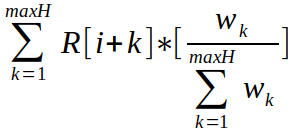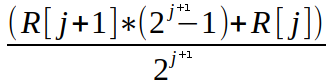Browse Source
Merge pull request #787 from caffix/develop
Initial Trust Metric Implementationpull/856/head
committed by
 GitHub
GitHub
No known key found for this signature in database
GPG Key ID: 4AEE18F83AFDEB23
7 changed files with 1067 additions and 7 deletions
Split View
Diff Options
-
+1 -1config/config.go
-
+238 -0docs/architecture/adr-006-trust-metric.md
-
BINdocs/architecture/img/formula1.png
-
BINdocs/architecture/img/formula2.png
-
+19 -6node/node.go
-
+575 -0p2p/trust/trustmetric.go
-
+234 -0p2p/trust/trustmetric_test.go
+ 1
- 1
config/config.go
View File
+ 238
- 0
docs/architecture/adr-006-trust-metric.md
View File
| @ -0,0 +1,238 @@ | |||
| # ADR 006: Trust Metric Design | |||
| ## Context | |||
| The proposed trust metric will allow Tendermint to maintain local trust rankings for peers it has directly interacted with, which can then be used to implement soft security controls. The calculations were obtained from the [TrustGuard](https://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=1060808) project. | |||
| ### Background | |||
| The Tendermint Core project developers would like to improve Tendermint security and reliability by keeping track of the level of trustworthiness peers have demonstrated within the peer-to-peer network. This way, undesirable outcomes from peers will not immediately result in them being dropped from the network (potentially causing drastic changes to take place). Instead, peers behavior can be monitored with appropriate metrics and be removed from the network once Tendermint Core is certain the peer is a threat. For example, when the PEXReactor makes a request for peers network addresses from a already known peer, and the returned network addresses are unreachable, this untrustworthy behavior should be tracked. Returning a few bad network addresses probably shouldn’t cause a peer to be dropped, while excessive amounts of this behavior does qualify the peer being dropped. | |||
| Trust metrics can be circumvented by malicious nodes through the use of strategic oscillation techniques, which adapts the malicious node’s behavior pattern in order to maximize its goals. For instance, if the malicious node learns that the time interval of the Tendermint trust metric is *X* hours, then it could wait *X* hours in-between malicious activities. We could try to combat this issue by increasing the interval length, yet this will make the system less adaptive to recent events. | |||
| Instead, having shorter intervals, but keeping a history of interval values, will give our metric the flexibility needed in order to keep the network stable, while also making it resilient against a strategic malicious node in the Tendermint peer-to-peer network. Also, the metric can access trust data over a rather long period of time while not greatly increasing its history size by aggregating older history values over a larger number of intervals, and at the same time, maintain great precision for the recent intervals. This approach is referred to as fading memories, and closely resembles the way human beings remember their experiences. The trade-off to using history data is that the interval values should be preserved in-between executions of the node. | |||
| ### References | |||
| S. Mudhakar, L. Xiong, and L. Liu, “TrustGuard: Countering Vulnerabilities in Reputation Management for Decentralized Overlay Networks,” in *Proceedings of the 14th international conference on World Wide Web, pp. 422-431*, May 2005. | |||
| ## Decision | |||
| The proposed trust metric will allow a developer to inform the trust metric store of all good and bad events relevant to a peer's behavior, and at any time, the metric can be queried for a peer's current trust ranking. | |||
| The three subsections below will cover the process being considered for calculating the trust ranking, the concept of the trust metric store, and the interface for the trust metric. | |||
| ### Proposed Process | |||
| The proposed trust metric will count good and bad events relevant to the object, and calculate the percent of counters that are good over an interval with a predefined duration. This is the procedure that will continue for the life of the trust metric. When the trust metric is queried for the current **trust value**, a resilient equation will be utilized to perform the calculation. | |||
| The equation being proposed resembles a Proportional-Integral-Derivative (PID) controller used in control systems. The proportional component allows us to be sensitive to the value of the most recent interval, while the integral component allows us to incorporate trust values stored in the history data, and the derivative component allows us to give weight to sudden changes in the behavior of a peer. We compute the trust value of a peer in interval i based on its current trust ranking, its trust rating history prior to interval *i* (over the past *maxH* number of intervals) and its trust ranking fluctuation. We will break up the equation into the three components. | |||
| ```math | |||
| (1) Proportional Value = a * R[i] | |||
