-trust (e.g. on the Cosmos Hub) seems likely in the future. | |||
| ### Linear Verification | |||
| The linear verification algorithm requires downloading all headers | |||
| between the `TrustHeight` and the `LatestHeight`. The lite client downloads the | |||
| full header for the provided `TrustHeight` and then proceeds to download `N+1` | |||
| headers and applies the [Tendermint validation | |||
| rules](https://github.com/tendermint/tendermint/blob/master/docs/spec/blockchain/blockchain.md#validation) | |||
| to each block. | |||
| ### Bisecting Verification | |||
| Bisecting Verification is a more bandwidth and compute intensive mechanism that | |||
| in the most optimistic case requires a light client to only download two block | |||
| headers to come into synchronization. | |||
| The bisection algorithm proceeds in the following fashion. The client downloads | |||
| and verifies the full block header for `TrustHeight` and then fetches | |||
| `LatestHeight` blocker header. The client then verifies the `LatestHeight` | |||
| header. Finally the client attempts to verify the `LatestHeight` header with | |||
| voting powers taken from `NextValidatorSet` in the `TrustHeight` header. This | |||
| verification will succeed if the validators from `TrustHeight` still have > 2/3 | |||
| +1 of voting power in the `LatestHeight`. If this succeeds, the client is fully | |||
| synchronized. If this fails, then following Bisection Algorithm should be | |||
| executed. | |||
| The Client tries to download the block at the mid-point block between | |||
| `LatestHeight` and `TrustHeight` and attempts that same algorithm as above | |||
| using `MidPointHeight` instead of `LatestHeight` and a different threshold - | |||
| 1/3 +1 of voting power for *non-adjacent headers*. In the case the of failure, | |||
| recursively perform the `MidPoint` verification until success then start over | |||
| with an updated `NextValidatorSet` and `TrustHeight`. | |||
| If the client encounters a forged header, it should submit the header along | |||
| with some other intermediate headers as the evidence of misbehavior to other | |||
| full nodes. After that, it can retry the bisection using another full node. An | |||
| optimal client will cache trusted headers from the previous run to minimize | |||
| network usage. | |||
| --- | |||
| Check out the formal specification | |||
| [here](https://github.com/tendermint/tendermint/blob/master/docs/spec/consensus/light-client.md). | |||
| ## Status | |||
| Accepted. | |||
| ## Consequences | |||
| ### Positive | |||
| * light client which is safe to use (it can go offline, but not for too long) | |||
| ### Negative | |||
| * complexity of bisection | |||
| ### Neutral | |||
| * social consensus can be prone to errors (for cases where a new light client | |||
| joins a network or it has been offline for too long) | |||
BIN
docs/architecture/img/state-sync.png
View File
+ 600
- 0
docs/guides/java.md
View File
| @ -0,0 +1,600 @@ | |||
| # Creating an application in Java | |||
| ## Guide Assumptions | |||
| This guide is designed for beginners who want to get started with a Tendermint | |||
| Core application from scratch. It does not assume that you have any prior | |||
| experience with Tendermint Core. | |||
| Tendermint Core is Byzantine Fault Tolerant (BFT) middleware that takes a state | |||
| transition machine (your application) - written in any programming language - and securely | |||
| replicates it on many machines. | |||
| By following along with this guide, you'll create a Tendermint Core project | |||
| called kvstore, a (very) simple distributed BFT key-value store. The application (which should | |||
| implementing the blockchain interface (ABCI)) will be written in Java. | |||
| This guide assumes that you are not new to JVM world. If you are new please see [JVM Minimal Survival Guide](https://hadihariri.com/2013/12/29/jvm-minimal-survival-guide-for-the-dotnet-developer/#java-the-language-java-the-ecosystem-java-the-jvm) and [Gradle Docs](https://docs.gradle.org/current/userguide/userguide.html). | |||
| ## Built-in app vs external app | |||
| If you use Golang, you can run your app and Tendermint Core in the same process to get maximum performance. | |||
| [Cosmos SDK](https://github.com/cosmos/cosmos-sdk) is written this way. | |||
| Please refer to [Writing a built-in Tendermint Core application in Go](./go-built-in.md) guide for details. | |||
| If you choose another language, like we did in this guide, you have to write a separate app, | |||
| which will communicate with Tendermint Core via a socket (UNIX or TCP) or gRPC. | |||
| This guide will show you how to build external application using RPC server. | |||
| Having a separate application might give you better security guarantees as two | |||
| processes would be communicating via established binary protocol. Tendermint | |||
| Core will not have access to application's state. | |||
| ## 1.1 Installing Java and Gradle | |||
| Please refer to [the Oracle's guide for installing JDK](https://www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/javase/downloads/index.html). | |||
| Verify that you have installed Java successfully: | |||
| ```sh | |||
| $ java -version | |||
| java version "12.0.2" 2019-07-16 | |||
| Java(TM) SE Runtime Environment (build 12.0.2+10) | |||
| Java HotSpot(TM) 64-Bit Server VM (build 12.0.2+10, mixed mode, sharing) | |||
| ``` | |||
| You can choose any version of Java higher or equal to 8. | |||
| This guide is written using Java SE Development Kit 12. | |||
| Make sure you have `$JAVA_HOME` environment variable set: | |||
| ```sh | |||
| $ echo $JAVA_HOME | |||
| /Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk-12.0.2.jdk/Contents/Home | |||
| ``` | |||
| For Gradle installation, please refer to [their official guide](https://gradle.org/install/). | |||
| ## 1.2 Creating a new Java project | |||
| We'll start by creating a new Gradle project. | |||
| ```sh | |||
| $ export KVSTORE_HOME=~/kvstore | |||
| $ mkdir $KVSTORE_HOME | |||
| $ cd $KVSTORE_HOME | |||
| ``` | |||
| Inside the example directory run: | |||
| ```sh | |||
| gradle init --dsl groovy --package io.example --project-name example --type java-application --test-framework junit | |||
| ``` | |||
| This will create a new project for you. The tree of files should look like: | |||
| ```sh | |||
| $ tree | |||
| . | |||
| |-- build.gradle | |||
| |-- gradle | |||
| | `-- wrapper | |||
| | |-- gradle-wrapper.jar | |||
| | `-- gradle-wrapper.properties | |||
| |-- gradlew | |||
| |-- gradlew.bat | |||
| |-- settings.gradle | |||
| `-- src | |||
| |-- main | |||
| | |-- java | |||
| | | `-- io | |||
| | | `-- example | |||
| | | `-- App.java | |||
| | `-- resources | |||
| `-- test | |||
| |-- java | |||
| | `-- io | |||
| | `-- example | |||
| | `-- AppTest.java | |||
| `-- resources | |||
| ``` | |||
| When run, this should print "Hello world." to the standard output. | |||
| ```sh | |||
| $ ./gradlew run | |||
| > Task :run | |||
| Hello world. | |||
| ``` | |||
| ## 1.3 Writing a Tendermint Core application | |||
| Tendermint Core communicates with the application through the Application | |||
| BlockChain Interface (ABCI). All message types are defined in the [protobuf | |||
| file](https://github.com/tendermint/tendermint/blob/develop/abci/types/types.proto). | |||
| This allows Tendermint Core to run applications written in any programming | |||
| language. | |||
| ### 1.3.1 Compile .proto files | |||
| Add the following piece to the top of the `build.gradle`: | |||
| ```groovy | |||
| buildscript { | |||
| repositories { | |||
| mavenCentral() | |||
| } | |||
| dependencies { | |||
| classpath 'com.google.protobuf:protobuf-gradle-plugin:0.8.8' | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| ``` | |||
| Enable the protobuf plugin in the `plugins` section of the `build.gradle`: | |||
| ```groovy | |||
| plugins { | |||
| id 'com.google.protobuf' version '0.8.8' | |||
| } | |||
| ``` | |||
| Add the following code to `build.gradle`: | |||
| ```groovy | |||
| protobuf { | |||
| protoc { | |||
| artifact = "com.google.protobuf:protoc:3.7.1" | |||
| } | |||
| plugins { | |||
| grpc { | |||
| artifact = 'io.grpc:protoc-gen-grpc-java:1.22.1' | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| generateProtoTasks { | |||
| all()*.plugins { | |||
| grpc {} | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| ``` | |||
| Now we should be ready to compile the `*.proto` files. | |||
| Copy the necessary `.proto` files to your project: | |||
| ```sh | |||
| mkdir -p \ | |||
| $KVSTORE_HOME/src/main/proto/github.com/tendermint/tendermint/abci/types \ | |||
| $KVSTORE_HOME/src/main/proto/github.com/tendermint/tendermint/crypto/merkle \ | |||
| $KVSTORE_HOME/src/main/proto/github.com/tendermint/tendermint/libs/common \ | |||
| $KVSTORE_HOME/src/main/proto/github.com/gogo/protobuf/gogoproto | |||
| cp $GOPATH/src/github.com/tendermint/tendermint/abci/types/types.proto \ | |||
| $KVSTORE_HOME/src/main/proto/github.com/tendermint/tendermint/abci/types/types.proto | |||
| cp $GOPATH/src/github.com/tendermint/tendermint/crypto/merkle/merkle.proto \ | |||
| $KVSTORE_HOME/src/main/proto/github.com/tendermint/tendermint/crypto/merkle/merkle.proto | |||
| cp $GOPATH/src/github.com/tendermint/tendermint/libs/common/types.proto \ | |||
| $KVSTORE_HOME/src/main/proto/github.com/tendermint/tendermint/libs/common/types.proto | |||
| cp $GOPATH/src/github.com/gogo/protobuf/gogoproto/gogo.proto \ | |||
| $KVSTORE_HOME/src/main/proto/github.com/gogo/protobuf/gogoproto/gogo.proto | |||
| ``` | |||
| Add these dependencies to `build.gradle`: | |||
| ```groovy | |||
| dependencies { | |||
| implementation 'io.grpc:grpc-protobuf:1.22.1' | |||
| implementation 'io.grpc:grpc-netty-shaded:1.22.1' | |||
| implementation 'io.grpc:grpc-stub:1.22.1' | |||
| } | |||
| ``` | |||
| To generate all protobuf-type classes run: | |||
| ```sh | |||
| ./gradlew generateProto | |||
| ``` | |||
| To verify that everything went smoothly, you can inspect the `build/generated/` directory: | |||
| ```sh | |||
| $ tree build/generated/ | |||
| build/generated/ | |||
| |-- source | |||
| | `-- proto | |||
| | `-- main | |||
| | |-- grpc | |||
| | | `-- types | |||
| | | `-- ABCIApplicationGrpc.java | |||
| | `-- java | |||
| | |-- com | |||
| | | `-- protobuf | |||
| | | `-- GoGoProtos.java | |||
| | |-- common | |||
| | | `-- Types.java | |||
| | |-- merkle | |||
| | | `-- Merkle.java | |||
| | `-- types | |||
| | `-- Types.java | |||
| ``` | |||
| ### 1.3.2 Implementing ABCI | |||
| The resulting `$KVSTORE_HOME/build/generated/source/proto/main/grpc/types/ABCIApplicationGrpc.java` file | |||
| contains the abstract class `ABCIApplicationImplBase`, which is an interface we'll need to implement. | |||
| Create `$KVSTORE_HOME/src/main/java/io/example/KVStoreApp.java` file with the following content: | |||
| ```java | |||
| package io.example; | |||
| import io.grpc.stub.StreamObserver; | |||
| import types.ABCIApplicationGrpc; | |||
| import types.Types.*; | |||
| class KVStoreApp extends ABCIApplicationGrpc.ABCIApplicationImplBase { | |||
| // methods implementation | |||
| } | |||
| ``` | |||
| Now I will go through each method of `ABCIApplicationImplBase` explaining when it's called and adding | |||
| required business logic. | |||
| ### 1.3.3 CheckTx | |||
| When a new transaction is added to the Tendermint Core, it will ask the | |||
| application to check it (validate the format, signatures, etc.). | |||
| ```java | |||
| @Override | |||
| public void checkTx(RequestCheckTx req, StreamObserver<ResponseCheckTx> responseObserver) { | |||
| var tx = req.getTx(); | |||
| int code = validate(tx); | |||
| var resp = ResponseCheckTx.newBuilder() | |||
| .setCode(code) | |||
| .setGasWanted(1) | |||
| .build(); | |||
| responseObserver.onNext(resp); | |||
| responseObserver.onCompleted(); | |||
| } | |||
| private int validate(ByteString tx) { | |||
| List<byte[]> parts = split(tx, '='); | |||
| if (parts.size() != 2) { | |||
| return 1; | |||
| } | |||
| byte[] key = parts.get(0); | |||
| byte[] value = parts.get(1); | |||
| // check if the same key=value already exists | |||
| var stored = getPersistedValue(key); | |||
| if (stored != null && Arrays.equals(stored, value)) { | |||
| return 2; | |||
| } | |||
| return 0; | |||
| } | |||
| private List<byte[]> split(ByteString tx, char separator) { | |||
| var arr = tx.toByteArray(); | |||
| int i; | |||
| for (i = 0; i < tx.size(); i++) { | |||
| if (arr[i] == (byte)separator) { | |||
| break; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| if (i == tx.size()) { | |||
| return Collections.emptyList(); | |||
| } | |||
| return List.of( | |||
| tx.substring(0, i).toByteArray(), | |||
| tx.substring(i + 1).toByteArray() | |||
| ); | |||
| } | |||
| ``` | |||
| Don't worry if this does not compile yet. | |||
| If the transaction does not have a form of `{bytes}={bytes}`, we return `1` | |||
| code. When the same key=value already exist (same key and value), we return `2` | |||
| code. For others, we return a zero code indicating that they are valid. | |||
| Note that anything with non-zero code will be considered invalid (`-1`, `100`, | |||
| etc.) by Tendermint Core. | |||
| Valid transactions will eventually be committed given they are not too big and | |||
| have enough gas. To learn more about gas, check out ["the | |||
| specification"](https://tendermint.com/docs/spec/abci/apps.html#gas). | |||
| For the underlying key-value store we'll use | |||
| [JetBrains Xodus](https://github.com/JetBrains/xodus), which is a transactional schema-less embedded high-performance database written in Java. | |||
| `build.gradle`: | |||
| ```groovy | |||
| dependencies { | |||
| implementation 'org.jetbrains.xodus:xodus-environment:1.3.91' | |||
| } | |||
| ``` | |||
| ```java | |||
| ... | |||
| import jetbrains.exodus.ArrayByteIterable; | |||
| import jetbrains.exodus.ByteIterable; | |||
| import jetbrains.exodus.env.Environment; | |||
| import jetbrains.exodus.env.Store; | |||
| import jetbrains.exodus.env.StoreConfig; | |||
| import jetbrains.exodus.env.Transaction; | |||
| class KVStoreApp extends ABCIApplicationGrpc.ABCIApplicationImplBase { | |||
| private Environment env; | |||
| private Transaction txn = null; | |||
| private Store store = null; | |||
| KVStoreApp(Environment env) { | |||
| this.env = env; | |||
| } | |||
| ... | |||
| private byte[] getPersistedValue(byte[] k) { | |||
| return env.computeInReadonlyTransaction(txn -> { | |||
| var store = env.openStore("store", StoreConfig.WITHOUT_DUPLICATES, txn); | |||
| ByteIterable byteIterable = store.get(txn, new ArrayByteIterable(k)); | |||
| if (byteIterable == null) { | |||
| return null; | |||
| } | |||
| return byteIterable.getBytesUnsafe(); | |||
| }); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| ``` | |||
| ### 1.3.4 BeginBlock -> DeliverTx -> EndBlock -> Commit | |||
| When Tendermint Core has decided on the block, it's transferred to the | |||
| application in 3 parts: `BeginBlock`, one `DeliverTx` per transaction and | |||
| `EndBlock` in the end. `DeliverTx` are being transferred asynchronously, but the | |||
| responses are expected to come in order. | |||
| ```java | |||
| @Override | |||
| public void beginBlock(RequestBeginBlock req, StreamObserver<ResponseBeginBlock> responseObserver) { | |||
| txn = env.beginTransaction(); | |||
| store = env.openStore("store", StoreConfig.WITHOUT_DUPLICATES, txn); | |||
| var resp = ResponseBeginBlock.newBuilder().build(); | |||
| responseObserver.onNext(resp); | |||
| responseObserver.onCompleted(); | |||
| } | |||
| ``` | |||
| Here we begin a new transaction, which will accumulate the block's transactions and open the corresponding store. | |||
| ```java | |||
| @Override | |||
| public void deliverTx(RequestDeliverTx req, StreamObserver<ResponseDeliverTx> responseObserver) { | |||
| var tx = req.getTx(); | |||
| int code = validate(tx); | |||
| if (code == 0) { | |||
| List<byte[]> parts = split(tx, '='); | |||
| var key = new ArrayByteIterable(parts.get(0)); | |||
| var value = new ArrayByteIterable(parts.get(1)); | |||
| store.put(txn, key, value); | |||
| } | |||
| var resp = ResponseDeliverTx.newBuilder() | |||
| .setCode(code) | |||
| .build(); | |||
| responseObserver.onNext(resp); | |||
| responseObserver.onCompleted(); | |||
| } | |||
| ``` | |||
| If the transaction is badly formatted or the same key=value already exist, we | |||
| again return the non-zero code. Otherwise, we add it to the store. | |||