| ``` | |||
| where *R*[*i*] denotes the raw trust value at time interval *i* (where *i* == 0 being current time) and *a* is the weight applied to the contribution of the current reports. The next component of our equation uses a weighted sum over the last *maxH* intervals to calculate the history value for time *i*: | |||
| `H[i] = `  | |||
| The weights can be chosen either optimistically or pessimistically. An optimistic weight creates larger weights for newer history data values, while the the pessimistic weight creates larger weights for time intervals with lower scores. The default weights used during the calculation of the history value are optimistic and calculated as *Wk* = 0.8^*k*, for time interval *k*. With the history value available, we can now finish calculating the integral value: | |||
| ```math | |||
| (2) Integral Value = b * H[i] | |||
| ``` | |||
| Where *H*[*i*] denotes the history value at time interval *i* and *b* is the weight applied to the contribution of past performance for the object being measured. The derivative component will be calculated as follows: | |||
| ```math | |||
| D[i] = R[i] – H[i] | |||
| (3) Derivative Value = c(D[i]) * D[i] | |||
| ``` | |||
| Where the value of *c* is selected based on the *D*[*i*] value relative to zero. The default selection process makes *c* equal to 0 unless *D*[*i*] is a negative value, in which case c is equal to 1. The result is that the maximum penalty is applied when current behavior is lower than previously experienced behavior. If the current behavior is better than the previously experienced behavior, then the Derivative Value has no impact on the trust value. With the three components brought together, our trust value equation is calculated as follows: | |||
| ```math | |||
| TrustValue[i] = a * R[i] + b * H[i] + c(D[i]) * D[i] | |||
| ``` | |||
| As a performance optimization that will keep the amount of raw interval data being saved to a reasonable size of *m*, while allowing us to represent 2^*m* - 1 history intervals, we can employ the fading memories technique that will trade space and time complexity for the precision of the history data values by summarizing larger quantities of less recent values. While our equation above attempts to access up to *maxH* (which can be 2^*m* - 1), we will map those requests down to *m* values using equation 4 below: | |||
| ```math | |||
| (4) j = index, where index > 0 | |||
| ``` | |||
| Where *j* is one of *(0, 1, 2, … , m – 1)* indices used to access history interval data. Now we can access the raw intervals using the following calculations: | |||
| ```math | |||
| R[0] = raw data for current time interval | |||
| ``` | |||
| `R[j] = `  | |||
| ### Trust Metric Store | |||
| Similar to the P2P subsystem AddrBook, the trust metric store will maintain information relevant to Tendermint peers. Additionally, the trust metric store will ensure that trust metrics will only be active for peers that a node is currently and directly engaged with. | |||
| Reactors will provide a peer key to the trust metric store in order to retrieve the associated trust metric. The trust metric can then record new positive and negative events experienced by the reactor, as well as provided the current trust score calculated by the metric. | |||
| When the node is shutting down, the trust metric store will save history data for trust metrics associated with all known peers. This saved information allows experiences with a peer to be preserved across node executions, which can span a tracking windows of days or weeks. The trust history data is loaded automatically during OnStart. | |||
| ### Interface Detailed Design | |||
| Each trust metric allows for the recording of positive/negative events, querying the current trust value/score, and the stopping/pausing of tracking over time intervals. This can be seen below: | |||
| ```go | |||
| // TrustMetric - keeps track of peer reliability | |||
| type TrustMetric struct { | |||
| // Private elements. | |||
| } | |||
| // Pause tells the metric to pause recording data over time intervals. | |||
| // All method calls that indicate events will unpause the metric | |||
| func (tm *TrustMetric) Pause() {} | |||
| // Stop tells the metric to stop recording data over time intervals | |||
| func (tm *TrustMetric) Stop() {} | |||
| // BadEvents indicates that an undesirable event(s) took place | |||
| func (tm *TrustMetric) BadEvents(num int) {} | |||
| // GoodEvents indicates that a desirable event(s) took place | |||
| func (tm *TrustMetric) GoodEvents(num int) {} | |||
| // TrustValue gets the dependable trust value; always between 0 and 1 | |||
| func (tm *TrustMetric) TrustValue() float64 {} | |||
| // TrustScore gets a score based on the trust value always between 0 and 100 | |||
| func (tm *TrustMetric) TrustScore() int {} | |||
| // NewMetric returns a trust metric with the default configuration | |||
| func NewMetric() *TrustMetric {} | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // For example | |||
| tm := NewMetric() | |||
| tm.BadEvents(1) | |||
| score := tm.TrustScore() | |||
| tm.Stop() | |||
| ``` | |||
| Some of the trust metric parameters can be configured. The weight values should probably be left alone in more cases, yet the time durations for the tracking window and individual time interval should be considered. | |||
| ```go | |||
| // TrustMetricConfig - Configures the weight functions and time intervals for the metric | |||
| type TrustMetricConfig struct { | |||
| // Determines the percentage given to current behavior | |||
| ProportionalWeight float64 | |||
| // Determines the percentage given to prior behavior | |||
| IntegralWeight float64 | |||
| // The window of time that the trust metric will track events across. | |||
| // This can be set to cover many days without issue | |||
| TrackingWindow time.Duration | |||
| // Each interval should be short for adapability. | |||
| // Less than 30 seconds is too sensitive, | |||
| // and greater than 5 minutes will make the metric numb | |||
| IntervalLength time.Duration | |||
| } | |||
| // DefaultConfig returns a config with values that have been tested and produce desirable results | |||
| func DefaultConfig() TrustMetricConfig {} | |||
| // NewMetricWithConfig returns a trust metric with a custom configuration | |||
| func NewMetricWithConfig(tmc TrustMetricConfig) *TrustMetric {} | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // For example | |||
| config := TrustMetricConfig{ | |||
| TrackingWindow: time.Minute * 60 * 24, // one day | |||
| IntervalLength: time.Minute * 2, | |||
| } | |||
| tm := NewMetricWithConfig(config) | |||
| tm.BadEvents(10) | |||
| tm.Pause() | |||
| tm.GoodEvents(1) // becomes active again | |||
| ``` | |||
| A trust metric store should be created with a DB that has persistent storage so it can save history data across node executions. All trust metrics instantiated by the store will be created with the provided TrustMetricConfig configuration. | |||
| When you attempt to fetch the trust metric for a peer, and an entry does not exist in the trust metric store, a new metric is automatically created and the entry made within the store. | |||
| In additional to the fetching method, GetPeerTrustMetric, the trust metric store provides a method to call when a peer has disconnected from the node. This is so the metric can be paused (history data will not be saved) for periods of time when the node is not having direct experiences with the peer. | |||
| ```go | |||
| // TrustMetricStore - Manages all trust metrics for peers | |||
| type TrustMetricStore struct { | |||
| cmn.BaseService | |||
| // Private elements | |||
| } | |||
| // OnStart implements Service | |||
| func (tms *TrustMetricStore) OnStart() error {} | |||
| // OnStop implements Service | |||
| func (tms *TrustMetricStore) OnStop() {} | |||
| // NewTrustMetricStore returns a store that saves data to the DB | |||
| // and uses the config when creating new trust metrics | |||
| func NewTrustMetricStore(db dbm.DB, tmc TrustMetricConfig) *TrustMetricStore {} | |||
| // Size returns the number of entries in the trust metric store | |||
| func (tms *TrustMetricStore) Size() int {} | |||
| // GetPeerTrustMetric returns a trust metric by peer key | |||
| func (tms *TrustMetricStore) GetPeerTrustMetric(key string) *TrustMetric {} | |||
| // PeerDisconnected pauses the trust metric associated with the peer identified by the key | |||
| func (tms *TrustMetricStore) PeerDisconnected(key string) {} | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // For example | |||
| db := dbm.NewDB("trusthistory", "goleveldb", dirPathStr) | |||
| tms := NewTrustMetricStore(db, DefaultConfig()) | |||
| tm := tms.GetPeerTrustMetric(key) | |||
| tm.BadEvents(1) | |||
| tms.PeerDisconnected(key) | |||
| ``` | |||
| ## Status | |||
| Approved. | |||
| ## Consequences | |||
| ### Positive | |||
| - The trust metric will allow Tendermint to make non-binary security and reliability decisions | |||
| - Will help Tendermint implement deterrents that provide soft security controls, yet avoids disruption on the network | |||
| - Will provide useful profiling information when analyzing performance over time related to peer interaction | |||
| ### Negative | |||
| - Requires saving the trust metric history data across node executions | |||
| ### Neutral | |||
| - Keep in mind that, good events need to be recorded just as bad events do using this implementation | |||
BIN
docs/architecture/img/formula1.png
View File
BIN
docs/architecture/img/formula2.png
View File
+ 19
- 6
node/node.go
View File
+ 575
- 0
p2p/trust/trustmetric.go
View File
| @ -0,0 +1,575 @@ | |||
| // Copyright 2017 Tendermint. All rights reserved. | |||
| // Use of this source code is governed by Apache 2 LICENSE that can be found in the LICENSE file. | |||
| package trust | |||
| import ( | |||
| "encoding/json" | |||
| "math" | |||
| "sync" | |||
| "time" | |||
| cmn "github.com/tendermint/tmlibs/common" | |||
| dbm "github.com/tendermint/tmlibs/db" | |||
| ) | |||
| const defaultStorePeriodicSaveInterval = 1 * time.Minute | |||
| // TrustMetricStore - Manages all trust metrics for peers | |||
| type TrustMetricStore struct { | |||
| cmn.BaseService | |||
| // Maps a Peer.Key to that peer's TrustMetric | |||