| In the current design, a block can include incorrect transactions (those who | |||
| passed `CheckTx`, but failed `DeliverTx` or transactions included by the proposer | |||
| directly). This is done for performance reasons. | |||
| Note we can't commit transactions inside the `DeliverTx` because in such case | |||
| `Query`, which may be called in parallel, will return inconsistent data (i.e. | |||
| it will report that some value already exist even when the actual block was not | |||
| yet committed). | |||
| `Commit` instructs the application to persist the new state. | |||
| ```java | |||
| @Override | |||
| public void commit(RequestCommit req, StreamObserver<ResponseCommit> responseObserver) { | |||
| txn.commit(); | |||
| var resp = ResponseCommit.newBuilder() | |||
| .setData(ByteString.copyFrom(new byte[8])) | |||
| .build(); | |||
| responseObserver.onNext(resp); | |||
| responseObserver.onCompleted(); | |||
| } | |||
| ``` | |||
| ### 1.3.5 Query | |||
| Now, when the client wants to know whenever a particular key/value exist, it | |||
| will call Tendermint Core RPC `/abci_query` endpoint, which in turn will call | |||
| the application's `Query` method. | |||
| Applications are free to provide their own APIs. But by using Tendermint Core | |||
| as a proxy, clients (including [light client | |||
| package](https://godoc.org/github.com/tendermint/tendermint/lite)) can leverage | |||
| the unified API across different applications. Plus they won't have to call the | |||
| otherwise separate Tendermint Core API for additional proofs. | |||
| Note we don't include a proof here. | |||
| ```java | |||
| @Override | |||
| public void query(RequestQuery req, StreamObserver<ResponseQuery> responseObserver) { | |||
| var k = req.getData().toByteArray(); | |||
| var v = getPersistedValue(k); | |||
| var builder = ResponseQuery.newBuilder(); | |||
| if (v == null) { | |||
| builder.setLog("does not exist"); | |||
| } else { | |||
| builder.setLog("exists"); | |||
| builder.setKey(ByteString.copyFrom(k)); | |||
| builder.setValue(ByteString.copyFrom(v)); | |||
| } | |||
| responseObserver.onNext(builder.build()); | |||
| responseObserver.onCompleted(); | |||
| } | |||
| ``` | |||
| The complete specification can be found | |||
| [here](https://tendermint.com/docs/spec/abci/). | |||
| ## 1.4 Starting an application and a Tendermint Core instances | |||
| Put the following code into the `$KVSTORE_HOME/src/main/java/io/example/App.java` file: | |||
| ```java | |||
| package io.example; | |||
| import jetbrains.exodus.env.Environment; | |||
| import jetbrains.exodus.env.Environments; | |||
| import java.io.IOException; | |||
| public class App { | |||
| public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException { | |||
| try (Environment env = Environments.newInstance("tmp/storage")) { | |||
| var app = new KVStoreApp(env); | |||
| var server = new GrpcServer(app, 26658); | |||
| server.start(); | |||
| server.blockUntilShutdown(); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| ``` | |||
| It is the entry point of the application. | |||
| Here we create a special object `Environment`, which knows where to store the application state. | |||
| Then we create and start the gRPC server to handle Tendermint Core requests. | |||
| Create the `$KVSTORE_HOME/src/main/java/io/example/GrpcServer.java` file with the following content: | |||
| ```java | |||
| package io.example; | |||
| import io.grpc.BindableService; | |||
| import io.grpc.Server; | |||
| import io.grpc.ServerBuilder; | |||
| import java.io.IOException; | |||
| class GrpcServer { | |||
| private Server server; | |||
| GrpcServer(BindableService service, int port) { | |||
| this.server = ServerBuilder.forPort(port) | |||
| .addService(service) | |||
| .build(); | |||
| } | |||
| void start() throws IOException { | |||
| server.start(); | |||
| System.out.println("gRPC server started, listening on $port"); | |||
| Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(new Thread(() -> { | |||
| System.out.println("shutting down gRPC server since JVM is shutting down"); | |||
| GrpcServer.this.stop(); | |||
| System.out.println("server shut down"); | |||
| })); | |||
| } | |||
| private void stop() { | |||
| server.shutdown(); | |||
| } | |||
| /** | |||
| * Await termination on the main thread since the grpc library uses daemon threads. | |||
| */ | |||
| void blockUntilShutdown() throws InterruptedException { | |||
| server.awaitTermination(); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| ``` | |||
| ## 1.5 Getting Up and Running | |||
| To create a default configuration, nodeKey and private validator files, let's | |||
| execute `tendermint init`. But before we do that, we will need to install | |||
| Tendermint Core. | |||
| ```sh | |||
| $ rm -rf /tmp/example | |||
| $ cd $GOPATH/src/github.com/tendermint/tendermint | |||
| $ make install | |||
| $ TMHOME="/tmp/example" tendermint init | |||
| I[2019-07-16|18:20:36.480] Generated private validator module=main keyFile=/tmp/example/config/priv_validator_key.json stateFile=/tmp/example2/data/priv_validator_state.json | |||
| I[2019-07-16|18:20:36.481] Generated node key module=main path=/tmp/example/config/node_key.json | |||
| I[2019-07-16|18:20:36.482] Generated genesis file module=main path=/tmp/example/config/genesis.json | |||
| ``` | |||
| Feel free to explore the generated files, which can be found at | |||
| `/tmp/example/config` directory. Documentation on the config can be found | |||
| [here](https://tendermint.com/docs/tendermint-core/configuration.html). | |||
| We are ready to start our application: | |||
| ```sh | |||
| ./gradlew run | |||
| gRPC server started, listening on 26658 | |||
| ``` | |||
| Then we need to start Tendermint Core and point it to our application. Staying | |||
| within the application directory execute: | |||
| ```sh | |||
| $ TMHOME="/tmp/example" tendermint node --abci grpc --proxy_app tcp://127.0.0.1:26658 | |||
| I[2019-07-28|15:44:53.632] Version info module=main software=0.32.1 block=10 p2p=7 | |||
| I[2019-07-28|15:44:53.677] Starting Node module=main impl=Node | |||
| I[2019-07-28|15:44:53.681] Started node module=main nodeInfo="{ProtocolVersion:{P2P:7 Block:10 App:0} ID_:7639e2841ccd47d5ae0f5aad3011b14049d3f452 ListenAddr:tcp://0.0.0.0:26656 Network:test-chain-Nhl3zk Version:0.32.1 Channels:4020212223303800 Moniker:Ivans-MacBook-Pro.local Other:{TxIndex:on RPCAddress:tcp://127.0.0.1:26657}}" | |||
| I[2019-07-28|15:44:54.801] Executed block module=state height=8 validTxs=0 invalidTxs=0 | |||
| I[2019-07-28|15:44:54.814] Committed state module=state height=8 txs=0 appHash=0000000000000000 | |||
| ``` | |||
| Now open another tab in your terminal and try sending a transaction: | |||
| ```sh | |||
| $ curl -s 'localhost:26657/broadcast_tx_commit?tx="tendermint=rocks"' | |||
| { | |||
| "jsonrpc": "2.0", | |||
| "id": "", | |||
| "result": { | |||
| "check_tx": { | |||
| "gasWanted": "1" | |||
| }, | |||
| "deliver_tx": {}, | |||
| "hash": "CDD3C6DFA0A08CAEDF546F9938A2EEC232209C24AA0E4201194E0AFB78A2C2BB", | |||
| "height": "33" | |||
| } | |||
| ``` | |||
| Response should contain the height where this transaction was committed. | |||
| Now let's check if the given key now exists and its value: | |||
| ```sh | |||
| $ curl -s 'localhost:26657/abci_query?data="tendermint"' | |||
| { | |||
| "jsonrpc": "2.0", | |||
| "id": "", | |||
| "result": { | |||
| "response": { | |||
| "log": "exists", | |||
| "key": "dGVuZGVybWludA==", | |||
| "value": "cm9ja3My" | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| ``` | |||
| `dGVuZGVybWludA==` and `cm9ja3M=` are the base64-encoding of the ASCII of `tendermint` and `rocks` accordingly. | |||
| ## Outro | |||
| I hope everything went smoothly and your first, but hopefully not the last, | |||
| Tendermint Core application is up and running. If not, please [open an issue on | |||
| Github](https://github.com/tendermint/tendermint/issues/new/choose). To dig | |||
| deeper, read [the docs](https://tendermint.com/docs/). | |||
| The full source code of this example project can be found [here](https://github.com/climber73/tendermint-abci-grpc-java). | |||
+ 31
- 32
docs/guides/kotlin.md
View File
+ 2
- 2
docs/spec/abci/apps.md
View File
+ 319
- 103
docs/spec/consensus/light-client.md
View File
| @ -1,113 +1,329 @@ | |||
| # Light Client | |||
| A light client is a process that connects to the Tendermint Full Node(s) and then tries to verify the Merkle proofs | |||
| about the blockchain application. In this document we describe mechanisms that ensures that the Tendermint light client | |||
| has the same level of security as Full Node processes (without being itself a Full Node). | |||
| To be able to validate a Merkle proof, a light client needs to validate the blockchain header that contains the root app hash. | |||
| Validating a blockchain header in Tendermint consists in verifying that the header is committed (signed) by >2/3 of the | |||
| voting power of the corresponding validator set. As the validator set is a dynamic set (it is changing), one of the | |||
| core functionality of the light client is updating the current validator set, that is then used to verify the | |||
| blockchain header, and further the corresponding Merkle proofs. | |||
| For the purpose of this light client specification, we assume that the Tendermint Full Node exposes the following functions over | |||
| Tendermint RPC: | |||
| ```golang | |||
| Header(height int64) (SignedHeader, error) // returns signed header for the given height | |||
| Validators(height int64) (ResultValidators, error) // returns validator set for the given height | |||
| LastHeader(valSetNumber int64) (SignedHeader, error) // returns last header signed by the validator set with the given validator set number | |||
| type SignedHeader struct { | |||
| Header Header | |||
| Commit Commit | |||
| ValSetNumber int64 | |||
| } | |||
| # Lite client | |||
| type ResultValidators struct { | |||
| BlockHeight int64 | |||
| Validators []Validator | |||
| // time the current validator set is initialised, i.e, time of the last validator change before header BlockHeight | |||
| ValSetTime int64 | |||
| } | |||
| A lite client is a process that connects to Tendermint full nodes and then tries to verify application data using the Merkle proofs. | |||
| ## Context of this document | |||
| In order to make sure that full nodes have the incentive to follow the protocol, we have to address the following three Issues | |||
| 1) The lite client needs a method to verify headers it obtains from full nodes according to trust assumptions -- this document. | |||
| 2) The lite client must be able to connect to one correct full node to detect and report on failures in the trust assumptions (i.e., conflicting headers) -- a future document. | |||
| 3) In the event the trust assumption fails (i.e., a lite client is fooled by a conflicting header), the Tendermint fork accountability protocol must account for the evidence -- see #3840 | |||
| ## Problem statement | |||
| We assume that the lite client knows a (base) header *inithead* it trusts (by social consensus or because the lite client has decided to trust the header before). The goal is to check whether another header *newhead* can be trusted based on the data in *inithead*. | |||
| The correctness of the protocol is based on the assumption that *inithead* was generated by an instance of Tendermint consensus. The term "trusting" above indicates that the correctness on the protocol depends on this assumption. It is in the responsibility of the user that runs the lite client to make sure that the risk of trusting a corrupted/forged *inithead* is negligible. | |||
| ## Definitions | |||
| ### Data structures | |||
| In the following, only the details of the data structures needed for this specification are given. | |||
| * header fields | |||
| - *height* | |||
| - *bfttime*: the chain time when the header (block) was generated | |||
| - *V*: validator set containing validators for this block. | |||
| - *NextV*: validator set for next block. | |||
| - *commit*: evidence that block with height *height* - 1 was committed by a set of validators (canonical commit). We will use ```signers(commit)``` to refer to the set of validators that committed the block. | |||
| * signed header fields: contains a header and a *commit* for the current header; a "seen commit". In the Tendermint consensus the "canonical commit" is stored in header *height* + 1. | |||
| * For each header *h* it has locally stored, the lite client stores whether | |||
| it trusts *h*. We write *trust(h) = true*, if this is the case. | |||
| * Validator fields. We will write a validator as a tuple *(v,p)* such that | |||
| + *v* is the identifier (we assume identifiers are unique in each validator set) | |||
| + *p* is its voting power | |||
| ### Functions | |||
| For the purpose of this lite client specification, we assume that the Tendermint Full Node exposes the following function over Tendermint RPC: | |||
| ```go | |||
| func Commit(height int64) (SignedHeader, error) | |||
| // returns signed header: header (with the fields from | |||
| // above) with Commit that include signatures of | |||
| // validators that signed the header | |||
| type SignedHeader struct { | |||
| Header Header | |||
| Commit Commit | |||
| } | |||
| ``` | |||
| We assume that Tendermint keeps track of the validator set changes and that each time a validator set is changed it is | |||
| being assigned the next sequence number. We can call this number the validator set sequence number. Tendermint also remembers | |||
| the Time from the header when the next validator set is initialised (starts to be in power), and we refer to this time | |||
| as validator set init time. | |||
| Furthermore, we assume that each validator set change is signed (committed) by the current validator set. More precisely, | |||
| given a block `H` that contains transactions that are modifying the current validator set, the Merkle root hash of the next | |||
| validator set (modified based on transactions from block H) will be in block `H+1` (and signed by the current validator | |||
| set), and then starting from the block `H+2`, it will be signed by the next validator set. | |||
| Note that the real Tendermint RPC API is slightly different (for example, response messages contain more data and function | |||
| names are slightly different); we shortened (and modified) it for the purpose of this document to make the spec more | |||
| clear and simple. Furthermore, note that in case of the third function, the returned header has `ValSetNumber` equals to | |||
| `valSetNumber+1`. | |||
| Locally, light client manages the following state: | |||
| ```golang | |||
| valSet []Validator // current validator set (last known and verified validator set) | |||
| valSetNumber int64 // sequence number of the current validator set | |||
| valSetHash []byte // hash of the current validator set | |||
| valSetTime int64 // time when the current validator set is initialised | |||
| ### Definitions | |||
| * *tp*: trusting period | |||
| * for realtime *t*, the predicate *correct(v,t)* is true if the validator *v* | |||
| follows the protocol until time *t* (we will see about recovery later). | |||
| ### Tendermint Failure Model | |||
| If a block *h* is generated at time *bfttime* (and this time is stored in the block), then a set of validators that hold more than 2/3 of the voting power in h.Header.NextV is correct until time h.Header.bfttime + tp. | |||
| Formally, | |||
| \[ | |||
| \sum_{(v,p) \in h.Header.NextV \wedge correct(v,h.Header.bfttime + tp)} p > | |||
| 2/3 \sum_{(v,p) \in h.Header.NextV} p | |||
| \] | |||
| *Assumption*: "correct" is defined w.r.t. realtime (some Newtonian global notion of time, i.e., wall time), while *bfttime* corresponds to the reading of the local clock of a validator (how this time is computed may change when the Tendermint consensus is modified). In this note, we assume that all clocks are synchronized to realtime. We can make this more precise eventually (incorporating clock drift, accuracy, precision, etc.). Right now, we consider this assumption sufficient, as clock synchronization (under NTP) is in the order of milliseconds and *tp* is in the order of weeks. | |||
| *Remark*: This failure model might change to a hybrid version that takes heights into account in the future. | |||