| peerMetrics map[string]*TrustMetric | |||
| // Mutex that protects the map and history data file | |||
| mtx sync.Mutex | |||
| // The db where peer trust metric history data will be stored | |||
| db dbm.DB | |||
| // This configuration will be used when creating new TrustMetrics | |||
| config TrustMetricConfig | |||
| } | |||
| // NewTrustMetricStore returns a store that saves data to the DB | |||
| // and uses the config when creating new trust metrics | |||
| func NewTrustMetricStore(db dbm.DB, tmc TrustMetricConfig) *TrustMetricStore { | |||
| tms := &TrustMetricStore{ | |||
| peerMetrics: make(map[string]*TrustMetric), | |||
| db: db, | |||
| config: tmc, | |||
| } | |||
| tms.BaseService = *cmn.NewBaseService(nil, "TrustMetricStore", tms) | |||
| return tms | |||
| } | |||
| // OnStart implements Service | |||
| func (tms *TrustMetricStore) OnStart() error { | |||
| tms.BaseService.OnStart() | |||
| tms.mtx.Lock() | |||
| defer tms.mtx.Unlock() | |||
| tms.loadFromDB() | |||
| go tms.saveRoutine() | |||
| return nil | |||
| } | |||
| // OnStop implements Service | |||
| func (tms *TrustMetricStore) OnStop() { | |||
| tms.BaseService.OnStop() | |||
| tms.mtx.Lock() | |||
| defer tms.mtx.Unlock() | |||
| // Stop all trust metric go-routines | |||
| for _, tm := range tms.peerMetrics { | |||
| tm.Stop() | |||
| } | |||
| // Make the final trust history data save | |||
| tms.saveToDB() | |||
| } | |||
| // Size returns the number of entries in the trust metric store | |||
| func (tms *TrustMetricStore) Size() int { | |||
| tms.mtx.Lock() | |||
| defer tms.mtx.Unlock() | |||
| return tms.size() | |||
| } | |||
| // GetPeerTrustMetric returns a trust metric by peer key | |||
| func (tms *TrustMetricStore) GetPeerTrustMetric(key string) *TrustMetric { | |||
| tms.mtx.Lock() | |||
| defer tms.mtx.Unlock() | |||
| tm, ok := tms.peerMetrics[key] | |||
| if !ok { | |||
| // If the metric is not available, we will create it | |||
| tm = NewMetricWithConfig(tms.config) | |||
| // The metric needs to be in the map | |||
| tms.peerMetrics[key] = tm | |||
| } | |||
| return tm | |||
| } | |||
| // PeerDisconnected pauses the trust metric associated with the peer identified by the key | |||
| func (tms *TrustMetricStore) PeerDisconnected(key string) { | |||
| tms.mtx.Lock() | |||
| defer tms.mtx.Unlock() | |||
| // If the Peer that disconnected has a metric, pause it | |||
| if tm, ok := tms.peerMetrics[key]; ok { | |||
| tm.Pause() | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| /* Private methods */ | |||
| // size returns the number of entries in the store without acquiring the mutex | |||
| func (tms *TrustMetricStore) size() int { | |||
| return len(tms.peerMetrics) | |||
| } | |||
| /* Loading & Saving */ | |||
| /* Both of these methods assume the mutex has been acquired, since they write to the map */ | |||
| var trustMetricKey = []byte("trustMetricStore") | |||
| type peerHistoryJSON struct { | |||
| NumIntervals int `json:"intervals"` | |||
| History []float64 `json:"history"` | |||
| } | |||
| // Loads the history data for all peers from the store DB | |||
| // cmn.Panics if file is corrupt | |||
| func (tms *TrustMetricStore) loadFromDB() bool { | |||
| // Obtain the history data we have so far | |||
| bytes := tms.db.Get(trustMetricKey) | |||
| if bytes == nil { | |||
| return false | |||
| } | |||
| peers := make(map[string]peerHistoryJSON, 0) | |||
| err := json.Unmarshal(bytes, &peers) | |||
| if err != nil { | |||
| cmn.PanicCrisis(cmn.Fmt("Could not unmarshal Trust Metric Store DB data: %v", err)) | |||
| } | |||
| // If history data exists in the file, | |||
| // load it into trust metrics and recalc | |||
| for key, p := range peers { | |||
| tm := NewMetricWithConfig(tms.config) | |||
| // Restore the number of time intervals we have previously tracked | |||
| if p.NumIntervals > tm.maxIntervals { | |||
| p.NumIntervals = tm.maxIntervals | |||
| } | |||
| tm.numIntervals = p.NumIntervals | |||
| // Restore the history and its current size | |||
| if len(p.History) > tm.historyMaxSize { | |||
| // Keep the history no larger than historyMaxSize | |||
| last := len(p.History) - tm.historyMaxSize | |||
| p.History = p.History[last:] | |||
| } | |||
| tm.history = p.History | |||
| tm.historySize = len(tm.history) | |||
| // Create the history weight values and weight sum | |||
| for i := 1; i <= tm.numIntervals; i++ { | |||
| x := math.Pow(defaultHistoryDataWeight, float64(i)) // Optimistic weight | |||
| tm.historyWeights = append(tm.historyWeights, x) | |||
| } | |||
| for _, v := range tm.historyWeights { | |||
| tm.historyWeightSum += v | |||
| } | |||
| // Calculate the history value based on the loaded history data | |||
| tm.historyValue = tm.calcHistoryValue() | |||
| // Load the peer trust metric into the store | |||
| tms.peerMetrics[key] = tm | |||
| } | |||
| return true | |||
| } | |||
| // Saves the history data for all peers to the store DB | |||
| func (tms *TrustMetricStore) saveToDB() { | |||
| tms.Logger.Info("Saving TrustHistory to DB", "size", tms.size()) | |||
| peers := make(map[string]peerHistoryJSON, 0) | |||
| for key, tm := range tms.peerMetrics { | |||