| The specification in this document considers an implementation of the lite client under this assumption. Issues like *counter-factual signing* and *fork accountability* and *evidence submission* are mechanisms that justify this assumption by incentivizing validators to follow the protocol. | |||
| If they don't, and we have more that 1/3 faults, safety may be violated. Our approach then is to *detect* these cases (after the fact), and take suitable repair actions (automatic and social). This is discussed in an upcoming document on "Fork accountability". (These safety violations include the lite client wrongly trusting a header, a fork in the blockchain, etc.) | |||
| ## Lite Client Trusting Spec | |||
| The lite client communicates with a full node and learns new headers. The goal is to locally decide whether to trust a header. Our implementation needs to ensure the following two properties: | |||
| - Lite Client Completeness: If header *h* was correctly generated by an instance of Tendermint consensus (and its age is less than the trusting period), then the lite client should eventually set *trust(h)* to true. | |||
| - Lite Client Accuracy: If header *h* was *not generated* by an instance of Tendermint consensus, then the lite client should never set *trust(h)* to true. | |||
| *Remark*: If in the course of the computation, the lite client obtains certainty that some headers were forged by adversaries (that is were not generated by an instance of Tendermint consensus), it may submit (a subset of) the headers it has seen as evidence of misbehavior. | |||
| *Remark*: In Completeness we use "eventually", while in practice *trust(h)* should be set to true before *h.Header.bfttime + tp*. If not, the block cannot be trusted because it is too old. | |||
| *Remark*: If a header *h* is marked with *trust(h)*, but it is too old (its bfttime is more than *tp* ago), then the lite client should set *trust(h)* to false again. | |||
| *Assumption*: Initially, the lite client has a header *inithead* that it trusts correctly, that is, *inithead* was correctly generated by the Tendermint consensus. | |||
| To reason about the correctness, we may prove the following invariant. | |||
| *Verification Condition: Lite Client Invariant.* | |||
| For each lite client *l* and each header *h*: | |||
| if *l* has set *trust(h) = true*, | |||
| then validators that are correct until time *h.Header.bfttime + tp* have more than two thirds of the voting power in *h.Header.NextV*. | |||
| Formally, | |||
| \[ | |||
| \sum_{(v,p) \in h.Header.NextV \wedge correct(v,h.Header.bfttime + tp)} p > | |||
| 2/3 \sum_{(v,p) \in h.Header.NextV} p | |||
| \] | |||
| *Remark.* To prove the invariant, we will have to prove that the lite client only trusts headers that were correctly generated by Tendermint consensus, then the formula above follows from the Tendermint failure model. | |||
| ## High Level Solution | |||
| Upon initialization, the lite client is given a header *inithead* it trusts (by | |||
| social consensus). It is assumed that *inithead* satisfies the lite client invariant. (If *inithead* has been correctly generated by Tendermint consensus, the invariant follows from the Tendermint Failure Model.) | |||
| When a lite clients sees a signed new header *snh*, it has to decide whether to trust the new | |||
| header. Trust can be obtained by (possibly) the combination of three methods. | |||
| 1. **Uninterrupted sequence of proof.** If a block is appended to the chain, where the last block | |||
| is trusted (and properly committed by the old validator set in the next block), | |||
| and the new block contains a new validator set, the new block is trusted if the lite client knows all headers in the prefix. | |||
| Intuitively, a trusted validator set is assumed to only chose a new validator set that will obey the Tendermint Failure Model. | |||
| 2. **Trusting period.** Based on a trusted block *h*, and the lite client | |||
| invariant, which ensures the fault assumption during the trusting period, we can check whether at least one validator, that has been continuously correct from *h.Header.bfttime* until now, has signed *snh*. | |||
| If this is the case, similarly to above, the chosen validator set in *snh* does not violate the Tendermint Failure Model. | |||
| 3. **Bisection.** If a check according to the trusting period fails, the lite client can try to obtain a header *hp* whose height lies between *h* and *snh* in order to check whether *h* can be used to get trust for *hp*, and *hp* can be used to get trust for *snh*. If this is the case we can trust *snh*; if not, we may continue recursively. | |||
| ## How to use it | |||
| We consider the following use case: | |||
| the lite client wants to verify a header for some given height *k*. Thus: | |||
| - it requests the signed header for height *k* from a full node | |||
| - it tries to verify this header with the methods described here. | |||
| This can be used in several settings: | |||
| - someone tells the lite client that application data that is relevant for it can be read in the block of height *k*. | |||
| - the lite clients wants the latest state. It asks a full nude for the current height, and uses the response for *k*. | |||
| ## Details | |||
| *Assumptions* | |||
| 1. *tp < unbonding period*. | |||
| 2. *snh.Header.bfttime < now* | |||
| 3. *snh.Header.bfttime < h.Header.bfttime+tp* | |||
| 4. *trust(h)=true* | |||
| **Observation 1.** If *h.Header.bfttime + tp > now*, we trust the old | |||
| validator set *h.Header.NextV*. | |||
| When we say we trust *h.Header.NextV* we do *not* trust that each individual validator in *h.Header.NextV* is correct, but we only trust the fact that at most 1/3 of them are faulty (more precisely, the faulty ones have at most 1/3 of the total voting power). | |||
| ### Functions | |||
| The function *Bisection* checks whether to trust header *h2* based on the trusted header *h1*. It does so by calling | |||
| the function *CheckSupport* in the process of | |||
| bisection/recursion. *CheckSupport* implements the trusted period method and, for two adjacent headers (in term of heights), it checks uninterrupted sequence of proof. | |||
| *Assumption*: In the following, we assume that *h2.Header.height > h1.Header.height*. We will quickly discuss the other case in the next section. | |||
| We consider the following set-up: | |||
| - the lite client communicates with one full node | |||
| - the lite client locally stores all the signed headers it obtained (trusted or not). In the pseudo code below we write *Store(header)* for this. | |||
| - If *Bisection* returns *false*, then the lite client has seen a forged header. | |||
| * However, it does not know which header(s) is/are the problematic one(s). | |||
| * In this case, the lite client can submit (some of) the headers it has seen as evidence. As the lite client communicates with one full node only when executing Bisection, there are two cases | |||
| - the full node is faulty | |||
| - the full node is correct and there was a fork in Tendermint consensus. Header *h1* is from a different branch than the one taken by the full node. This case is not focus of this document, but will be treated in the document on fork accountability. | |||
| - the lite client must retry to retrieve correct headers from another full node | |||
| * it picks a new full node | |||
| * it restarts *Bisection* | |||
| * there might be optimizations; a lite client may not need to call *Commit(k)*, for a height *k* for which it already has a signed header it trusts. | |||
| * how to make sure that a lite client can communicate with a correct full node will be the focus of a separate document (recall Issue 3 from "Context of this document"). | |||
| **Auxiliary Functions.** We will use the function ```votingpower_in(V1,V2)``` to compute the voting power the validators in set V1 have according to their voting power in set V2; | |||
| we will write ```totalVotingPower(V)``` for ```votingpower_in(V,V)```, which returns the total voting power in V. | |||
| We further use the function ```signers(Commit)``` that returns the set of validators that signed the Commit. | |||
| **CheckSupport.** The following function checks whether we can trust the header h2 based on header h1 following the trusting period method. | |||
| ```go | |||
| func CheckSupport(h1,h2,trustlevel) bool { | |||
| if h1.Header.bfttime + tp < now { // Observation 1 | |||
| return false // old header was once trusted but it is expired | |||
| } | |||
| vp_all := totalVotingPower(h1.Header.NextV) | |||
| // total sum of voting power of validators in h2 | |||
| if h2.Header.height == h1.Header.height + 1 { | |||
| // specific check for adjacent headers; everything must be | |||
| // properly signed. | |||
| // also check that h2.Header.V == h1.Header.NextV | |||
| // Plus the following check that 2/3 of the voting power | |||
| // in h1 signed h2 | |||
| return (votingpower_in(signers(h2.Commit),h1.Header.NextV) > | |||
| 2/3 * vp_all) | |||
| // signing validators are more than two third in h1. | |||
| } | |||
| return (votingpower_in(signers(h2.Commit),h1.Header.NextV) > | |||
| max(1/3,trustlevel) * vp_all) | |||
| // get validators in h1 that signed h2 | |||
| // sum of voting powers in h1 of | |||
| // validators that signed h2 | |||
| // is more than a third in h1 | |||
| } | |||
| ``` | |||
| The light client is initialised with the trusted validator set, for example based on the known validator set hash, | |||
| validator set sequence number and the validator set init time. | |||
| The core of the light client logic is captured by the VerifyAndUpdate function that is used to 1) verify if the given header is valid, | |||
| and 2) update the validator set (when the given header is valid and it is more recent than the seen headers). | |||
| *Remark*: Basic header verification must be done for *h2*. Similar checks are done in: | |||
| https://github.com/tendermint/tendermint/blob/master/types/validator_set.go#L591-L633 | |||
| *Remark*: There are some sanity checks which are not in the code: | |||
| *h2.Header.height > h1.Header.height* and *h2.Header.bfttime > h1.Header.bfttime* and *h2.Header.bfttime < now*. | |||
| *Remark*: ```return (votingpower_in(signers(h2.Commit),h1.Header.NextV) > max(1/3,trustlevel) * vp_all)``` may return false even if *h2* was properly generated by Tendermint consensus in the case of big changes in the validator sets. However, the check ```return (votingpower_in(signers(h2.Commit),h1.Header.NextV) > | |||
| 2/3 * vp_all)``` must return true if *h1* and *h2* were generated by Tendermint consensus. | |||
| *Remark*: The 1/3 check differs from a previously proposed method that was based on intersecting validator sets and checking that the new validator set contains "enough" correct validators. We found that the old check is not suited for realistic changes in the validator sets. The new method is not only based on cardinalities, but also exploits that we can trust what is signed by a correct validator (i.e., signed by more than 1/3 of the voting power). | |||
| ```golang | |||
| VerifyAndUpdate(signedHeader SignedHeader): | |||
| assertThat signedHeader.valSetNumber >= valSetNumber | |||
| if isValid(signedHeader) and signedHeader.Header.Time <= valSetTime + UNBONDING_PERIOD then | |||
| setValidatorSet(signedHeader) | |||
| *Correctness arguments* | |||
| Towards Lite Client Accuracy: | |||
| - Assume by contradiction that *h2* was not generated correctly and the lite client sets trust to true because *CheckSupport* returns true. | |||
| - h1 is trusted and sufficiently new | |||
| - by Tendermint Fault Model, less than 1/3 of voting power held by faulty validators => at least one correct validator *v* has signed *h2*. | |||
| - as *v* is correct up to now, it followed the Tendermint consensus protocol at least up to signing *h2* => *h2* was correctly generated, we arrive at the required contradiction. | |||
| Towards Lite Client Completeness: | |||
| - The check is successful if sufficiently many validators of *h1* are still validators in *h2* and signed *h2*. | |||
| - If *h2.Header.height = h1.Header.height + 1*, and both headers were generated correctly, the test passes | |||
| *Verification Condition:* We may need a Tendermint invariant stating that if *h2.Header.height = h1.Header.height + 1* then *signers(h2.Commit) \subseteq h1.Header.NextV*. | |||
| *Remark*: The variable *trustlevel* can be used if the user believes that relying on one correct validator is not sufficient. However, in case of (frequent) changes in the validator set, the higher the *trustlevel* is chosen, the more unlikely it becomes that CheckSupport returns true for non-adjacent headers. | |||
| **Bisection.** The following function uses CheckSupport in a recursion to find intermediate headers that allow to establish a sequence of trust. | |||
| ```go | |||
| func Bisection(h1,h2,trustlevel) bool{ | |||
| if CheckSupport(h1,h2,trustlevel) { | |||
| return true | |||
| else | |||
| updateValidatorSet(signedHeader.ValSetNumber) | |||
| return VerifyAndUpdate(signedHeader) | |||
| isValid(signedHeader SignedHeader): | |||
| valSetOfTheHeader = Validators(signedHeader.Header.Height) | |||
| assertThat Hash(valSetOfTheHeader) == signedHeader.Header.ValSetHash | |||
| assertThat signedHeader is passing basic validation | |||
| if votingPower(signedHeader.Commit) > 2/3 * votingPower(valSetOfTheHeader) then return true | |||
| else | |||
| } | |||
| if h2.Header.height == h1.Header.height + 1 { | |||
| // we have adjacent headers that are not matching (failed | |||
| // the CheckSupport) | |||
| // we could submit evidence here | |||
| return false | |||
| } | |||
| pivot := (h1.Header.height + h2.Header.height) / 2 | |||
| hp := Commit(pivot) | |||
| // ask a full node for header of height pivot | |||
| Store(hp) | |||
| // store header hp locally | |||
| if Bisection(h1,hp,trustlevel) { | |||
| // only check right branch if hp is trusted | |||
| // (otherwise a lot of unnecessary computation may be done) | |||
| return Bisection(hp,h2,trustlevel) | |||
| } | |||
| else { | |||
| return false | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| ``` | |||
| setValidatorSet(signedHeader SignedHeader): | |||
| nextValSet = Validators(signedHeader.Header.Height) | |||
| assertThat Hash(nextValSet) == signedHeader.Header.ValidatorsHash | |||
| valSet = nextValSet.Validators | |||
| valSetHash = signedHeader.Header.ValidatorsHash | |||
| valSetNumber = signedHeader.ValSetNumber | |||
| valSetTime = nextValSet.ValSetTime | |||
| votingPower(commit Commit): | |||
| votingPower = 0 | |||
| for each precommit in commit.Precommits do: | |||
| if precommit.ValidatorAddress is in valSet and signature of the precommit verifies then | |||
| votingPower += valSet[precommit.ValidatorAddress].VotingPower | |||
| return votingPower | |||
| votingPower(validatorSet []Validator): | |||
| for each validator in validatorSet do: | |||
| votingPower += validator.VotingPower | |||
| return votingPower | |||
| updateValidatorSet(valSetNumberOfTheHeader): | |||
| while valSetNumber != valSetNumberOfTheHeader do | |||
| signedHeader = LastHeader(valSetNumber) | |||
| if isValid(signedHeader) then | |||
| setValidatorSet(signedHeader) | |||
| else return error | |||
| return | |||
| ``` | |||
| Note that in the logic above we assume that the light client will always go upward with respect to header verifications, | |||
| i.e., that it will always be used to verify more recent headers. In case a light client needs to be used to verify older | |||
| headers (go backward) the same mechanisms and similar logic can be used. In case a call to the FullNode or subsequent | |||
| checks fail, a light client need to implement some recovery strategy, for example connecting to other FullNode. | |||
| *Correctness arguments (sketch)* | |||
| Lite Client Accuracy: | |||
| - Assume by contradiction that *h2* was not generated correctly and the lite client sets trust to true because Bisection returns true. | |||
| - Bisection returns true only if all calls to CheckSupport in the recursion return true. | |||
| - Thus we have a sequence of headers that all satisfied the CheckSupport | |||
| - again a contradiction | |||
| Lite Client Completeness: | |||
| This is only ensured if upon *Commit(pivot)* the lite client is always provided with a correctly generated header. | |||
| *Stalling* | |||
| With Bisection, a faulty full node could stall a lite client by creating a long sequence of headers that are queried one-by-one by the lite client and look OK, before the lite client eventually detects a problem. There are several ways to address this: | |||