| // Add an entry for the peer identified by key | |||
| peers[key] = peerHistoryJSON{ | |||
| NumIntervals: tm.numIntervals, | |||
| History: tm.history, | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| // Write all the data back to the DB | |||
| bytes, err := json.Marshal(peers) | |||
| if err != nil { | |||
| tms.Logger.Error("Failed to encode the TrustHistory", "err", err) | |||
| return | |||
| } | |||
| tms.db.SetSync(trustMetricKey, bytes) | |||
| } | |||
| // Periodically saves the trust history data to the DB | |||
| func (tms *TrustMetricStore) saveRoutine() { | |||
| t := time.NewTicker(defaultStorePeriodicSaveInterval) | |||
| defer t.Stop() | |||
| loop: | |||
| for { | |||
| select { | |||
| case <-t.C: | |||
| tms.mtx.Lock() | |||
| tms.saveToDB() | |||
| tms.mtx.Unlock() | |||
| case <-tms.Quit: | |||
| break loop | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| //--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| const ( | |||
| // The number of event updates that can be sent on a single metric before blocking | |||
| defaultUpdateChanCapacity = 10 | |||
| // The number of trust value requests that can be made simultaneously before blocking | |||
| defaultRequestChanCapacity = 10 | |||
| // The weight applied to the derivative when current behavior is >= previous behavior | |||
| defaultDerivativeGamma1 = 0 | |||
| // The weight applied to the derivative when current behavior is less than previous behavior | |||
| defaultDerivativeGamma2 = 1.0 | |||
| // The weight applied to history data values when calculating the history value | |||
| defaultHistoryDataWeight = 0.8 | |||
| ) | |||
| // TrustMetric - keeps track of peer reliability | |||
| // See tendermint/docs/architecture/adr-006-trust-metric.md for details | |||
| type TrustMetric struct { | |||
| // Determines the percentage given to current behavior | |||
| proportionalWeight float64 | |||
| // Determines the percentage given to prior behavior | |||
| integralWeight float64 | |||
| // Count of how many time intervals this metric has been tracking | |||
| numIntervals int | |||
| // Size of the time interval window for this trust metric | |||
| maxIntervals int | |||
| // The time duration for a single time interval | |||
| intervalLen time.Duration | |||
| // Stores the trust history data for this metric | |||
| history []float64 | |||
| // Weights applied to the history data when calculating the history value | |||
| historyWeights []float64 | |||
| // The sum of the history weights used when calculating the history value | |||
| historyWeightSum float64 | |||
| // The current number of history data elements | |||
| historySize int | |||
| // The maximum number of history data elements | |||
| historyMaxSize int | |||
| // The calculated history value for the current time interval | |||
| historyValue float64 | |||
| // The number of recorded good and bad events for the current time interval | |||
| bad, good float64 | |||
| // While true, history data is not modified | |||
| paused bool | |||
| // Sending true on this channel stops tracking, while false pauses tracking | |||
| stop chan bool | |||
| // For sending information about new good/bad events to be recorded | |||
| update chan *updateBadGood | |||
| // The channel to request a newly calculated trust value | |||
| trustValue chan *reqTrustValue | |||
| } | |||
| // For the TrustMetric update channel | |||
| type updateBadGood struct { | |||
| IsBad bool | |||
| Add int | |||
| } | |||
| // For the TrustMetric trustValue channel | |||
| type reqTrustValue struct { | |||
| // The requested trust value is sent back on this channel | |||
| Resp chan float64 | |||
| } | |||
| // Pause tells the metric to pause recording data over time intervals. | |||
| // All method calls that indicate events will unpause the metric | |||
| func (tm *TrustMetric) Pause() { | |||
| tm.stop <- false | |||
| } | |||
| // Stop tells the metric to stop recording data over time intervals | |||
| func (tm *TrustMetric) Stop() { | |||
| tm.stop <- true | |||
| } | |||
| // BadEvents indicates that an undesirable event(s) took place | |||
| func (tm *TrustMetric) BadEvents(num int) { | |||
| tm.update <- &updateBadGood{IsBad: true, Add: num} | |||
| } | |||
| // GoodEvents indicates that a desirable event(s) took place | |||
| func (tm *TrustMetric) GoodEvents(num int) { | |||
| tm.update <- &updateBadGood{IsBad: false, Add: num} | |||
| } | |||
| // TrustValue gets the dependable trust value; always between 0 and 1 | |||
| func (tm *TrustMetric) TrustValue() float64 { | |||
| resp := make(chan float64, 1) | |||
| tm.trustValue <- &reqTrustValue{Resp: resp} | |||
| return <-resp | |||
| } | |||
| // TrustScore gets a score based on the trust value always between 0 and 100 | |||
| func (tm *TrustMetric) TrustScore() int { | |||
| score := tm.TrustValue() * 100 | |||
| return int(math.Floor(score)) | |||
| } | |||
| // TrustMetricConfig - Configures the weight functions and time intervals for the metric | |||
| type TrustMetricConfig struct { | |||
| // Determines the percentage given to current behavior | |||
| ProportionalWeight float64 | |||
| // Determines the percentage given to prior behavior | |||
| IntegralWeight float64 | |||
| // The window of time that the trust metric will track events across. | |||
| // This can be set to cover many days without issue | |||
| TrackingWindow time.Duration | |||
| // Each interval should be short for adapability. | |||
| // Less than 30 seconds is too sensitive, | |||
| // and greater than 5 minutes will make the metric numb | |||
| IntervalLength time.Duration | |||
| } | |||
| // DefaultConfig returns a config with values that have been tested and produce desirable results | |||
| func DefaultConfig() TrustMetricConfig { | |||
| return TrustMetricConfig{ | |||
| ProportionalWeight: 0.4, | |||
| IntegralWeight: 0.6, | |||
| TrackingWindow: (time.Minute * 60 * 24) * 14, // 14 days. | |||
| IntervalLength: 1 * time.Minute, | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| // NewMetric returns a trust metric with the default configuration | |||
| func NewMetric() *TrustMetric { | |||
| return NewMetricWithConfig(DefaultConfig()) | |||
| } | |||
| // NewMetricWithConfig returns a trust metric with a custom configuration | |||
| func NewMetricWithConfig(tmc TrustMetricConfig) *TrustMetric { | |||
| tm := new(TrustMetric) | |||
| config := customConfig(tmc) | |||
| // Setup using the configuration values | |||
| tm.proportionalWeight = config.ProportionalWeight | |||
| tm.integralWeight = config.IntegralWeight | |||
| tm.intervalLen = config.IntervalLength | |||
| // The maximum number of time intervals is the tracking window / interval length | |||
| tm.maxIntervals = int(config.TrackingWindow / tm.intervalLen) | |||
| // The history size will be determined by the maximum number of time intervals | |||
| tm.historyMaxSize = intervalToHistoryOffset(tm.maxIntervals) + 1 | |||
| // This metric has a perfect history so far | |||
| tm.historyValue = 1.0 | |||
| // Setup the channels | |||
| tm.update = make(chan *updateBadGood, defaultUpdateChanCapacity) | |||
| tm.trustValue = make(chan *reqTrustValue, defaultRequestChanCapacity) | |||
| tm.stop = make(chan bool, 1) | |||
| go tm.processRequests() | |||
| return tm | |||
| } | |||
| /* Private methods */ | |||
| // Ensures that all configuration elements have valid values | |||
| func customConfig(tmc TrustMetricConfig) TrustMetricConfig { | |||
| config := DefaultConfig() | |||
| // Check the config for set values, and setup appropriately | |||
| if tmc.ProportionalWeight > 0 { | |||
| config.ProportionalWeight = tmc.ProportionalWeight | |||
| } | |||
| if tmc.IntegralWeight > 0 { | |||
| config.IntegralWeight = tmc.IntegralWeight | |||
| } | |||
| if tmc.IntervalLength > time.Duration(0) { | |||
| config.IntervalLength = tmc.IntervalLength | |||
| } | |||
| if tmc.TrackingWindow > time.Duration(0) && | |||
| tmc.TrackingWindow >= config.IntervalLength { | |||
| config.TrackingWindow = tmc.TrackingWindow | |||
| } | |||
| return config | |||
| } | |||
| // Calculates the derivative component | |||
| func (tm *TrustMetric) derivativeValue() float64 { | |||
| return tm.proportionalValue() - tm.historyValue | |||
| } | |||
| // Strengthens the derivative component when the change is negative | |||
| func (tm *TrustMetric) weightedDerivative() float64 { | |||
| var weight float64 = defaultDerivativeGamma1 | |||
| d := tm.derivativeValue() | |||
| if d < 0 { | |||
| weight = defaultDerivativeGamma2 | |||
| } | |||
| return weight * d | |||
| } | |||
| // Performs the update for our Faded Memories process, which allows the | |||
| // trust metric tracking window to be large while maintaining a small | |||
| // number of history data values | |||
| func (tm *TrustMetric) updateFadedMemory() { | |||
| if tm.historySize < 2 { | |||
| return | |||
| } | |||
| end := tm.historySize - 1 | |||
| // Keep the most recent history element | |||
| for count := 1; count < tm.historySize; count++ { | |||
| i := end - count | |||
| // The older the data is, the more we spread it out | |||
| x := math.Pow(2, float64(count)) | |||
| // Two history data values are merged into a single value | |||
| tm.history[i] = ((tm.history[i] * (x - 1)) + tm.history[i+1]) / x | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| // Map the interval value down to an offset from the beginning of history | |||
| func intervalToHistoryOffset(interval int) int { | |||
| // The system maintains 2^m interval values in the form of m history | |||
| // data values. Therefore, we access the ith interval by obtaining | |||
| // the history data index = the floor of log2(i) | |||
| return int(math.Floor(math.Log2(float64(interval)))) | |||
| } | |||
| // Retrieves the actual history data value that represents the requested time interval | |||
| func (tm *TrustMetric) fadedMemoryValue(interval int) float64 { | |||
| first := tm.historySize - 1 | |||
| if interval == 0 { | |||
| // Base case | |||
| return tm.history[first] | |||
| } | |||
| offset := intervalToHistoryOffset(interval) | |||
| return tm.history[first-offset] | |||
| } | |||
| // Calculates the integral (history) component of the trust value | |||
| func (tm *TrustMetric) calcHistoryValue() float64 { | |||