| * Each call to ```Commit``` could be issued to a different full node | |||
| * Instead of querying header by header, the lite client tells a full node which header it trusts, and the height of the header it needs. The full node responds with the header along with a proof consisting of intermediate headers that the light client can use to verify. Roughly, Bisection would then be executed at the full node. | |||
| * We may set a timeout how long bisection may take. | |||
| ### The case *h2.Header.height < h1.Header.height* | |||
| In the use case where someone tells the lite client that application data that is relevant for it can be read in the block of height *k* and the lite client trusts a more recent header, we can use the hashes to verify headers "down the chain." That is, we iterate down the heights and check the hashes in each step. | |||
| *Remark.* For the case were the lite client trusts two headers *i* and *j* with *i < k < j*, we should discuss/experiment whether the forward or the backward method is more effective. | |||
| ```go | |||
| func Backwards(h1,h2) bool { | |||
| assert (h2.Header.height < h1.Header.height) | |||
| old := h1 | |||
| for i := h1.Header.height - 1; i > h2.Header.height; i-- { | |||
| new := Commit(i) | |||
| Store(new) | |||
| if (hash(new) != old.Header.hash) { | |||
| return false | |||
| } | |||
| old := new | |||
| } | |||
| return (hash(h2) == old.Header.hash) | |||
| } | |||
| ``` | |||
+ 1
- 1
docs/spec/p2p/connection.md
View File
+ 3
- 3
docs/spec/reactors/mempool/messages.md
View File
+ 25
- 0
docs/spec/rpc/index.html
View File
| @ -0,0 +1,25 @@ | |||
| <!-- HTML for static distribution bundle build --> | |||
| <!DOCTYPE html> | |||
| <html lang="en"> | |||
| <head> | |||
| <meta charset="UTF-8"> | |||
| <title>Tendermint RPC</title> | |||
| <link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="//unpkg.com/swagger-ui-dist@3/swagger-ui.css" > | |||
| <link rel="icon" type="image/png" href="//unpkg.com/swagger-ui-dist@3/favicon-16x16.png"/> | |||
| <script src="//unpkg.com/swagger-ui-dist@3/swagger-ui-bundle.js"></script> | |||
| </head> | |||
| <body> | |||
| <div id="swagger-ui"></div> | |||
| <script> | |||
| window.onload = function() { | |||
| window.ui = SwaggerUIBundle({ | |||
| url: "./swagger.yaml", | |||
| dom_id: '#swagger-ui', | |||
| deepLinking: true, | |||
| layout: "BaseLayout" | |||
| }); | |||
| } | |||
| </script> | |||
| </body> | |||
| </html> | |||
+ 2679
- 0
docs/spec/rpc/swagger.yaml
File diff suppressed because it is too large
View File
+ 4
- 3
docs/tendermint-core/configuration.md
View File
+ 33
- 0
dredd.yml
View File
| @ -0,0 +1,33 @@ | |||
| color: true | |||
| dry-run: null | |||
| hookfiles: build/contract_tests | |||
| language: go | |||
| require: null | |||
| server: make localnet-start | |||
| server-wait: 30 | |||
| init: false | |||
| custom: {} | |||
| names: false | |||
| only: [] | |||
| reporter: [] | |||
| output: [] | |||
| header: [] | |||
| sorted: false | |||
| user: null | |||
| inline-errors: false | |||
| details: false | |||
| method: [GET] | |||
| loglevel: warning | |||
| path: [] | |||
| hooks-worker-timeout: 5000 | |||
| hooks-worker-connect-timeout: 1500 | |||
| hooks-worker-connect-retry: 500 | |||
| hooks-worker-after-connect-wait: 100 | |||
| hooks-worker-term-timeout: 5000 | |||
| hooks-worker-term-retry: 500 | |||
| hooks-worker-handler-host: 127.0.0.1 | |||
| hooks-worker-handler-port: 61321 | |||
| config: ./dredd.yml | |||
| # This path accepts no variables | |||
| blueprint: ./docs/spec/rpc/swagger.yaml | |||
| endpoint: 'http://127.0.0.1:26657/' | |||
+ 1
- 0
go.mod
View File
+ 2
- 2
go.sum
View File
+ 4
- 3
libs/autofile/group.go
View File
+ 8
- 6
libs/common/async_test.go
View File
+ 1
- 1
libs/common/errors.go
View File
+ 5
- 4
libs/log/tmfmt_logger.go
View File
+ 4
- 2
lite/base_verifier.go
View File
+ 13
- 25
lite/errors/errors.go
View File
+ 4
- 7
lite/proxy/errors.go
View File
+ 4
- 3
lite/proxy/query.go
View File
+ 4
- 3
lite/proxy/verifier.go
View File
+ 2
- 2
mempool/clist_mempool.go
View File
+ 3
- 3
mempool/clist_mempool_test.go
View File
+ 6
- 5
mempool/reactor.go
View File
+ 17
- 29
node/node.go
View File
+ 18
- 11
node/node_test.go
View File
+ 6
- 3
p2p/conn/connection.go
View File
+ 4
- 3
p2p/fuzz.go
View File
+ 15
- 12
p2p/netaddress.go
View File
+ 1
- 1
p2p/node_info_test.go
View File
+ 4
- 3
p2p/peer_test.go
View File
+ 2
- 3
p2p/switch.go
View File
+ 3
- 1
p2p/test_util.go
View File
+ 6
- 6
privval/doc.go
View File
+ 13
- 2
privval/errors.go
View File
+ 4
- 4
privval/file_deprecated_test.go
View File
+ 2
- 1
privval/file_test.go
View File
+ 13
- 10
privval/messages.go
View File
+ 131
- 0
privval/signer_client.go
View File
| @ -0,0 +1,131 @@ | |||
| package privval | |||
| import ( | |||
| "time" | |||
| "github.com/pkg/errors" | |||
| "github.com/tendermint/tendermint/crypto" | |||
| "github.com/tendermint/tendermint/types" | |||
| ) | |||
| // SignerClient implements PrivValidator. | |||
| // Handles remote validator connections that provide signing services | |||
| type SignerClient struct { | |||
| endpoint *SignerListenerEndpoint | |||
| } | |||
| var _ types.PrivValidator = (*SignerClient)(nil) | |||
| // NewSignerClient returns an instance of SignerClient. | |||
| // it will start the endpoint (if not already started) | |||
| func NewSignerClient(endpoint *SignerListenerEndpoint) (*SignerClient, error) { | |||
| if !endpoint.IsRunning() { | |||
| if err := endpoint.Start(); err != nil { | |||
| return nil, errors.Wrap(err, "failed to start listener endpoint") | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| return &SignerClient{endpoint: endpoint}, nil | |||
| } | |||
| // Close closes the underlying connection | |||
| func (sc *SignerClient) Close() error { | |||
| return sc.endpoint.Close() | |||
| } | |||
| // IsConnected indicates with the signer is connected to a remote signing service | |||
| func (sc *SignerClient) IsConnected() bool { | |||
| return sc.endpoint.IsConnected() | |||
| } | |||
| // WaitForConnection waits maxWait for a connection or returns a timeout error | |||
| func (sc *SignerClient) WaitForConnection(maxWait time.Duration) error { | |||
| return sc.endpoint.WaitForConnection(maxWait) | |||
| } | |||
| //-------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| // Implement PrivValidator | |||
| // Ping sends a ping request to the remote signer | |||
| func (sc *SignerClient) Ping() error { | |||
| response, err := sc.endpoint.SendRequest(&PingRequest{}) | |||
| if err != nil { | |||
| sc.endpoint.Logger.Error("SignerClient::Ping", "err", err) | |||
| return nil | |||
| } | |||
| _, ok := response.(*PingResponse) | |||
| if !ok { | |||
| sc.endpoint.Logger.Error("SignerClient::Ping", "err", "response != PingResponse") | |||
| return err | |||
| } | |||
| return nil | |||
| } | |||
| // GetPubKey retrieves a public key from a remote signer | |||
| func (sc *SignerClient) GetPubKey() crypto.PubKey { | |||
| response, err := sc.endpoint.SendRequest(&PubKeyRequest{}) | |||
| if err != nil { | |||
| sc.endpoint.Logger.Error("SignerClient::GetPubKey", "err", err) | |||
| return nil | |||
| } | |||
| pubKeyResp, ok := response.(*PubKeyResponse) | |||
| if !ok { | |||
| sc.endpoint.Logger.Error("SignerClient::GetPubKey", "err", "response != PubKeyResponse") | |||
| return nil | |||
| } | |||
| if pubKeyResp.Error != nil { | |||
| sc.endpoint.Logger.Error("failed to get private validator's public key", "err", pubKeyResp.Error) | |||
| return nil | |||
| } | |||
| return pubKeyResp.PubKey | |||
| } | |||
| // SignVote requests a remote signer to sign a vote | |||
| func (sc *SignerClient) SignVote(chainID string, vote *types.Vote) error { | |||
| response, err := sc.endpoint.SendRequest(&SignVoteRequest{Vote: vote}) | |||
| if err != nil { | |||
| sc.endpoint.Logger.Error("SignerClient::SignVote", "err", err) | |||
| return err | |||
| } | |||
| resp, ok := response.(*SignedVoteResponse) | |||
| if !ok { | |||
| sc.endpoint.Logger.Error("SignerClient::GetPubKey", "err", "response != SignedVoteResponse") | |||
| return ErrUnexpectedResponse | |||
| } | |||
| if resp.Error != nil { | |||
| return resp.Error | |||
| } | |||
| *vote = *resp.Vote | |||
| return nil | |||
| } | |||
| // SignProposal requests a remote signer to sign a proposal | |||
| func (sc *SignerClient) SignProposal(chainID string, proposal *types.Proposal) error { | |||
| response, err := sc.endpoint.SendRequest(&SignProposalRequest{Proposal: proposal}) | |||
| if err != nil { | |||
| sc.endpoint.Logger.Error("SignerClient::SignProposal", "err", err) | |||
| return err | |||
| } | |||
| resp, ok := response.(*SignedProposalResponse) | |||
| if !ok { | |||
| sc.endpoint.Logger.Error("SignerClient::SignProposal", "err", "response != SignedProposalResponse") | |||
| return ErrUnexpectedResponse | |||
| } | |||
| if resp.Error != nil { | |||
| return resp.Error | |||
| } | |||
| *proposal = *resp.Proposal | |||
| return nil | |||
| } | |||
+ 257
- 0
privval/signer_client_test.go
View File
| @ -0,0 +1,257 @@ | |||
| package privval | |||
| import ( | |||
| "fmt" | |||
| "testing" | |||
| "time" | |||
| "github.com/stretchr/testify/assert" | |||
| "github.com/stretchr/testify/require" | |||
| "github.com/tendermint/tendermint/libs/common" | |||
| "github.com/tendermint/tendermint/types" | |||
| ) | |||
| type signerTestCase struct { | |||
| chainID string | |||
| mockPV types.PrivValidator | |||
| signerClient *SignerClient | |||
| signerServer *SignerServer | |||
| } | |||
| func getSignerTestCases(t *testing.T) []signerTestCase { | |||
| testCases := make([]signerTestCase, 0) | |||
| // Get test cases for each possible dialer (DialTCP / DialUnix / etc) | |||
| for _, dtc := range getDialerTestCases(t) { | |||
| chainID := common.RandStr(12) | |||
| mockPV := types.NewMockPV() | |||
| // get a pair of signer listener, signer dialer endpoints | |||
| sl, sd := getMockEndpoints(t, dtc.addr, dtc.dialer) | |||
| sc, err := NewSignerClient(sl) | |||
| require.NoError(t, err) | |||
| ss := NewSignerServer(sd, chainID, mockPV) | |||
| err = ss.Start() | |||
| require.NoError(t, err) | |||
| tc := signerTestCase{ | |||
| chainID: chainID, | |||
| mockPV: mockPV, | |||
| signerClient: sc, | |||
| signerServer: ss, | |||
| } | |||
| testCases = append(testCases, tc) | |||
| } | |||
| return testCases | |||
| } | |||
| func TestSignerClose(t *testing.T) { | |||
| for _, tc := range getSignerTestCases(t) { | |||
| err := tc.signerClient.Close() | |||
| assert.NoError(t, err) | |||
| err = tc.signerServer.Stop() | |||
| assert.NoError(t, err) | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| func TestSignerPing(t *testing.T) { | |||
| for _, tc := range getSignerTestCases(t) { | |||
| defer tc.signerServer.Stop() | |||
| defer tc.signerClient.Close() | |||
| err := tc.signerClient.Ping() | |||
| assert.NoError(t, err) | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| func TestSignerGetPubKey(t *testing.T) { | |||
| for _, tc := range getSignerTestCases(t) { | |||
| defer tc.signerServer.Stop() | |||
| defer tc.signerClient.Close() | |||
| pubKey := tc.signerClient.GetPubKey() | |||
| expectedPubKey := tc.mockPV.GetPubKey() | |||
| assert.Equal(t, expectedPubKey, pubKey) | |||
| addr := tc.signerClient.GetPubKey().Address() | |||
| expectedAddr := tc.mockPV.GetPubKey().Address() | |||
| assert.Equal(t, expectedAddr, addr) | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| func TestSignerProposal(t *testing.T) { | |||
| for _, tc := range getSignerTestCases(t) { | |||
| ts := time.Now() | |||
| want := &types.Proposal{Timestamp: ts} | |||
| have := &types.Proposal{Timestamp: ts} | |||
| defer tc.signerServer.Stop() | |||
| defer tc.signerClient.Close() | |||
| require.NoError(t, tc.mockPV.SignProposal(tc.chainID, want)) | |||
| require.NoError(t, tc.signerClient.SignProposal(tc.chainID, have)) | |||
| assert.Equal(t, want.Signature, have.Signature) | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| func TestSignerVote(t *testing.T) { | |||
| for _, tc := range getSignerTestCases(t) { | |||
| ts := time.Now() | |||
| want := &types.Vote{Timestamp: ts, Type: types.PrecommitType} | |||
| have := &types.Vote{Timestamp: ts, Type: types.PrecommitType} | |||
| defer tc.signerServer.Stop() | |||
| defer tc.signerClient.Close() | |||
| require.NoError(t, tc.mockPV.SignVote(tc.chainID, want)) | |||
| require.NoError(t, tc.signerClient.SignVote(tc.chainID, have)) | |||
| assert.Equal(t, want.Signature, have.Signature) | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| func TestSignerVoteResetDeadline(t *testing.T) { | |||
| for _, tc := range getSignerTestCases(t) { | |||
| ts := time.Now() | |||
| want := &types.Vote{Timestamp: ts, Type: types.PrecommitType} | |||
| have := &types.Vote{Timestamp: ts, Type: types.PrecommitType} | |||
| defer tc.signerServer.Stop() | |||
| defer tc.signerClient.Close() | |||
| time.Sleep(testTimeoutReadWrite2o3) | |||
| require.NoError(t, tc.mockPV.SignVote(tc.chainID, want)) | |||
| require.NoError(t, tc.signerClient.SignVote(tc.chainID, have)) | |||
| assert.Equal(t, want.Signature, have.Signature) | |||
| // TODO(jleni): Clarify what is actually being tested | |||
| // This would exceed the deadline if it was not extended by the previous message | |||
| time.Sleep(testTimeoutReadWrite2o3) | |||
| require.NoError(t, tc.mockPV.SignVote(tc.chainID, want)) | |||
| require.NoError(t, tc.signerClient.SignVote(tc.chainID, have)) | |||
| assert.Equal(t, want.Signature, have.Signature) | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| func TestSignerVoteKeepAlive(t *testing.T) { | |||
| for _, tc := range getSignerTestCases(t) { | |||
| ts := time.Now() | |||
| want := &types.Vote{Timestamp: ts, Type: types.PrecommitType} | |||
| have := &types.Vote{Timestamp: ts, Type: types.PrecommitType} | |||
| defer tc.signerServer.Stop() | |||
| defer tc.signerClient.Close() | |||
| // Check that even if the client does not request a | |||
| // signature for a long time. The service is still available | |||
| // in this particular case, we use the dialer logger to ensure that | |||
| // test messages are properly interleaved in the test logs | |||
| tc.signerServer.Logger.Debug("TEST: Forced Wait -------------------------------------------------") | |||
| time.Sleep(testTimeoutReadWrite * 3) | |||
| tc.signerServer.Logger.Debug("TEST: Forced Wait DONE---------------------------------------------") | |||
| require.NoError(t, tc.mockPV.SignVote(tc.chainID, want)) | |||
| require.NoError(t, tc.signerClient.SignVote(tc.chainID, have)) | |||
| assert.Equal(t, want.Signature, have.Signature) | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| func TestSignerSignProposalErrors(t *testing.T) { | |||
| for _, tc := range getSignerTestCases(t) { | |||
| // Replace service with a mock that always fails | |||
| tc.signerServer.privVal = types.NewErroringMockPV() | |||
| tc.mockPV = types.NewErroringMockPV() | |||
| defer tc.signerServer.Stop() | |||
| defer tc.signerClient.Close() | |||
| ts := time.Now() | |||
| proposal := &types.Proposal{Timestamp: ts} | |||
| err := tc.signerClient.SignProposal(tc.chainID, proposal) | |||
| require.Equal(t, err.(*RemoteSignerError).Description, types.ErroringMockPVErr.Error()) | |||
| err = tc.mockPV.SignProposal(tc.chainID, proposal) | |||
| require.Error(t, err) | |||
| err = tc.signerClient.SignProposal(tc.chainID, proposal) | |||
| require.Error(t, err) | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| func TestSignerSignVoteErrors(t *testing.T) { | |||
| for _, tc := range getSignerTestCases(t) { | |||
| ts := time.Now() | |||
| vote := &types.Vote{Timestamp: ts, Type: types.PrecommitType} | |||
| // Replace signer service privval with one that always fails | |||
| tc.signerServer.privVal = types.NewErroringMockPV() | |||
| tc.mockPV = types.NewErroringMockPV() | |||
| defer tc.signerServer.Stop() | |||
| defer tc.signerClient.Close() | |||
| err := tc.signerClient.SignVote(tc.chainID, vote) | |||
| require.Equal(t, err.(*RemoteSignerError).Description, types.ErroringMockPVErr.Error()) | |||
| err = tc.mockPV.SignVote(tc.chainID, vote) | |||
| require.Error(t, err) | |||
| err = tc.signerClient.SignVote(tc.chainID, vote) | |||
| require.Error(t, err) | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| func brokenHandler(privVal types.PrivValidator, request SignerMessage, chainID string) (SignerMessage, error) { | |||
| var res SignerMessage | |||
| var err error | |||
| switch r := request.(type) { | |||
| // This is broken and will answer most requests with a pubkey response | |||
| case *PubKeyRequest: | |||
| res = &PubKeyResponse{nil, nil} | |||
| case *SignVoteRequest: | |||
| res = &PubKeyResponse{nil, nil} | |||
| case *SignProposalRequest: | |||
| res = &PubKeyResponse{nil, nil} | |||
| case *PingRequest: | |||
| err, res = nil, &PingResponse{} | |||
| default: | |||
| err = fmt.Errorf("unknown msg: %v", r) | |||
| } | |||
| return res, err | |||
| } | |||
| func TestSignerUnexpectedResponse(t *testing.T) { | |||
| for _, tc := range getSignerTestCases(t) { | |||
| tc.signerServer.privVal = types.NewMockPV() | |||
| tc.mockPV = types.NewMockPV() | |||
| tc.signerServer.SetRequestHandler(brokenHandler) | |||
| defer tc.signerServer.Stop() | |||
| defer tc.signerClient.Close() | |||
| ts := time.Now() | |||
| want := &types.Vote{Timestamp: ts, Type: types.PrecommitType} | |||
| e := tc.signerClient.SignVote(tc.chainID, want) | |||
| assert.EqualError(t, e, "received unexpected response") | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
+ 84
- 0
privval/signer_dialer_endpoint.go
View File
| @ -0,0 +1,84 @@ | |||
| package privval | |||
| import ( | |||
| "time" | |||
| cmn "github.com/tendermint/tendermint/libs/common" | |||
| "github.com/tendermint/tendermint/libs/log" | |||
| ) | |||
| const ( | |||
| defaultMaxDialRetries = 10 | |||
| defaultRetryWaitMilliseconds = 100 | |||
| ) | |||
| // SignerServiceEndpointOption sets an optional parameter on the SignerDialerEndpoint. | |||
| type SignerServiceEndpointOption func(*SignerDialerEndpoint) | |||
| // SignerDialerEndpointTimeoutReadWrite sets the read and write timeout for connections | |||
| // from external signing processes. | |||
| func SignerDialerEndpointTimeoutReadWrite(timeout time.Duration) SignerServiceEndpointOption { | |||
| return func(ss *SignerDialerEndpoint) { ss.timeoutReadWrite = timeout } | |||
| } | |||
| // SignerDialerEndpointConnRetries sets the amount of attempted retries to acceptNewConnection. | |||
| func SignerDialerEndpointConnRetries(retries int) SignerServiceEndpointOption { | |||
| return func(ss *SignerDialerEndpoint) { ss.maxConnRetries = retries } | |||
| } | |||
| // SignerDialerEndpoint dials using its dialer and responds to any | |||
| // signature requests using its privVal. | |||
| type SignerDialerEndpoint struct { | |||
| signerEndpoint | |||
| dialer SocketDialer | |||
| retryWait time.Duration | |||
| maxConnRetries int | |||
| } | |||
| // NewSignerDialerEndpoint returns a SignerDialerEndpoint that will dial using the given | |||
| // dialer and respond to any signature requests over the connection | |||
| // using the given privVal. | |||
| func NewSignerDialerEndpoint( | |||
| logger log.Logger, | |||
| dialer SocketDialer, | |||
| ) *SignerDialerEndpoint { | |||
| sd := &SignerDialerEndpoint{ | |||
| dialer: dialer, | |||
| retryWait: defaultRetryWaitMilliseconds * time.Millisecond, | |||
| maxConnRetries: defaultMaxDialRetries, | |||
| } | |||
| sd.BaseService = *cmn.NewBaseService(logger, "SignerDialerEndpoint", sd) | |||
| sd.signerEndpoint.timeoutReadWrite = defaultTimeoutReadWriteSeconds * time.Second | |||
| return sd | |||
| } | |||
| func (sd *SignerDialerEndpoint) ensureConnection() error { | |||
| if sd.IsConnected() { | |||
| return nil | |||
| } | |||
| retries := 0 | |||
| for retries < sd.maxConnRetries { | |||
| conn, err := sd.dialer() | |||
| if err != nil { | |||
| retries++ | |||
| sd.Logger.Debug("SignerDialer: Reconnection failed", "retries", retries, "max", sd.maxConnRetries, "err", err) | |||
| // Wait between retries | |||
| time.Sleep(sd.retryWait) | |||
| } else { | |||
| sd.SetConnection(conn) | |||
| sd.Logger.Debug("SignerDialer: Connection Ready") | |||
| return nil | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| sd.Logger.Debug("SignerDialer: Max retries exceeded", "retries", retries, "max", sd.maxConnRetries) | |||
| return ErrNoConnection | |||
| } | |||
+ 156
- 0
privval/signer_endpoint.go
View File
| @ -0,0 +1,156 @@ | |||
| package privval | |||
| import ( | |||
| "fmt" | |||
| "net" | |||
| "sync" | |||
| "time" | |||
| "github.com/pkg/errors" | |||
| cmn "github.com/tendermint/tendermint/libs/common" | |||
| ) | |||
| const ( | |||
| defaultTimeoutReadWriteSeconds = 3 | |||
| ) | |||
| type signerEndpoint struct { | |||
| cmn.BaseService | |||
| connMtx sync.Mutex | |||
| conn net.Conn | |||
| timeoutReadWrite time.Duration | |||
| } | |||
| // Close closes the underlying net.Conn. | |||
| func (se *signerEndpoint) Close() error { | |||
| se.DropConnection() | |||
| return nil | |||
| } | |||
| // IsConnected indicates if there is an active connection | |||
| func (se *signerEndpoint) IsConnected() bool { | |||
| se.connMtx.Lock() | |||
| defer se.connMtx.Unlock() | |||
| return se.isConnected() | |||
| } | |||
| // TryGetConnection retrieves a connection if it is already available | |||
| func (se *signerEndpoint) GetAvailableConnection(connectionAvailableCh chan net.Conn) bool { | |||
| se.connMtx.Lock() | |||
| defer se.connMtx.Unlock() | |||
| // Is there a connection ready? | |||
| select { | |||
| case se.conn = <-connectionAvailableCh: | |||
| return true | |||
| default: | |||
| } | |||
| return false | |||
| } | |||
| // TryGetConnection retrieves a connection if it is already available | |||
| func (se *signerEndpoint) WaitConnection(connectionAvailableCh chan net.Conn, maxWait time.Duration) error { | |||
| se.connMtx.Lock() | |||
| defer se.connMtx.Unlock() | |||
| select { | |||
| case se.conn = <-connectionAvailableCh: | |||
| case <-time.After(maxWait): | |||
| return ErrConnectionTimeout | |||
| } | |||
| return nil | |||
| } | |||
| // SetConnection replaces the current connection object | |||
| func (se *signerEndpoint) SetConnection(newConnection net.Conn) { | |||
| se.connMtx.Lock() | |||
| defer se.connMtx.Unlock() | |||
| se.conn = newConnection | |||
| } | |||
| // IsConnected indicates if there is an active connection | |||
| func (se *signerEndpoint) DropConnection() { | |||
| se.connMtx.Lock() | |||
| defer se.connMtx.Unlock() | |||
| se.dropConnection() | |||
| } | |||
| // ReadMessage reads a message from the endpoint | |||
| func (se *signerEndpoint) ReadMessage() (msg SignerMessage, err error) { | |||
| se.connMtx.Lock() | |||
| defer se.connMtx.Unlock() | |||
| if !se.isConnected() { | |||
| return nil, fmt.Errorf("endpoint is not connected") | |||
| } | |||
| // Reset read deadline | |||
| deadline := time.Now().Add(se.timeoutReadWrite) | |||
| err = se.conn.SetReadDeadline(deadline) | |||
| if err != nil { | |||
| return | |||
| } | |||
| const maxRemoteSignerMsgSize = 1024 * 10 | |||
| _, err = cdc.UnmarshalBinaryLengthPrefixedReader(se.conn, &msg, maxRemoteSignerMsgSize) | |||
| if _, ok := err.(timeoutError); ok { | |||
| if err != nil { | |||
| err = errors.Wrap(ErrReadTimeout, err.Error()) | |||
| } else { | |||
| err = errors.Wrap(ErrReadTimeout, "Empty error") | |||
| } | |||
| se.Logger.Debug("Dropping [read]", "obj", se) | |||
| se.dropConnection() | |||
| } | |||
| return | |||
| } | |||
| // WriteMessage writes a message from the endpoint | |||
| func (se *signerEndpoint) WriteMessage(msg SignerMessage) (err error) { | |||
| se.connMtx.Lock() | |||
| defer se.connMtx.Unlock() | |||
| if !se.isConnected() { | |||
| return errors.Wrap(ErrNoConnection, "endpoint is not connected") | |||
| } | |||
| // Reset read deadline | |||
| deadline := time.Now().Add(se.timeoutReadWrite) | |||
| se.Logger.Debug("Write::Error Resetting deadline", "obj", se) | |||
| err = se.conn.SetWriteDeadline(deadline) | |||
| if err != nil { | |||
| return | |||
| } | |||
| _, err = cdc.MarshalBinaryLengthPrefixedWriter(se.conn, msg) | |||
| if _, ok := err.(timeoutError); ok { | |||
| if err != nil { | |||
| err = errors.Wrap(ErrWriteTimeout, err.Error()) | |||
| } else { | |||
| err = errors.Wrap(ErrWriteTimeout, "Empty error") | |||
| } | |||
| se.dropConnection() | |||
| } | |||
| return | |||
| } | |||
| func (se *signerEndpoint) isConnected() bool { | |||
| return se.conn != nil | |||
| } | |||
| func (se *signerEndpoint) dropConnection() { | |||
| if se.conn != nil { | |||
| if err := se.conn.Close(); err != nil { | |||
| se.Logger.Error("signerEndpoint::dropConnection", "err", err) | |||
| } | |||
| se.conn = nil | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
+ 198
- 0
privval/signer_listener_endpoint.go
View File
| @ -0,0 +1,198 @@ | |||
| package privval | |||
| import ( | |||
| "fmt" | |||
| "net" | |||
| "sync" | |||
| "time" | |||
| cmn "github.com/tendermint/tendermint/libs/common" | |||
| "github.com/tendermint/tendermint/libs/log" | |||
| ) | |||
| // SignerValidatorEndpointOption sets an optional parameter on the SocketVal. | |||
| type SignerValidatorEndpointOption func(*SignerListenerEndpoint) | |||
| // SignerListenerEndpoint listens for an external process to dial in | |||
| // and keeps the connection alive by dropping and reconnecting | |||
| type SignerListenerEndpoint struct { | |||
| signerEndpoint | |||
| listener net.Listener | |||
| connectRequestCh chan struct{} | |||
| connectionAvailableCh chan net.Conn | |||
| timeoutAccept time.Duration | |||
| pingTimer *time.Ticker | |||
| instanceMtx sync.Mutex // Ensures instance public methods access, i.e. SendRequest | |||
| } | |||
| // NewSignerListenerEndpoint returns an instance of SignerListenerEndpoint. | |||
| func NewSignerListenerEndpoint( | |||
| logger log.Logger, | |||
| listener net.Listener, | |||
| ) *SignerListenerEndpoint { | |||
| sc := &SignerListenerEndpoint{ | |||
| listener: listener, | |||
| timeoutAccept: defaultTimeoutAcceptSeconds * time.Second, | |||
| } | |||
| sc.BaseService = *cmn.NewBaseService(logger, "SignerListenerEndpoint", sc) | |||
| sc.signerEndpoint.timeoutReadWrite = defaultTimeoutReadWriteSeconds * time.Second | |||
| return sc | |||
| } | |||
| // OnStart implements cmn.Service. | |||
| func (sl *SignerListenerEndpoint) OnStart() error { | |||
| sl.connectRequestCh = make(chan struct{}) | |||
| sl.connectionAvailableCh = make(chan net.Conn) | |||
| sl.pingTimer = time.NewTicker(defaultPingPeriodMilliseconds * time.Millisecond) | |||
| go sl.serviceLoop() | |||
| go sl.pingLoop() | |||
| sl.connectRequestCh <- struct{}{} | |||
| return nil | |||
| } | |||
| // OnStop implements cmn.Service | |||
| func (sl *SignerListenerEndpoint) OnStop() { | |||
| sl.instanceMtx.Lock() | |||
| defer sl.instanceMtx.Unlock() | |||
| _ = sl.Close() | |||
| // Stop listening | |||
| if sl.listener != nil { | |||
| if err := sl.listener.Close(); err != nil { | |||
| sl.Logger.Error("Closing Listener", "err", err) | |||
| sl.listener = nil | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| sl.pingTimer.Stop() | |||
| } | |||
| // WaitForConnection waits maxWait for a connection or returns a timeout error | |||
| func (sl *SignerListenerEndpoint) WaitForConnection(maxWait time.Duration) error { | |||
| sl.instanceMtx.Lock() | |||
| defer sl.instanceMtx.Unlock() | |||
| return sl.ensureConnection(maxWait) | |||
| } | |||
| // SendRequest ensures there is a connection, sends a request and waits for a response | |||
| func (sl *SignerListenerEndpoint) SendRequest(request SignerMessage) (SignerMessage, error) { | |||
| sl.instanceMtx.Lock() | |||
| defer sl.instanceMtx.Unlock() | |||
| err := sl.ensureConnection(sl.timeoutAccept) | |||
| if err != nil { | |||
| return nil, err | |||
| } | |||
| err = sl.WriteMessage(request) | |||
| if err != nil { | |||
| return nil, err | |||
| } | |||
| res, err := sl.ReadMessage() | |||
| if err != nil { | |||
| return nil, err | |||
| } | |||
| return res, nil | |||
| } | |||
| func (sl *SignerListenerEndpoint) ensureConnection(maxWait time.Duration) error { | |||
| if sl.IsConnected() { | |||
| return nil | |||
| } | |||
| // Is there a connection ready? then use it | |||
| if sl.GetAvailableConnection(sl.connectionAvailableCh) { | |||
| return nil | |||
| } | |||
| // block until connected or timeout | |||
| sl.triggerConnect() | |||
| err := sl.WaitConnection(sl.connectionAvailableCh, maxWait) | |||
| if err != nil { | |||
| return err | |||
| } | |||
| return nil | |||
| } | |||
| func (sl *SignerListenerEndpoint) acceptNewConnection() (net.Conn, error) { | |||
| if !sl.IsRunning() || sl.listener == nil { | |||
| return nil, fmt.Errorf("endpoint is closing") | |||
| } | |||
| // wait for a new conn | |||
| sl.Logger.Info("SignerListener: Listening for new connection") | |||
| conn, err := sl.listener.Accept() | |||
| if err != nil { | |||
| return nil, err | |||
| } | |||
| return conn, nil | |||
| } | |||
| func (sl *SignerListenerEndpoint) triggerConnect() { | |||
| select { | |||
| case sl.connectRequestCh <- struct{}{}: | |||
| default: | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| func (sl *SignerListenerEndpoint) triggerReconnect() { | |||
| sl.DropConnection() | |||
| sl.triggerConnect() | |||
| } | |||
| func (sl *SignerListenerEndpoint) serviceLoop() { | |||
| for { | |||
| select { | |||
| case <-sl.connectRequestCh: | |||
| { | |||
| conn, err := sl.acceptNewConnection() | |||
| if err == nil { | |||
| sl.Logger.Info("SignerListener: Connected") | |||
| // We have a good connection, wait for someone that needs one otherwise cancellation | |||
| select { | |||
| case sl.connectionAvailableCh <- conn: | |||
| case <-sl.Quit(): | |||
| return | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| select { | |||
| case sl.connectRequestCh <- struct{}{}: | |||
| default: | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| case <-sl.Quit(): | |||
| return | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| func (sl *SignerListenerEndpoint) pingLoop() { | |||
| for { | |||
| select { | |||
| case <-sl.pingTimer.C: | |||
| { | |||
| _, err := sl.SendRequest(&PingRequest{}) | |||
| if err != nil { | |||
| sl.Logger.Error("SignerListener: Ping timeout") | |||
| sl.triggerReconnect() | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| case <-sl.Quit(): | |||
| return | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
+ 198
- 0
privval/signer_listener_endpoint_test.go
View File
| @ -0,0 +1,198 @@ | |||
| package privval | |||
| import ( | |||
| "net" | |||
| "testing" | |||
| "time" | |||
| "github.com/stretchr/testify/assert" | |||
| "github.com/stretchr/testify/require" | |||
| "github.com/tendermint/tendermint/crypto/ed25519" | |||
| cmn "github.com/tendermint/tendermint/libs/common" | |||
| "github.com/tendermint/tendermint/libs/log" | |||
| "github.com/tendermint/tendermint/types" | |||
| ) | |||
| var ( | |||
| testTimeoutAccept = defaultTimeoutAcceptSeconds * time.Second | |||
| testTimeoutReadWrite = 100 * time.Millisecond | |||
| testTimeoutReadWrite2o3 = 60 * time.Millisecond // 2/3 of the other one | |||
| ) | |||
| type dialerTestCase struct { | |||
| addr string | |||
| dialer SocketDialer | |||
| } | |||
| // TestSignerRemoteRetryTCPOnly will test connection retry attempts over TCP. We | |||
| // don't need this for Unix sockets because the OS instantly knows the state of | |||
| // both ends of the socket connection. This basically causes the | |||
| // SignerDialerEndpoint.dialer() call inside SignerDialerEndpoint.acceptNewConnection() to return | |||
| // successfully immediately, putting an instant stop to any retry attempts. | |||
| func TestSignerRemoteRetryTCPOnly(t *testing.T) { | |||
| var ( | |||
| attemptCh = make(chan int) | |||
| retries = 10 | |||
| ) | |||
| ln, err := net.Listen("tcp", "127.0.0.1:0") | |||
| require.NoError(t, err) | |||
| // Continuously Accept connection and close {attempts} times | |||
| go func(ln net.Listener, attemptCh chan<- int) { | |||
| attempts := 0 | |||
| for { | |||
| conn, err := ln.Accept() | |||
| require.NoError(t, err) | |||
| err = conn.Close() | |||
| require.NoError(t, err) | |||
| attempts++ | |||
| if attempts == retries { | |||
| attemptCh <- attempts | |||
| break | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| }(ln, attemptCh) | |||
| dialerEndpoint := NewSignerDialerEndpoint( | |||
| log.TestingLogger(), | |||
| DialTCPFn(ln.Addr().String(), testTimeoutReadWrite, ed25519.GenPrivKey()), | |||
| ) | |||
| SignerDialerEndpointTimeoutReadWrite(time.Millisecond)(dialerEndpoint) | |||
| SignerDialerEndpointConnRetries(retries)(dialerEndpoint) | |||
| chainId := cmn.RandStr(12) | |||
| mockPV := types.NewMockPV() | |||
| signerServer := NewSignerServer(dialerEndpoint, chainId, mockPV) | |||
| err = signerServer.Start() | |||
| require.NoError(t, err) | |||
| defer signerServer.Stop() | |||