| var hv float64 | |||
| for i := 0; i < tm.numIntervals; i++ { | |||
| hv += tm.fadedMemoryValue(i) * tm.historyWeights[i] | |||
| } | |||
| return hv / tm.historyWeightSum | |||
| } | |||
| // Calculates the current score for good/bad experiences | |||
| func (tm *TrustMetric) proportionalValue() float64 { | |||
| value := 1.0 | |||
| total := tm.good + tm.bad | |||
| if total > 0 { | |||
| value = tm.good / total | |||
| } | |||
| return value | |||
| } | |||
| // Calculates the trust value for the request processing | |||
| func (tm *TrustMetric) calcTrustValue() float64 { | |||
| weightedP := tm.proportionalWeight * tm.proportionalValue() | |||
| weightedI := tm.integralWeight * tm.historyValue | |||
| weightedD := tm.weightedDerivative() | |||
| tv := weightedP + weightedI + weightedD | |||
| // Do not return a negative value. | |||
| if tv < 0 { | |||
| tv = 0 | |||
| } | |||
| return tv | |||
| } | |||
| // This method is for a goroutine that handles all requests on the metric | |||
| func (tm *TrustMetric) processRequests() { | |||
| t := time.NewTicker(tm.intervalLen) | |||
| defer t.Stop() | |||
| loop: | |||
| for { | |||
| select { | |||
| case bg := <-tm.update: | |||
| // Check if this is the first experience with | |||
| // what we are tracking since being paused | |||
| if tm.paused { | |||
| tm.good = 0 | |||
| tm.bad = 0 | |||
| // New events cause us to unpause the metric | |||
| tm.paused = false | |||
| } | |||
| if bg.IsBad { | |||
| tm.bad += float64(bg.Add) | |||
| } else { | |||
| tm.good += float64(bg.Add) | |||
| } | |||
| case rtv := <-tm.trustValue: | |||
| rtv.Resp <- tm.calcTrustValue() | |||
| case <-t.C: | |||
| if !tm.paused { | |||
| // Add the current trust value to the history data | |||
| newHist := tm.calcTrustValue() | |||
| tm.history = append(tm.history, newHist) | |||
| // Update history and interval counters | |||
| if tm.historySize < tm.historyMaxSize { | |||
| tm.historySize++ | |||
| } else { | |||
| // Keep the history no larger than historyMaxSize | |||
| last := len(tm.history) - tm.historyMaxSize | |||
| tm.history = tm.history[last:] | |||
| } | |||
| if tm.numIntervals < tm.maxIntervals { | |||
| tm.numIntervals++ | |||
| // Add the optimistic weight for the new time interval | |||
| wk := math.Pow(defaultHistoryDataWeight, float64(tm.numIntervals)) | |||
| tm.historyWeights = append(tm.historyWeights, wk) | |||
| tm.historyWeightSum += wk | |||
| } | |||
| // Update the history data using Faded Memories | |||
| tm.updateFadedMemory() | |||
| // Calculate the history value for the upcoming time interval | |||
| tm.historyValue = tm.calcHistoryValue() | |||
| tm.good = 0 | |||
| tm.bad = 0 | |||
| } | |||
| case stop := <-tm.stop: | |||
| if stop { | |||
| // Stop all further tracking for this metric | |||
| break loop | |||
| } | |||
| // Pause the metric for now | |||
| tm.paused = true | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
+ 234
- 0
p2p/trust/trustmetric_test.go
View File
| @ -0,0 +1,234 @@ | |||
| // Copyright 2017 Tendermint. All rights reserved. | |||
| // Use of this source code is governed by Apache 2 LICENSE that can be found in the LICENSE file. | |||
| package trust | |||
| import ( | |||
| "fmt" | |||
| "io/ioutil" | |||
| "os" | |||
| "testing" | |||
| "time" | |||
| "github.com/stretchr/testify/assert" | |||
| dbm "github.com/tendermint/tmlibs/db" | |||
| "github.com/tendermint/tmlibs/log" | |||
| ) | |||
| func TestTrustMetricStoreSaveLoad(t *testing.T) { | |||
| dir, err := ioutil.TempDir("", "trust_test") | |||
| if err != nil { | |||
| panic(err) | |||
| } | |||
| defer os.Remove(dir) | |||
| historyDB := dbm.NewDB("trusthistory", "goleveldb", dir) | |||
| config := TrustMetricConfig{ | |||
| TrackingWindow: 5 * time.Minute, | |||
| IntervalLength: 50 * time.Millisecond, | |||
| } | |||
| // 0 peers saved | |||
| store := NewTrustMetricStore(historyDB, config) | |||
| store.SetLogger(log.TestingLogger()) | |||
| store.saveToDB() | |||
| // Load the data from the file | |||
| store = NewTrustMetricStore(historyDB, config) | |||
| store.SetLogger(log.TestingLogger()) | |||
| store.loadFromDB() | |||
| // Make sure we still have 0 entries | |||
| assert.Zero(t, store.Size()) | |||
| // 100 peers | |||
| for i := 0; i < 100; i++ { | |||
| key := fmt.Sprintf("peer_%d", i) | |||
| tm := store.GetPeerTrustMetric(key) | |||
| tm.BadEvents(10) | |||
| tm.GoodEvents(1) | |||
| } | |||
| // Check that we have 100 entries and save | |||
| assert.Equal(t, 100, store.Size()) | |||
| // Give the metrics time to process the history data | |||
| time.Sleep(1 * time.Second) | |||
| // Stop all the trust metrics and save | |||
| for _, tm := range store.peerMetrics { | |||
| tm.Stop() | |||
| } | |||
| store.saveToDB() | |||
| // Load the data from the DB | |||
| store = NewTrustMetricStore(historyDB, config) | |||
| store.SetLogger(log.TestingLogger()) | |||
| store.loadFromDB() | |||
| // Check that we still have 100 peers with imperfect trust values | |||
| assert.Equal(t, 100, store.Size()) | |||
| for _, tm := range store.peerMetrics { | |||
| assert.NotEqual(t, 1.0, tm.TrustValue()) | |||
| } | |||