| select { | |||
| case attempts := <-attemptCh: | |||
| assert.Equal(t, retries, attempts) | |||
| case <-time.After(1500 * time.Millisecond): | |||
| t.Error("expected remote to observe connection attempts") | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| func TestRetryConnToRemoteSigner(t *testing.T) { | |||
| for _, tc := range getDialerTestCases(t) { | |||
| var ( | |||
| logger = log.TestingLogger() | |||
| chainID = cmn.RandStr(12) | |||
| mockPV = types.NewMockPV() | |||
| endpointIsOpenCh = make(chan struct{}) | |||
| thisConnTimeout = testTimeoutReadWrite | |||
| listenerEndpoint = newSignerListenerEndpoint(logger, tc.addr, thisConnTimeout) | |||
| ) | |||
| dialerEndpoint := NewSignerDialerEndpoint( | |||
| logger, | |||
| tc.dialer, | |||
| ) | |||
| SignerDialerEndpointTimeoutReadWrite(testTimeoutReadWrite)(dialerEndpoint) | |||
| SignerDialerEndpointConnRetries(10)(dialerEndpoint) | |||
| signerServer := NewSignerServer(dialerEndpoint, chainID, mockPV) | |||
| startListenerEndpointAsync(t, listenerEndpoint, endpointIsOpenCh) | |||
| defer listenerEndpoint.Stop() | |||
| require.NoError(t, signerServer.Start()) | |||
| assert.True(t, signerServer.IsRunning()) | |||
| <-endpointIsOpenCh | |||
| signerServer.Stop() | |||
| dialerEndpoint2 := NewSignerDialerEndpoint( | |||
| logger, | |||
| tc.dialer, | |||
| ) | |||
| signerServer2 := NewSignerServer(dialerEndpoint2, chainID, mockPV) | |||
| // let some pings pass | |||
| require.NoError(t, signerServer2.Start()) | |||
| assert.True(t, signerServer2.IsRunning()) | |||
| defer signerServer2.Stop() | |||
| // give the client some time to re-establish the conn to the remote signer | |||
| // should see sth like this in the logs: | |||
| // | |||
| // E[10016-01-10|17:12:46.128] Ping err="remote signer timed out" | |||
| // I[10016-01-10|17:16:42.447] Re-created connection to remote signer impl=SocketVal | |||
| time.Sleep(testTimeoutReadWrite * 2) | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| /////////////////////////////////// | |||
| func newSignerListenerEndpoint(logger log.Logger, addr string, timeoutReadWrite time.Duration) *SignerListenerEndpoint { | |||
| proto, address := cmn.ProtocolAndAddress(addr) | |||
| ln, err := net.Listen(proto, address) | |||
| logger.Info("SignerListener: Listening", "proto", proto, "address", address) | |||
| if err != nil { | |||
| panic(err) | |||
| } | |||
| var listener net.Listener | |||
| if proto == "unix" { | |||
| unixLn := NewUnixListener(ln) | |||
| UnixListenerTimeoutAccept(testTimeoutAccept)(unixLn) | |||
| UnixListenerTimeoutReadWrite(timeoutReadWrite)(unixLn) | |||
| listener = unixLn | |||
| } else { | |||
| tcpLn := NewTCPListener(ln, ed25519.GenPrivKey()) | |||
| TCPListenerTimeoutAccept(testTimeoutAccept)(tcpLn) | |||
| TCPListenerTimeoutReadWrite(timeoutReadWrite)(tcpLn) | |||
| listener = tcpLn | |||
| } | |||
| return NewSignerListenerEndpoint(logger, listener) | |||
| } | |||
| func startListenerEndpointAsync(t *testing.T, sle *SignerListenerEndpoint, endpointIsOpenCh chan struct{}) { | |||
| go func(sle *SignerListenerEndpoint) { | |||
| require.NoError(t, sle.Start()) | |||
| assert.True(t, sle.IsRunning()) | |||
| close(endpointIsOpenCh) | |||
| }(sle) | |||
| } | |||
| func getMockEndpoints( | |||
| t *testing.T, | |||
| addr string, | |||
| socketDialer SocketDialer, | |||
| ) (*SignerListenerEndpoint, *SignerDialerEndpoint) { | |||
| var ( | |||
| logger = log.TestingLogger() | |||
| endpointIsOpenCh = make(chan struct{}) | |||
| dialerEndpoint = NewSignerDialerEndpoint( | |||
| logger, | |||
| socketDialer, | |||
| ) | |||
| listenerEndpoint = newSignerListenerEndpoint(logger, addr, testTimeoutReadWrite) | |||
| ) | |||
| SignerDialerEndpointTimeoutReadWrite(testTimeoutReadWrite)(dialerEndpoint) | |||
| SignerDialerEndpointConnRetries(1e6)(dialerEndpoint) | |||
| startListenerEndpointAsync(t, listenerEndpoint, endpointIsOpenCh) | |||
| require.NoError(t, dialerEndpoint.Start()) | |||
| assert.True(t, dialerEndpoint.IsRunning()) | |||
| <-endpointIsOpenCh | |||
| return listenerEndpoint, dialerEndpoint | |||
| } | |||
+ 0
- 192
privval/signer_remote.go
View File
| @ -1,192 +0,0 @@ | |||
| package privval | |||
| import ( | |||
| "fmt" | |||
| "io" | |||
| "net" | |||
| "github.com/pkg/errors" | |||
| "github.com/tendermint/tendermint/crypto" | |||
| cmn "github.com/tendermint/tendermint/libs/common" | |||
| "github.com/tendermint/tendermint/types" | |||
| ) | |||
| // SignerRemote implements PrivValidator. | |||
| // It uses a net.Conn to request signatures from an external process. | |||
| type SignerRemote struct { | |||
| conn net.Conn | |||
| // memoized | |||
| consensusPubKey crypto.PubKey | |||
| } | |||
| // Check that SignerRemote implements PrivValidator. | |||
| var _ types.PrivValidator = (*SignerRemote)(nil) | |||
| // NewSignerRemote returns an instance of SignerRemote. | |||
| func NewSignerRemote(conn net.Conn) (*SignerRemote, error) { | |||
| // retrieve and memoize the consensus public key once. | |||
| pubKey, err := getPubKey(conn) | |||
| if err != nil { | |||
| return nil, cmn.ErrorWrap(err, "error while retrieving public key for remote signer") | |||
| } | |||
| return &SignerRemote{ | |||
| conn: conn, | |||
| consensusPubKey: pubKey, | |||
| }, nil | |||
| } | |||
| // Close calls Close on the underlying net.Conn. | |||
| func (sc *SignerRemote) Close() error { | |||
| return sc.conn.Close() | |||
| } | |||
| // GetPubKey implements PrivValidator. | |||
| func (sc *SignerRemote) GetPubKey() crypto.PubKey { | |||
| return sc.consensusPubKey | |||
| } | |||
| // not thread-safe (only called on startup). | |||
| func getPubKey(conn net.Conn) (crypto.PubKey, error) { | |||
| err := writeMsg(conn, &PubKeyRequest{}) | |||
| if err != nil { | |||
| return nil, err | |||
| } | |||
| res, err := readMsg(conn) | |||
| if err != nil { | |||
| return nil, err | |||
| } | |||
| pubKeyResp, ok := res.(*PubKeyResponse) | |||
| if !ok { | |||
| return nil, errors.Wrap(ErrUnexpectedResponse, "response is not PubKeyResponse") | |||
| } | |||
| if pubKeyResp.Error != nil { | |||
| return nil, errors.Wrap(pubKeyResp.Error, "failed to get private validator's public key") | |||
| } | |||
| return pubKeyResp.PubKey, nil | |||
| } | |||
| // SignVote implements PrivValidator. | |||
| func (sc *SignerRemote) SignVote(chainID string, vote *types.Vote) error { | |||
| err := writeMsg(sc.conn, &SignVoteRequest{Vote: vote}) | |||
| if err != nil { | |||
| return err | |||
| } | |||
| res, err := readMsg(sc.conn) | |||
| if err != nil { | |||
| return err | |||
| } | |||
| resp, ok := res.(*SignedVoteResponse) | |||
| if !ok { | |||
| return ErrUnexpectedResponse | |||
| } | |||
| if resp.Error != nil { | |||
| return resp.Error | |||
| } | |||
| *vote = *resp.Vote | |||
| return nil | |||
| } | |||
| // SignProposal implements PrivValidator. | |||
| func (sc *SignerRemote) SignProposal(chainID string, proposal *types.Proposal) error { | |||
| err := writeMsg(sc.conn, &SignProposalRequest{Proposal: proposal}) | |||
| if err != nil { | |||
| return err | |||
| } | |||
| res, err := readMsg(sc.conn) | |||
| if err != nil { | |||
| return err | |||
| } | |||
| resp, ok := res.(*SignedProposalResponse) | |||
| if !ok { | |||
| return ErrUnexpectedResponse | |||
| } | |||
| if resp.Error != nil { | |||
| return resp.Error | |||
| } | |||
| *proposal = *resp.Proposal | |||
| return nil | |||
| } | |||
| // Ping is used to check connection health. | |||
| func (sc *SignerRemote) Ping() error { | |||
| err := writeMsg(sc.conn, &PingRequest{}) | |||
| if err != nil { | |||
| return err | |||
| } | |||
| res, err := readMsg(sc.conn) | |||
| if err != nil { | |||
| return err | |||
| } | |||
| _, ok := res.(*PingResponse) | |||
| if !ok { | |||
| return ErrUnexpectedResponse | |||
| } | |||
| return nil | |||
| } | |||
| func readMsg(r io.Reader) (msg RemoteSignerMsg, err error) { | |||
| const maxRemoteSignerMsgSize = 1024 * 10 | |||
| _, err = cdc.UnmarshalBinaryLengthPrefixedReader(r, &msg, maxRemoteSignerMsgSize) | |||
| if _, ok := err.(timeoutError); ok { | |||
| err = cmn.ErrorWrap(ErrConnTimeout, err.Error()) | |||
| } | |||
| return | |||
| } | |||
| func writeMsg(w io.Writer, msg interface{}) (err error) { | |||
| _, err = cdc.MarshalBinaryLengthPrefixedWriter(w, msg) | |||
| if _, ok := err.(timeoutError); ok { | |||
| err = cmn.ErrorWrap(ErrConnTimeout, err.Error()) | |||
| } | |||
| return | |||
| } | |||
| func handleRequest(req RemoteSignerMsg, chainID string, privVal types.PrivValidator) (RemoteSignerMsg, error) { | |||
| var res RemoteSignerMsg | |||
| var err error | |||
| switch r := req.(type) { | |||
| case *PubKeyRequest: | |||
| var p crypto.PubKey | |||
| p = privVal.GetPubKey() | |||
| res = &PubKeyResponse{p, nil} | |||
| case *SignVoteRequest: | |||
| err = privVal.SignVote(chainID, r.Vote) | |||
| if err != nil { | |||
| res = &SignedVoteResponse{nil, &RemoteSignerError{0, err.Error()}} | |||
| } else { | |||
| res = &SignedVoteResponse{r.Vote, nil} | |||
| } | |||
| case *SignProposalRequest: | |||
| err = privVal.SignProposal(chainID, r.Proposal) | |||
| if err != nil { | |||
| res = &SignedProposalResponse{nil, &RemoteSignerError{0, err.Error()}} | |||
| } else { | |||
| res = &SignedProposalResponse{r.Proposal, nil} | |||
| } | |||
| case *PingRequest: | |||
| res = &PingResponse{} | |||
| default: | |||
| err = fmt.Errorf("unknown msg: %v", r) | |||
| } | |||
| return res, err | |||
| } | |||
+ 0
- 68
privval/signer_remote_test.go
View File
| @ -1,68 +0,0 @@ | |||
| package privval | |||
| import ( | |||
| "net" | |||
| "testing" | |||
| "time" | |||
| "github.com/stretchr/testify/assert" | |||
| "github.com/stretchr/testify/require" | |||
| "github.com/tendermint/tendermint/crypto/ed25519" | |||
| cmn "github.com/tendermint/tendermint/libs/common" | |||
| "github.com/tendermint/tendermint/libs/log" | |||
| "github.com/tendermint/tendermint/types" | |||
| ) | |||
| // TestSignerRemoteRetryTCPOnly will test connection retry attempts over TCP. We | |||
| // don't need this for Unix sockets because the OS instantly knows the state of | |||
| // both ends of the socket connection. This basically causes the | |||
| // SignerServiceEndpoint.dialer() call inside SignerServiceEndpoint.connect() to return | |||
| // successfully immediately, putting an instant stop to any retry attempts. | |||
| func TestSignerRemoteRetryTCPOnly(t *testing.T) { | |||
| var ( | |||
| attemptCh = make(chan int) | |||
| retries = 2 | |||
| ) | |||
| ln, err := net.Listen("tcp", "127.0.0.1:0") | |||
| require.NoError(t, err) | |||
| go func(ln net.Listener, attemptCh chan<- int) { | |||
| attempts := 0 | |||
| for { | |||
| conn, err := ln.Accept() | |||
| require.NoError(t, err) | |||
| err = conn.Close() | |||
| require.NoError(t, err) | |||
| attempts++ | |||
| if attempts == retries { | |||
| attemptCh <- attempts | |||
| break | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| }(ln, attemptCh) | |||
| serviceEndpoint := NewSignerServiceEndpoint( | |||
| log.TestingLogger(), | |||
| cmn.RandStr(12), | |||
| types.NewMockPV(), | |||
| DialTCPFn(ln.Addr().String(), testTimeoutReadWrite, ed25519.GenPrivKey()), | |||
| ) | |||
| defer serviceEndpoint.Stop() | |||
| SignerServiceEndpointTimeoutReadWrite(time.Millisecond)(serviceEndpoint) | |||
| SignerServiceEndpointConnRetries(retries)(serviceEndpoint) | |||
| assert.Equal(t, serviceEndpoint.Start(), ErrDialRetryMax) | |||
| select { | |||
| case attempts := <-attemptCh: | |||
| assert.Equal(t, retries, attempts) | |||
| case <-time.After(100 * time.Millisecond): | |||
| t.Error("expected remote to observe connection attempts") | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
+ 44
- 0
privval/signer_requestHandler.go
View File
| @ -0,0 +1,44 @@ | |||
| package privval | |||
| import ( | |||
| "fmt" | |||
| "github.com/tendermint/tendermint/crypto" | |||
| "github.com/tendermint/tendermint/types" | |||
| ) | |||
| func DefaultValidationRequestHandler(privVal types.PrivValidator, req SignerMessage, chainID string) (SignerMessage, error) { | |||
| var res SignerMessage | |||
| var err error | |||
| switch r := req.(type) { | |||
| case *PubKeyRequest: | |||
| var p crypto.PubKey | |||
| p = privVal.GetPubKey() | |||
| res = &PubKeyResponse{p, nil} | |||
| case *SignVoteRequest: | |||
| err = privVal.SignVote(chainID, r.Vote) | |||
| if err != nil { | |||
| res = &SignedVoteResponse{nil, &RemoteSignerError{0, err.Error()}} | |||
| } else { | |||
| res = &SignedVoteResponse{r.Vote, nil} | |||
| } | |||
| case *SignProposalRequest: | |||
| err = privVal.SignProposal(chainID, r.Proposal) | |||
| if err != nil { | |||
| res = &SignedProposalResponse{nil, &RemoteSignerError{0, err.Error()}} | |||
| } else { | |||
| res = &SignedProposalResponse{r.Proposal, nil} | |||
| } | |||
| case *PingRequest: | |||
| err, res = nil, &PingResponse{} | |||
| default: | |||
| err = fmt.Errorf("unknown msg: %v", r) | |||
| } | |||
| return res, err | |||
| } | |||
+ 107
- 0
privval/signer_server.go
View File
| @ -0,0 +1,107 @@ | |||
| package privval | |||
| import ( | |||
| "io" | |||
| "sync" | |||
| cmn "github.com/tendermint/tendermint/libs/common" | |||
| "github.com/tendermint/tendermint/types" | |||
| ) | |||
| // ValidationRequestHandlerFunc handles different remoteSigner requests | |||
| type ValidationRequestHandlerFunc func( | |||
| privVal types.PrivValidator, | |||
| requestMessage SignerMessage, | |||
| chainID string) (SignerMessage, error) | |||
| type SignerServer struct { | |||
| cmn.BaseService | |||
| endpoint *SignerDialerEndpoint | |||
| chainID string | |||
| privVal types.PrivValidator | |||
| handlerMtx sync.Mutex | |||
| validationRequestHandler ValidationRequestHandlerFunc | |||
| } | |||
| func NewSignerServer(endpoint *SignerDialerEndpoint, chainID string, privVal types.PrivValidator) *SignerServer { | |||
| ss := &SignerServer{ | |||
| endpoint: endpoint, | |||
| chainID: chainID, | |||
| privVal: privVal, | |||
| validationRequestHandler: DefaultValidationRequestHandler, | |||
| } | |||
| ss.BaseService = *cmn.NewBaseService(endpoint.Logger, "SignerServer", ss) | |||
| return ss | |||
| } | |||
| // OnStart implements cmn.Service. | |||
| func (ss *SignerServer) OnStart() error { | |||
| go ss.serviceLoop() | |||
| return nil | |||
| } | |||
| // OnStop implements cmn.Service. | |||
| func (ss *SignerServer) OnStop() { | |||
| ss.endpoint.Logger.Debug("SignerServer: OnStop calling Close") | |||
| _ = ss.endpoint.Close() | |||
| } | |||
| // SetRequestHandler override the default function that is used to service requests | |||
| func (ss *SignerServer) SetRequestHandler(validationRequestHandler ValidationRequestHandlerFunc) { | |||
| ss.handlerMtx.Lock() | |||
| defer ss.handlerMtx.Unlock() | |||
| ss.validationRequestHandler = validationRequestHandler | |||
| } | |||
| func (ss *SignerServer) servicePendingRequest() { | |||
| if !ss.IsRunning() { | |||
| return // Ignore error from closing. | |||
| } | |||
| req, err := ss.endpoint.ReadMessage() | |||
| if err != nil { | |||
| if err != io.EOF { | |||
| ss.Logger.Error("SignerServer: HandleMessage", "err", err) | |||
| } | |||
| return | |||
| } | |||
| var res SignerMessage | |||
| { | |||
| // limit the scope of the lock | |||
| ss.handlerMtx.Lock() | |||
| defer ss.handlerMtx.Unlock() | |||
| res, err = ss.validationRequestHandler(ss.privVal, req, ss.chainID) | |||
| if err != nil { | |||
| // only log the error; we'll reply with an error in res | |||
| ss.Logger.Error("SignerServer: handleMessage", "err", err) | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| if res != nil { | |||
| err = ss.endpoint.WriteMessage(res) | |||
| if err != nil { | |||
| ss.Logger.Error("SignerServer: writeMessage", "err", err) | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| func (ss *SignerServer) serviceLoop() { | |||
| for { | |||
| select { | |||
| default: | |||
| err := ss.endpoint.ensureConnection() | |||
| if err != nil { | |||
| return | |||
| } | |||
| ss.servicePendingRequest() | |||
| case <-ss.Quit(): | |||
| return | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
+ 0
- 139
privval/signer_service_endpoint.go
View File
| @ -1,139 +0,0 @@ | |||
| package privval | |||
| import ( | |||
| "io" | |||
| "net" | |||
| "time" | |||
| cmn "github.com/tendermint/tendermint/libs/common" | |||
| "github.com/tendermint/tendermint/libs/log" | |||
| "github.com/tendermint/tendermint/types" | |||
| ) | |||
| // SignerServiceEndpointOption sets an optional parameter on the SignerServiceEndpoint. | |||
| type SignerServiceEndpointOption func(*SignerServiceEndpoint) | |||
| // SignerServiceEndpointTimeoutReadWrite sets the read and write timeout for connections | |||
| // from external signing processes. | |||
| func SignerServiceEndpointTimeoutReadWrite(timeout time.Duration) SignerServiceEndpointOption { | |||
| return func(ss *SignerServiceEndpoint) { ss.timeoutReadWrite = timeout } | |||
| } | |||
| // SignerServiceEndpointConnRetries sets the amount of attempted retries to connect. | |||
| func SignerServiceEndpointConnRetries(retries int) SignerServiceEndpointOption { | |||
| return func(ss *SignerServiceEndpoint) { ss.connRetries = retries } | |||
| } | |||
| // SignerServiceEndpoint dials using its dialer and responds to any | |||
| // signature requests using its privVal. | |||
| type SignerServiceEndpoint struct { | |||
| cmn.BaseService | |||
| chainID string | |||
| timeoutReadWrite time.Duration | |||
| connRetries int | |||
| privVal types.PrivValidator | |||
| dialer SocketDialer | |||
| conn net.Conn | |||
| } | |||
| // NewSignerServiceEndpoint returns a SignerServiceEndpoint that will dial using the given | |||
| // dialer and respond to any signature requests over the connection | |||
| // using the given privVal. | |||
| func NewSignerServiceEndpoint( | |||
| logger log.Logger, | |||
| chainID string, | |||
| privVal types.PrivValidator, | |||
| dialer SocketDialer, | |||
| ) *SignerServiceEndpoint { | |||
| se := &SignerServiceEndpoint{ | |||
| chainID: chainID, | |||
| timeoutReadWrite: time.Second * defaultTimeoutReadWriteSeconds, | |||
| connRetries: defaultMaxDialRetries, | |||
| privVal: privVal, | |||
| dialer: dialer, | |||
| } | |||
| se.BaseService = *cmn.NewBaseService(logger, "SignerServiceEndpoint", se) | |||
| return se | |||
| } | |||
| // OnStart implements cmn.Service. | |||
| func (se *SignerServiceEndpoint) OnStart() error { | |||
| conn, err := se.connect() | |||
| if err != nil { | |||
| se.Logger.Error("OnStart", "err", err) | |||
| return err | |||
| } | |||
| se.conn = conn | |||
| go se.handleConnection(conn) | |||
| return nil | |||
| } | |||
| // OnStop implements cmn.Service. | |||
| func (se *SignerServiceEndpoint) OnStop() { | |||
| if se.conn == nil { | |||
| return | |||
| } | |||
| if err := se.conn.Close(); err != nil { | |||
| se.Logger.Error("OnStop", "err", cmn.ErrorWrap(err, "closing listener failed")) | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| func (se *SignerServiceEndpoint) connect() (net.Conn, error) { | |||
| for retries := 0; retries < se.connRetries; retries++ { | |||
| // Don't sleep if it is the first retry. | |||
| if retries > 0 { | |||
| time.Sleep(se.timeoutReadWrite) | |||
| } | |||
| conn, err := se.dialer() | |||
| if err == nil { | |||
| return conn, nil | |||
| } | |||
| se.Logger.Error("dialing", "err", err) | |||
| } | |||
| return nil, ErrDialRetryMax | |||
| } | |||
| func (se *SignerServiceEndpoint) handleConnection(conn net.Conn) { | |||
| for { | |||
| if !se.IsRunning() { | |||
| return // Ignore error from listener closing. | |||
| } | |||
| // Reset the connection deadline | |||
| deadline := time.Now().Add(se.timeoutReadWrite) | |||
| err := conn.SetDeadline(deadline) | |||
| if err != nil { | |||
| return | |||
| } | |||
| req, err := readMsg(conn) | |||
| if err != nil { | |||
| if err != io.EOF { | |||
| se.Logger.Error("handleConnection readMsg", "err", err) | |||
| } | |||
| return | |||
| } | |||
| res, err := handleRequest(req, se.chainID, se.privVal) | |||
| if err != nil { | |||
| // only log the error; we'll reply with an error in res | |||
| se.Logger.Error("handleConnection handleRequest", "err", err) | |||
| } | |||
| err = writeMsg(conn, res) | |||
| if err != nil { | |||
| se.Logger.Error("handleConnection writeMsg", "err", err) | |||
| return | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
+ 0
- 230
privval/signer_validator_endpoint.go
View File
| @ -1,230 +0,0 @@ | |||
| package privval | |||
| import ( | |||
| "fmt" | |||
| "net" | |||
| "sync" | |||
| "time" | |||
| "github.com/tendermint/tendermint/crypto" | |||
| cmn "github.com/tendermint/tendermint/libs/common" | |||
| "github.com/tendermint/tendermint/libs/log" | |||
| "github.com/tendermint/tendermint/types" | |||
| ) | |||
| const ( | |||
| defaultHeartbeatSeconds = 2 | |||
| defaultMaxDialRetries = 10 | |||
| ) | |||
| var ( | |||
| heartbeatPeriod = time.Second * defaultHeartbeatSeconds | |||
| ) | |||
| // SignerValidatorEndpointOption sets an optional parameter on the SocketVal. | |||
| type SignerValidatorEndpointOption func(*SignerValidatorEndpoint) | |||
| // SignerValidatorEndpointSetHeartbeat sets the period on which to check the liveness of the | |||
| // connected Signer connections. | |||
| func SignerValidatorEndpointSetHeartbeat(period time.Duration) SignerValidatorEndpointOption { | |||
| return func(sc *SignerValidatorEndpoint) { sc.heartbeatPeriod = period } | |||
| } | |||
| // SocketVal implements PrivValidator. | |||
| // It listens for an external process to dial in and uses | |||
| // the socket to request signatures. | |||
| type SignerValidatorEndpoint struct { | |||
| cmn.BaseService | |||
| listener net.Listener | |||
| // ping | |||
| cancelPingCh chan struct{} | |||
| pingTicker *time.Ticker | |||
| heartbeatPeriod time.Duration | |||
| // signer is mutable since it can be reset if the connection fails. | |||
| // failures are detected by a background ping routine. | |||
| // All messages are request/response, so we hold the mutex | |||
| // so only one request/response pair can happen at a time. | |||
| // Methods on the underlying net.Conn itself are already goroutine safe. | |||
| mtx sync.Mutex | |||
| // TODO: Signer should encapsulate and hide the endpoint completely. Invert the relation | |||
| signer *SignerRemote | |||
| } | |||
| // Check that SignerValidatorEndpoint implements PrivValidator. | |||
| var _ types.PrivValidator = (*SignerValidatorEndpoint)(nil) | |||
| // NewSignerValidatorEndpoint returns an instance of SignerValidatorEndpoint. | |||
| func NewSignerValidatorEndpoint(logger log.Logger, listener net.Listener) *SignerValidatorEndpoint { | |||
| sc := &SignerValidatorEndpoint{ | |||
| listener: listener, | |||
| heartbeatPeriod: heartbeatPeriod, | |||
| } | |||
| sc.BaseService = *cmn.NewBaseService(logger, "SignerValidatorEndpoint", sc) | |||
| return sc | |||
| } | |||
| //-------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| // Implement PrivValidator | |||
| // GetPubKey implements PrivValidator. | |||
| func (ve *SignerValidatorEndpoint) GetPubKey() crypto.PubKey { | |||
| ve.mtx.Lock() | |||
| defer ve.mtx.Unlock() | |||
| return ve.signer.GetPubKey() | |||
| } | |||
| // SignVote implements PrivValidator. | |||
| func (ve *SignerValidatorEndpoint) SignVote(chainID string, vote *types.Vote) error { | |||
| ve.mtx.Lock() | |||
| defer ve.mtx.Unlock() | |||
| return ve.signer.SignVote(chainID, vote) | |||
| } | |||
| // SignProposal implements PrivValidator. | |||
| func (ve *SignerValidatorEndpoint) SignProposal(chainID string, proposal *types.Proposal) error { | |||
| ve.mtx.Lock() | |||
| defer ve.mtx.Unlock() | |||
| return ve.signer.SignProposal(chainID, proposal) | |||
| } | |||
| //-------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| // More thread safe methods proxied to the signer | |||
| // Ping is used to check connection health. | |||
| func (ve *SignerValidatorEndpoint) Ping() error { | |||
| ve.mtx.Lock() | |||
| defer ve.mtx.Unlock() | |||
| return ve.signer.Ping() | |||
| } | |||
| // Close closes the underlying net.Conn. | |||
| func (ve *SignerValidatorEndpoint) Close() { | |||
| ve.mtx.Lock() | |||
| defer ve.mtx.Unlock() | |||
| if ve.signer != nil { | |||
| if err := ve.signer.Close(); err != nil { | |||
| ve.Logger.Error("OnStop", "err", err) | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| if ve.listener != nil { | |||
| if err := ve.listener.Close(); err != nil { | |||
| ve.Logger.Error("OnStop", "err", err) | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| //-------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| // Service start and stop | |||
| // OnStart implements cmn.Service. | |||
| func (ve *SignerValidatorEndpoint) OnStart() error { | |||
| if closed, err := ve.reset(); err != nil { | |||
| ve.Logger.Error("OnStart", "err", err) | |||
| return err | |||
| } else if closed { | |||
| return fmt.Errorf("listener is closed") | |||
| } | |||
| // Start a routine to keep the connection alive | |||
| ve.cancelPingCh = make(chan struct{}, 1) | |||
| ve.pingTicker = time.NewTicker(ve.heartbeatPeriod) | |||
| go func() { | |||
| for { | |||
| select { | |||
| case <-ve.pingTicker.C: | |||
| err := ve.Ping() | |||
| if err != nil { | |||
| ve.Logger.Error("Ping", "err", err) | |||
| if err == ErrUnexpectedResponse { | |||
| return | |||
| } | |||
| closed, err := ve.reset() | |||
| if err != nil { | |||
| ve.Logger.Error("Reconnecting to remote signer failed", "err", err) | |||
| continue | |||
| } | |||
| if closed { | |||
| ve.Logger.Info("listener is closing") | |||
| return | |||
| } | |||
| ve.Logger.Info("Re-created connection to remote signer", "impl", ve) | |||
| } | |||
| case <-ve.cancelPingCh: | |||
| ve.pingTicker.Stop() | |||
| return | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| }() | |||
| return nil | |||
| } | |||
| // OnStop implements cmn.Service. | |||
| func (ve *SignerValidatorEndpoint) OnStop() { | |||
| if ve.cancelPingCh != nil { | |||
| close(ve.cancelPingCh) | |||
| } | |||
| ve.Close() | |||
| } | |||
| //-------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| // Connection and signer management | |||
| // waits to accept and sets a new connection. | |||
| // connection is closed in OnStop. | |||
| // returns true if the listener is closed | |||
| // (ie. it returns a nil conn). | |||
| func (ve *SignerValidatorEndpoint) reset() (closed bool, err error) { | |||
| ve.mtx.Lock() | |||
| defer ve.mtx.Unlock() | |||
| // first check if the conn already exists and close it. | |||
| if ve.signer != nil { | |||
| if tmpErr := ve.signer.Close(); tmpErr != nil { | |||
| ve.Logger.Error("error closing socket val connection during reset", "err", tmpErr) | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| // wait for a new conn | |||
| conn, err := ve.acceptConnection() | |||
| if err != nil { | |||
| return false, err | |||
| } | |||
| // listener is closed | |||
| if conn == nil { | |||
| return true, nil | |||
| } | |||
| ve.signer, err = NewSignerRemote(conn) | |||
| if err != nil { | |||
| // failed to fetch the pubkey. close out the connection. | |||
| if tmpErr := conn.Close(); tmpErr != nil { | |||
| ve.Logger.Error("error closing connection", "err", tmpErr) | |||
| } | |||
| return false, err | |||
| } | |||
| return false, nil | |||
| } | |||
| // Attempt to accept a connection. | |||
| // Times out after the listener's timeoutAccept | |||
| func (ve *SignerValidatorEndpoint) acceptConnection() (net.Conn, error) { | |||
| conn, err := ve.listener.Accept() | |||
| if err != nil { | |||
| if !ve.IsRunning() { | |||
| return nil, nil // Ignore error from listener closing. | |||
| } | |||
| return nil, err | |||
| } | |||
| return conn, nil | |||
| } | |||
+ 0
- 506
privval/signer_validator_endpoint_test.go
View File
| @ -1,506 +0,0 @@ | |||
| package privval | |||
| import ( | |||
| "fmt" | |||
| "net" | |||
| "testing" | |||
| "time" | |||
| "github.com/stretchr/testify/assert" | |||
| "github.com/stretchr/testify/require" | |||
| "github.com/tendermint/tendermint/crypto/ed25519" | |||
| cmn "github.com/tendermint/tendermint/libs/common" | |||
| "github.com/tendermint/tendermint/libs/log" | |||
| "github.com/tendermint/tendermint/types" | |||
| ) | |||
| var ( | |||
| testTimeoutAccept = defaultTimeoutAcceptSeconds * time.Second | |||
| testTimeoutReadWrite = 100 * time.Millisecond | |||
| testTimeoutReadWrite2o3 = 66 * time.Millisecond // 2/3 of the other one | |||
| testTimeoutHeartbeat = 10 * time.Millisecond | |||
| testTimeoutHeartbeat3o2 = 6 * time.Millisecond // 3/2 of the other one | |||
| ) | |||
| type socketTestCase struct { | |||
| addr string | |||
| dialer SocketDialer | |||
| } | |||
| func socketTestCases(t *testing.T) []socketTestCase { | |||
| tcpAddr := fmt.Sprintf("tcp://%s", testFreeTCPAddr(t)) | |||
| unixFilePath, err := testUnixAddr() | |||
| require.NoError(t, err) | |||
| unixAddr := fmt.Sprintf("unix://%s", unixFilePath) | |||
| return []socketTestCase{ | |||
| { | |||
| addr: tcpAddr, | |||
| dialer: DialTCPFn(tcpAddr, testTimeoutReadWrite, ed25519.GenPrivKey()), | |||
| }, | |||
| { | |||
| addr: unixAddr, | |||
| dialer: DialUnixFn(unixFilePath), | |||
| }, | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| func TestSocketPVAddress(t *testing.T) { | |||
| for _, tc := range socketTestCases(t) { | |||
| // Execute the test within a closure to ensure the deferred statements | |||
| // are called between each for loop iteration, for isolated test cases. | |||
| func() { | |||
| var ( | |||
| chainID = cmn.RandStr(12) | |||
| validatorEndpoint, serviceEndpoint = testSetupSocketPair(t, chainID, types.NewMockPV(), tc.addr, tc.dialer) | |||
| ) | |||
| defer validatorEndpoint.Stop() | |||
| defer serviceEndpoint.Stop() | |||
| serviceAddr := serviceEndpoint.privVal.GetPubKey().Address() | |||
| validatorAddr := validatorEndpoint.GetPubKey().Address() | |||
| assert.Equal(t, serviceAddr, validatorAddr) | |||
| }() | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| func TestSocketPVPubKey(t *testing.T) { | |||
| for _, tc := range socketTestCases(t) { | |||
| func() { | |||
| var ( | |||
| chainID = cmn.RandStr(12) | |||
| validatorEndpoint, serviceEndpoint = testSetupSocketPair( | |||
| t, | |||
| chainID, | |||
| types.NewMockPV(), | |||
| tc.addr, | |||
| tc.dialer) | |||
| ) | |||
| defer validatorEndpoint.Stop() | |||
| defer serviceEndpoint.Stop() | |||
| clientKey := validatorEndpoint.GetPubKey() | |||
| privvalPubKey := serviceEndpoint.privVal.GetPubKey() | |||
| assert.Equal(t, privvalPubKey, clientKey) | |||
| }() | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| func TestSocketPVProposal(t *testing.T) { | |||
| for _, tc := range socketTestCases(t) { | |||
| func() { | |||
| var ( | |||
| chainID = cmn.RandStr(12) | |||
| validatorEndpoint, serviceEndpoint = testSetupSocketPair( | |||
| t, | |||
| chainID, | |||
| types.NewMockPV(), | |||
| tc.addr, | |||
| tc.dialer) | |||
| ts = time.Now() | |||
| privProposal = &types.Proposal{Timestamp: ts} | |||
| clientProposal = &types.Proposal{Timestamp: ts} | |||
| ) | |||
| defer validatorEndpoint.Stop() | |||
| defer serviceEndpoint.Stop() | |||
| require.NoError(t, serviceEndpoint.privVal.SignProposal(chainID, privProposal)) | |||
| require.NoError(t, validatorEndpoint.SignProposal(chainID, clientProposal)) | |||
| assert.Equal(t, privProposal.Signature, clientProposal.Signature) | |||
| }() | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| func TestSocketPVVote(t *testing.T) { | |||
| for _, tc := range socketTestCases(t) { | |||
| func() { | |||
| var ( | |||
| chainID = cmn.RandStr(12) | |||
| validatorEndpoint, serviceEndpoint = testSetupSocketPair( | |||
| t, | |||
| chainID, | |||
| types.NewMockPV(), | |||
| tc.addr, | |||
| tc.dialer) | |||
| ts = time.Now() | |||
| vType = types.PrecommitType | |||
| want = &types.Vote{Timestamp: ts, Type: vType} | |||
| have = &types.Vote{Timestamp: ts, Type: vType} | |||
| ) | |||
| defer validatorEndpoint.Stop() | |||
| defer serviceEndpoint.Stop() | |||
| require.NoError(t, serviceEndpoint.privVal.SignVote(chainID, want)) | |||
| require.NoError(t, validatorEndpoint.SignVote(chainID, have)) | |||
| assert.Equal(t, want.Signature, have.Signature) | |||
| }() | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| func TestSocketPVVoteResetDeadline(t *testing.T) { | |||
| for _, tc := range socketTestCases(t) { | |||
| func() { | |||
| var ( | |||
| chainID = cmn.RandStr(12) | |||
| validatorEndpoint, serviceEndpoint = testSetupSocketPair( | |||
| t, | |||
| chainID, | |||
| types.NewMockPV(), | |||
| tc.addr, | |||
| tc.dialer) | |||
| ts = time.Now() | |||
| vType = types.PrecommitType | |||
| want = &types.Vote{Timestamp: ts, Type: vType} | |||
| have = &types.Vote{Timestamp: ts, Type: vType} | |||
| ) | |||
| defer validatorEndpoint.Stop() | |||
| defer serviceEndpoint.Stop() | |||
| time.Sleep(testTimeoutReadWrite2o3) | |||
| require.NoError(t, serviceEndpoint.privVal.SignVote(chainID, want)) | |||