| // Stop all the trust metrics | |||
| for _, tm := range store.peerMetrics { | |||
| tm.Stop() | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| func TestTrustMetricStoreConfig(t *testing.T) { | |||
| historyDB := dbm.NewDB("", "memdb", "") | |||
| config := TrustMetricConfig{ | |||
| ProportionalWeight: 0.5, | |||
| IntegralWeight: 0.5, | |||
| } | |||
| // Create a store with custom config | |||
| store := NewTrustMetricStore(historyDB, config) | |||
| store.SetLogger(log.TestingLogger()) | |||
| // Have the store make us a metric with the config | |||
| tm := store.GetPeerTrustMetric("TestKey") | |||
| // Check that the options made it to the metric | |||
| assert.Equal(t, 0.5, tm.proportionalWeight) | |||
| assert.Equal(t, 0.5, tm.integralWeight) | |||
| tm.Stop() | |||
| } | |||
| func TestTrustMetricStoreLookup(t *testing.T) { | |||
| historyDB := dbm.NewDB("", "memdb", "") | |||
| store := NewTrustMetricStore(historyDB, DefaultConfig()) | |||
| store.SetLogger(log.TestingLogger()) | |||
| // Create 100 peers in the trust metric store | |||
| for i := 0; i < 100; i++ { | |||
| key := fmt.Sprintf("peer_%d", i) | |||
| store.GetPeerTrustMetric(key) | |||
| // Check that the trust metric was successfully entered | |||
| ktm := store.peerMetrics[key] | |||
| assert.NotNil(t, ktm, "Expected to find TrustMetric %s but wasn't there.", key) | |||
| } | |||
| // Stop all the trust metrics | |||
| for _, tm := range store.peerMetrics { | |||
| tm.Stop() | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| func TestTrustMetricStorePeerScore(t *testing.T) { | |||
| historyDB := dbm.NewDB("", "memdb", "") | |||
| store := NewTrustMetricStore(historyDB, DefaultConfig()) | |||
| store.SetLogger(log.TestingLogger()) | |||
| key := "TestKey" | |||
| tm := store.GetPeerTrustMetric(key) | |||
| // This peer is innocent so far | |||
| first := tm.TrustScore() | |||
| assert.Equal(t, 100, first) | |||
| // Add some undesirable events and disconnect | |||
| tm.BadEvents(1) | |||
| first = tm.TrustScore() | |||
| assert.NotEqual(t, 100, first) | |||
| tm.BadEvents(10) | |||
| second := tm.TrustScore() | |||
| if second > first { | |||
| t.Errorf("A greater number of bad events should lower the trust score") | |||
| } | |||
| store.PeerDisconnected(key) | |||
| // We will remember our experiences with this peer | |||
| tm = store.GetPeerTrustMetric(key) | |||
| assert.NotEqual(t, 100, tm.TrustScore()) | |||
| tm.Stop() | |||
| } | |||
| func TestTrustMetricScores(t *testing.T) { | |||
| tm := NewMetric() | |||
| // Perfect score | |||
| tm.GoodEvents(1) | |||
| score := tm.TrustScore() | |||
| assert.Equal(t, 100, score) | |||
| // Less than perfect score | |||
| tm.BadEvents(10) | |||
| score = tm.TrustScore() | |||
| assert.NotEqual(t, 100, score) | |||
| tm.Stop() | |||
| } | |||
| func TestTrustMetricConfig(t *testing.T) { | |||
| // 7 days | |||
| window := time.Minute * 60 * 24 * 7 | |||
| config := TrustMetricConfig{ | |||
| TrackingWindow: window, | |||
| IntervalLength: 2 * time.Minute, | |||
| } | |||
| tm := NewMetricWithConfig(config) | |||
| // The max time intervals should be the TrackingWindow / IntervalLen | |||
| assert.Equal(t, int(config.TrackingWindow/config.IntervalLength), tm.maxIntervals) | |||
| dc := DefaultConfig() | |||
| // These weights should still be the default values | |||
| assert.Equal(t, dc.ProportionalWeight, tm.proportionalWeight) | |||
| assert.Equal(t, dc.IntegralWeight, tm.integralWeight) | |||
| tm.Stop() | |||
| config.ProportionalWeight = 0.3 | |||
| config.IntegralWeight = 0.7 | |||
| tm = NewMetricWithConfig(config) | |||
| // These weights should be equal to our custom values | |||
| assert.Equal(t, config.ProportionalWeight, tm.proportionalWeight) | |||
| assert.Equal(t, config.IntegralWeight, tm.integralWeight) | |||
| tm.Stop() | |||
| } | |||
| func TestTrustMetricStopPause(t *testing.T) { | |||
| // Cause time intervals to pass quickly | |||
| config := TrustMetricConfig{ | |||
| TrackingWindow: 5 * time.Minute, | |||
| IntervalLength: 10 * time.Millisecond, | |||
| } | |||
| tm := NewMetricWithConfig(config) | |||
| // Allow some time intervals to pass and pause | |||
| time.Sleep(50 * time.Millisecond) | |||
| tm.Pause() | |||
| // Give the pause some time to take place | |||
| time.Sleep(10 * time.Millisecond) | |||
| first := tm.numIntervals | |||
| // Allow more time to pass and check the intervals are unchanged | |||
| time.Sleep(50 * time.Millisecond) | |||
| assert.Equal(t, first, tm.numIntervals) | |||
| // Get the trust metric activated again | |||
| tm.GoodEvents(5) | |||
| // Allow some time intervals to pass and stop | |||
| time.Sleep(50 * time.Millisecond) | |||
| tm.Stop() | |||
| // Give the stop some time to take place | |||
| time.Sleep(10 * time.Millisecond) | |||
| second := tm.numIntervals | |||
| // Allow more time to pass and check the intervals are unchanged | |||
| time.Sleep(50 * time.Millisecond) | |||
| assert.Equal(t, second, tm.numIntervals) | |||
| if first >= second { | |||
| t.Fatalf("numIntervals should always increase or stay the same over time") | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||