| require.NoError(t, validatorEndpoint.SignVote(chainID, have)) | |||
| assert.Equal(t, want.Signature, have.Signature) | |||
| // This would exceed the deadline if it was not extended by the previous message | |||
| time.Sleep(testTimeoutReadWrite2o3) | |||
| require.NoError(t, serviceEndpoint.privVal.SignVote(chainID, want)) | |||
| require.NoError(t, validatorEndpoint.SignVote(chainID, have)) | |||
| assert.Equal(t, want.Signature, have.Signature) | |||
| }() | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| func TestSocketPVVoteKeepalive(t *testing.T) { | |||
| for _, tc := range socketTestCases(t) { | |||
| func() { | |||
| var ( | |||
| chainID = cmn.RandStr(12) | |||
| validatorEndpoint, serviceEndpoint = testSetupSocketPair( | |||
| t, | |||
| chainID, | |||
| types.NewMockPV(), | |||
| tc.addr, | |||
| tc.dialer) | |||
| ts = time.Now() | |||
| vType = types.PrecommitType | |||
| want = &types.Vote{Timestamp: ts, Type: vType} | |||
| have = &types.Vote{Timestamp: ts, Type: vType} | |||
| ) | |||
| defer validatorEndpoint.Stop() | |||
| defer serviceEndpoint.Stop() | |||
| time.Sleep(testTimeoutReadWrite * 2) | |||
| require.NoError(t, serviceEndpoint.privVal.SignVote(chainID, want)) | |||
| require.NoError(t, validatorEndpoint.SignVote(chainID, have)) | |||
| assert.Equal(t, want.Signature, have.Signature) | |||
| }() | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| func TestSocketPVDeadline(t *testing.T) { | |||
| for _, tc := range socketTestCases(t) { | |||
| func() { | |||
| var ( | |||
| listenc = make(chan struct{}) | |||
| thisConnTimeout = 100 * time.Millisecond | |||
| validatorEndpoint = newSignerValidatorEndpoint(log.TestingLogger(), tc.addr, thisConnTimeout) | |||
| ) | |||
| go func(sc *SignerValidatorEndpoint) { | |||
| defer close(listenc) | |||
| // Note: the TCP connection times out at the accept() phase, | |||
| // whereas the Unix domain sockets connection times out while | |||
| // attempting to fetch the remote signer's public key. | |||
| assert.True(t, IsConnTimeout(sc.Start())) | |||
| assert.False(t, sc.IsRunning()) | |||
| }(validatorEndpoint) | |||
| for { | |||
| _, err := cmn.Connect(tc.addr) | |||
| if err == nil { | |||
| break | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| <-listenc | |||
| }() | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| func TestRemoteSignVoteErrors(t *testing.T) { | |||
| for _, tc := range socketTestCases(t) { | |||
| func() { | |||
| var ( | |||
| chainID = cmn.RandStr(12) | |||
| validatorEndpoint, serviceEndpoint = testSetupSocketPair( | |||
| t, | |||
| chainID, | |||
| types.NewErroringMockPV(), | |||
| tc.addr, | |||
| tc.dialer) | |||
| ts = time.Now() | |||
| vType = types.PrecommitType | |||
| vote = &types.Vote{Timestamp: ts, Type: vType} | |||
| ) | |||
| defer validatorEndpoint.Stop() | |||
| defer serviceEndpoint.Stop() | |||
| err := validatorEndpoint.SignVote("", vote) | |||
| require.Equal(t, err.(*RemoteSignerError).Description, types.ErroringMockPVErr.Error()) | |||
| err = serviceEndpoint.privVal.SignVote(chainID, vote) | |||
| require.Error(t, err) | |||
| err = validatorEndpoint.SignVote(chainID, vote) | |||
| require.Error(t, err) | |||
| }() | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| func TestRemoteSignProposalErrors(t *testing.T) { | |||
| for _, tc := range socketTestCases(t) { | |||
| func() { | |||
| var ( | |||
| chainID = cmn.RandStr(12) | |||
| validatorEndpoint, serviceEndpoint = testSetupSocketPair( | |||
| t, | |||
| chainID, | |||
| types.NewErroringMockPV(), | |||
| tc.addr, | |||
| tc.dialer) | |||
| ts = time.Now() | |||
| proposal = &types.Proposal{Timestamp: ts} | |||
| ) | |||
| defer validatorEndpoint.Stop() | |||
| defer serviceEndpoint.Stop() | |||
| err := validatorEndpoint.SignProposal("", proposal) | |||
| require.Equal(t, err.(*RemoteSignerError).Description, types.ErroringMockPVErr.Error()) | |||
| err = serviceEndpoint.privVal.SignProposal(chainID, proposal) | |||
| require.Error(t, err) | |||
| err = validatorEndpoint.SignProposal(chainID, proposal) | |||
| require.Error(t, err) | |||
| }() | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| func TestErrUnexpectedResponse(t *testing.T) { | |||
| for _, tc := range socketTestCases(t) { | |||
| func() { | |||
| var ( | |||
| logger = log.TestingLogger() | |||
| chainID = cmn.RandStr(12) | |||
| readyCh = make(chan struct{}) | |||
| errCh = make(chan error, 1) | |||
| serviceEndpoint = NewSignerServiceEndpoint( | |||
| logger, | |||
| chainID, | |||
| types.NewMockPV(), | |||
| tc.dialer, | |||
| ) | |||
| validatorEndpoint = newSignerValidatorEndpoint( | |||
| logger, | |||
| tc.addr, | |||
| testTimeoutReadWrite) | |||
| ) | |||
| testStartEndpoint(t, readyCh, validatorEndpoint) | |||
| defer validatorEndpoint.Stop() | |||
| SignerServiceEndpointTimeoutReadWrite(time.Millisecond)(serviceEndpoint) | |||
| SignerServiceEndpointConnRetries(100)(serviceEndpoint) | |||
| // we do not want to Start() the remote signer here and instead use the connection to | |||
| // reply with intentionally wrong replies below: | |||
| rsConn, err := serviceEndpoint.connect() | |||
| require.NoError(t, err) | |||
| require.NotNil(t, rsConn) | |||
| defer rsConn.Close() | |||
| // send over public key to get the remote signer running: | |||
| go testReadWriteResponse(t, &PubKeyResponse{}, rsConn) | |||
| <-readyCh | |||
| // Proposal: | |||
| go func(errc chan error) { | |||
| errc <- validatorEndpoint.SignProposal(chainID, &types.Proposal{}) | |||
| }(errCh) | |||
| // read request and write wrong response: | |||
| go testReadWriteResponse(t, &SignedVoteResponse{}, rsConn) | |||
| err = <-errCh | |||
| require.Error(t, err) | |||
| require.Equal(t, err, ErrUnexpectedResponse) | |||
| // Vote: | |||
| go func(errc chan error) { | |||
| errc <- validatorEndpoint.SignVote(chainID, &types.Vote{}) | |||
| }(errCh) | |||
| // read request and write wrong response: | |||
| go testReadWriteResponse(t, &SignedProposalResponse{}, rsConn) | |||
| err = <-errCh | |||
| require.Error(t, err) | |||
| require.Equal(t, err, ErrUnexpectedResponse) | |||
| }() | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| func TestRetryConnToRemoteSigner(t *testing.T) { | |||
| for _, tc := range socketTestCases(t) { | |||
| func() { | |||
| var ( | |||
| logger = log.TestingLogger() | |||
| chainID = cmn.RandStr(12) | |||
| readyCh = make(chan struct{}) | |||
| serviceEndpoint = NewSignerServiceEndpoint( | |||
| logger, | |||
| chainID, | |||
| types.NewMockPV(), | |||
| tc.dialer, | |||
| ) | |||
| thisConnTimeout = testTimeoutReadWrite | |||
| validatorEndpoint = newSignerValidatorEndpoint(logger, tc.addr, thisConnTimeout) | |||
| ) | |||
| // Ping every: | |||
| SignerValidatorEndpointSetHeartbeat(testTimeoutHeartbeat)(validatorEndpoint) | |||
| SignerServiceEndpointTimeoutReadWrite(testTimeoutReadWrite)(serviceEndpoint) | |||
| SignerServiceEndpointConnRetries(10)(serviceEndpoint) | |||
| testStartEndpoint(t, readyCh, validatorEndpoint) | |||
| defer validatorEndpoint.Stop() | |||
| require.NoError(t, serviceEndpoint.Start()) | |||
| assert.True(t, serviceEndpoint.IsRunning()) | |||
| <-readyCh | |||
| time.Sleep(testTimeoutHeartbeat * 2) | |||
| serviceEndpoint.Stop() | |||
| rs2 := NewSignerServiceEndpoint( | |||
| logger, | |||
| chainID, | |||
| types.NewMockPV(), | |||
| tc.dialer, | |||
| ) | |||
| // let some pings pass | |||
| time.Sleep(testTimeoutHeartbeat3o2) | |||
| require.NoError(t, rs2.Start()) | |||
| assert.True(t, rs2.IsRunning()) | |||
| defer rs2.Stop() | |||
| // give the client some time to re-establish the conn to the remote signer | |||
| // should see sth like this in the logs: | |||
| // | |||
| // E[10016-01-10|17:12:46.128] Ping err="remote signer timed out" | |||
| // I[10016-01-10|17:16:42.447] Re-created connection to remote signer impl=SocketVal | |||
| time.Sleep(testTimeoutReadWrite * 2) | |||
| }() | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| func newSignerValidatorEndpoint(logger log.Logger, addr string, timeoutReadWrite time.Duration) *SignerValidatorEndpoint { | |||
| proto, address := cmn.ProtocolAndAddress(addr) | |||
| ln, err := net.Listen(proto, address) | |||
| logger.Info("Listening at", "proto", proto, "address", address) | |||
| if err != nil { | |||
| panic(err) | |||
| } | |||
| var listener net.Listener | |||
| if proto == "unix" { | |||
| unixLn := NewUnixListener(ln) | |||
| UnixListenerTimeoutAccept(testTimeoutAccept)(unixLn) | |||
| UnixListenerTimeoutReadWrite(timeoutReadWrite)(unixLn) | |||
| listener = unixLn | |||
| } else { | |||
| tcpLn := NewTCPListener(ln, ed25519.GenPrivKey()) | |||
| TCPListenerTimeoutAccept(testTimeoutAccept)(tcpLn) | |||
| TCPListenerTimeoutReadWrite(timeoutReadWrite)(tcpLn) | |||
| listener = tcpLn | |||
| } | |||
| return NewSignerValidatorEndpoint(logger, listener) | |||
| } | |||
| func testSetupSocketPair( | |||
| t *testing.T, | |||
| chainID string, | |||
| privValidator types.PrivValidator, | |||
| addr string, | |||
| socketDialer SocketDialer, | |||
| ) (*SignerValidatorEndpoint, *SignerServiceEndpoint) { | |||
| var ( | |||
| logger = log.TestingLogger() | |||
| privVal = privValidator | |||
| readyc = make(chan struct{}) | |||
| serviceEndpoint = NewSignerServiceEndpoint( | |||
| logger, | |||
| chainID, | |||
| privVal, | |||
| socketDialer, | |||
| ) | |||
| thisConnTimeout = testTimeoutReadWrite | |||
| validatorEndpoint = newSignerValidatorEndpoint(logger, addr, thisConnTimeout) | |||
| ) | |||
| SignerValidatorEndpointSetHeartbeat(testTimeoutHeartbeat)(validatorEndpoint) | |||
| SignerServiceEndpointTimeoutReadWrite(testTimeoutReadWrite)(serviceEndpoint) | |||
| SignerServiceEndpointConnRetries(1e6)(serviceEndpoint) | |||
| testStartEndpoint(t, readyc, validatorEndpoint) | |||
| require.NoError(t, serviceEndpoint.Start()) | |||
| assert.True(t, serviceEndpoint.IsRunning()) | |||
| <-readyc | |||
| return validatorEndpoint, serviceEndpoint | |||
| } | |||
| func testReadWriteResponse(t *testing.T, resp RemoteSignerMsg, rsConn net.Conn) { | |||
| _, err := readMsg(rsConn) | |||
| require.NoError(t, err) | |||
| err = writeMsg(rsConn, resp) | |||
| require.NoError(t, err) | |||
| } | |||
| func testStartEndpoint(t *testing.T, readyCh chan struct{}, sc *SignerValidatorEndpoint) { | |||
| go func(sc *SignerValidatorEndpoint) { | |||
| require.NoError(t, sc.Start()) | |||
| assert.True(t, sc.IsRunning()) | |||
| readyCh <- struct{}{} | |||
| }(sc) | |||
| } | |||
| // testFreeTCPAddr claims a free port so we don't block on listener being ready. | |||
| func testFreeTCPAddr(t *testing.T) string { | |||
| ln, err := net.Listen("tcp", "127.0.0.1:0") | |||
| require.NoError(t, err) | |||
| defer ln.Close() | |||
| return fmt.Sprintf("127.0.0.1:%d", ln.Addr().(*net.TCPAddr).Port) | |||
| } | |||
+ 27
- 4
privval/socket_dialers_test.go
View File
| @ -1,26 +1,49 @@ | |||
| package privval | |||
| import ( | |||
| "fmt" | |||
| "testing" | |||
| "time" | |||
| "github.com/pkg/errors" | |||
| "github.com/stretchr/testify/assert" | |||
| "github.com/stretchr/testify/require" | |||
| "github.com/tendermint/tendermint/crypto/ed25519" | |||
| cmn "github.com/tendermint/tendermint/libs/common" | |||
| ) | |||
| func getDialerTestCases(t *testing.T) []dialerTestCase { | |||
| tcpAddr := GetFreeLocalhostAddrPort() | |||
| unixFilePath, err := testUnixAddr() | |||
| require.NoError(t, err) | |||
| unixAddr := fmt.Sprintf("unix://%s", unixFilePath) | |||
| return []dialerTestCase{ | |||
| { | |||
| addr: tcpAddr, | |||
| dialer: DialTCPFn(tcpAddr, testTimeoutReadWrite, ed25519.GenPrivKey()), | |||
| }, | |||
| { | |||
| addr: unixAddr, | |||
| dialer: DialUnixFn(unixFilePath), | |||
| }, | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| func TestIsConnTimeoutForFundamentalTimeouts(t *testing.T) { | |||
| // Generate a networking timeout | |||
| dialer := DialTCPFn(testFreeTCPAddr(t), time.Millisecond, ed25519.GenPrivKey()) | |||
| tcpAddr := GetFreeLocalhostAddrPort() | |||
| dialer := DialTCPFn(tcpAddr, time.Millisecond, ed25519.GenPrivKey()) | |||
| _, err := dialer() | |||
| assert.Error(t, err) | |||
| assert.True(t, IsConnTimeout(err)) | |||
| } | |||
| func TestIsConnTimeoutForWrappedConnTimeouts(t *testing.T) { | |||
| dialer := DialTCPFn(testFreeTCPAddr(t), time.Millisecond, ed25519.GenPrivKey()) | |||
| tcpAddr := GetFreeLocalhostAddrPort() | |||
| dialer := DialTCPFn(tcpAddr, time.Millisecond, ed25519.GenPrivKey()) | |||
| _, err := dialer() | |||
| assert.Error(t, err) | |||
| err = cmn.ErrorWrap(ErrConnTimeout, err.Error()) | |||
| err = errors.Wrap(ErrConnectionTimeout, err.Error()) | |||
| assert.True(t, IsConnTimeout(err)) | |||
| } | |||
+ 2
- 2
privval/socket_listeners.go
View File
+ 49
- 7
privval/utils.go
View File
| @ -1,20 +1,62 @@ | |||
| package privval | |||
| import ( | |||
| "fmt" | |||
| "net" | |||
| "github.com/pkg/errors" | |||
| "github.com/tendermint/tendermint/crypto/ed25519" | |||
| cmn "github.com/tendermint/tendermint/libs/common" | |||
| "github.com/tendermint/tendermint/libs/log" | |||
| ) | |||
| // IsConnTimeout returns a boolean indicating whether the error is known to | |||
| // report that a connection timeout occurred. This detects both fundamental | |||
| // network timeouts, as well as ErrConnTimeout errors. | |||
| func IsConnTimeout(err error) bool { | |||
| if cmnErr, ok := err.(cmn.Error); ok { | |||
| if cmnErr.Data() == ErrConnTimeout { | |||
| return true | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| if _, ok := err.(timeoutError); ok { | |||
| switch errors.Cause(err).(type) { | |||
| case EndpointTimeoutError: | |||
| return true | |||
| case timeoutError: | |||
| return true | |||
| default: | |||
| return false | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| // NewSignerListener creates a new SignerListenerEndpoint using the corresponding listen address | |||
| func NewSignerListener(listenAddr string, logger log.Logger) (*SignerListenerEndpoint, error) { | |||
| var listener net.Listener | |||
| protocol, address := cmn.ProtocolAndAddress(listenAddr) | |||
| ln, err := net.Listen(protocol, address) | |||
| if err != nil { | |||
| return nil, err | |||
| } | |||
| switch protocol { | |||
| case "unix": | |||
| listener = NewUnixListener(ln) | |||
| case "tcp": | |||
| // TODO: persist this key so external signer can actually authenticate us | |||
| listener = NewTCPListener(ln, ed25519.GenPrivKey()) | |||
| default: | |||
| return nil, fmt.Errorf( | |||
| "wrong listen address: expected either 'tcp' or 'unix' protocols, got %s", | |||
| protocol, | |||
| ) | |||
| } | |||
| pve := NewSignerListenerEndpoint(logger.With("module", "privval"), listener) | |||
| return pve, nil | |||
| } | |||
| // GetFreeLocalhostAddrPort returns a free localhost:port address | |||
| func GetFreeLocalhostAddrPort() string { | |||
| port, err := cmn.GetFreePort() | |||
| if err != nil { | |||
| panic(err) | |||
| } | |||
| return false | |||
| return fmt.Sprintf("127.0.0.1:%d", port) | |||
| } | |||
+ 3
- 4
privval/utils_test.go
View File
| @ -1,14 +1,13 @@ | |||
| package privval | |||
| import ( | |||
| "fmt" | |||
| "testing" | |||
| "github.com/pkg/errors" | |||
| "github.com/stretchr/testify/assert" | |||
| cmn "github.com/tendermint/tendermint/libs/common" | |||
| ) | |||
| func TestIsConnTimeoutForNonTimeoutErrors(t *testing.T) { | |||
| assert.False(t, IsConnTimeout(cmn.ErrorWrap(ErrDialRetryMax, "max retries exceeded"))) | |||
| assert.False(t, IsConnTimeout(fmt.Errorf("completely irrelevant error"))) | |||
| assert.False(t, IsConnTimeout(errors.Wrap(ErrDialRetryMax, "max retries exceeded"))) | |||
| assert.False(t, IsConnTimeout(errors.New("completely irrelevant error"))) | |||
| } | |||
+ 2
- 0
rpc/client/httpclient.go
View File
+ 1
- 1
rpc/core/routes.go
View File
+ 4
- 3
rpc/lib/client/http_client.go
View File
+ 4
- 3
rpc/lib/server/handlers.go
View File
+ 14
- 0
scripts/get_nodejs.sh
View File
| @ -0,0 +1,14 @@ | |||
| #!/usr/bin/env bash | |||
| VERSION=v12.9.0 | |||
| NODE_FULL=node-${VERSION}-linux-x64 | |||
| mkdir -p ~/.local/bin | |||
| mkdir -p ~/.local/node | |||
| wget http://nodejs.org/dist/${VERSION}/${NODE_FULL}.tar.gz -O ~/.local/node/${NODE_FULL}.tar.gz | |||
| tar -xzf ~/.local/node/${NODE_FULL}.tar.gz -C ~/.local/node/ | |||
| ln -s ~/.local/node/${NODE_FULL}/bin/node ~/.local/bin/node | |||
| ln -s ~/.local/node/${NODE_FULL}/bin/npm ~/.local/bin/npm | |||
| export PATH=~/.local/bin:$PATH | |||
| npm i -g dredd | |||
| ln -s ~/.local/node/${NODE_FULL}/bin/dredd ~/.local/bin/dredd | |||